Apple described the original Apple Vision Pro as “a revolutionary spatial computer that seamlessly blends digital content with the physical world, while allowing users to stay present and connected to others.” While other companies at the time were producing “Augmented Reality” and “Virtual Reality” headsets and glasses, Apple chose to forego the AR/VR descriptions completely use the term “Spatial Computing.”
Apple did not invent the term or concept of spatial computing. The term “Spatial Computing” in the context used by Apple Vision Pro is attributed to MIT researcher Simon Greenwold and is the title of a paper he wrote on 2003. Greenwold’s paper defined the term as “human interaction with a machine in which the machine retains and manipulates referents to real objects and spaces.” He added, “Ideally, these real objects and spaces have prior significance to the user.”
Apple does, however, claim that they created the world’s first spatial operating system, visionOS. Apple Vision Pro works with visionOS to allow “users interact with digital content in a way that feels like it is physically present in their space.” A FastCompany article explains the differences among AR, VR, and spatial computing by noting that the Vision Pro has:
“12 cameras and five sensors that help the device know everything from the level of light in a physical space to where objects are in relation to each other, to where your eyes are looking, and how your hands move… In spatial computing, you can interact with those virtual objects by simply using your hands in the physical space in front of you.”
By contrast, in virtual reality “you are completely immersed in a virtual world and can see none of the real world around you,” while augmented reality “displays virtual elements on top of the real world.” The three terms are related because spatial computing uses elements from both AR and VR.
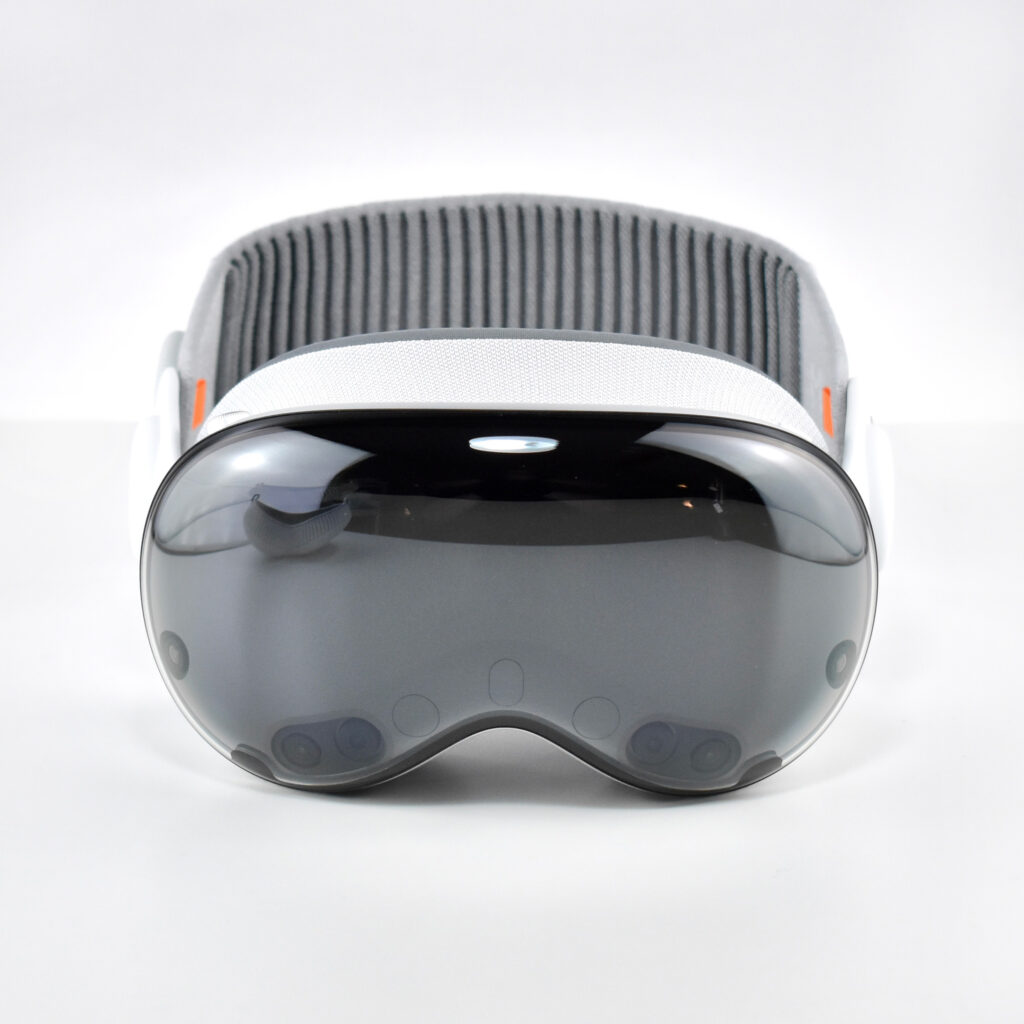
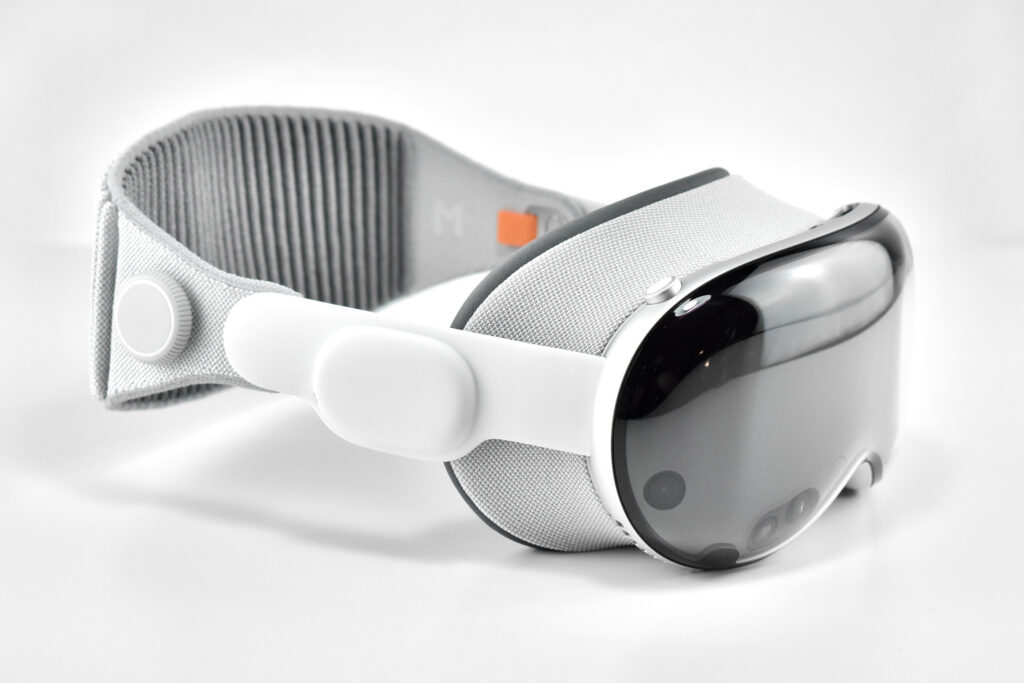
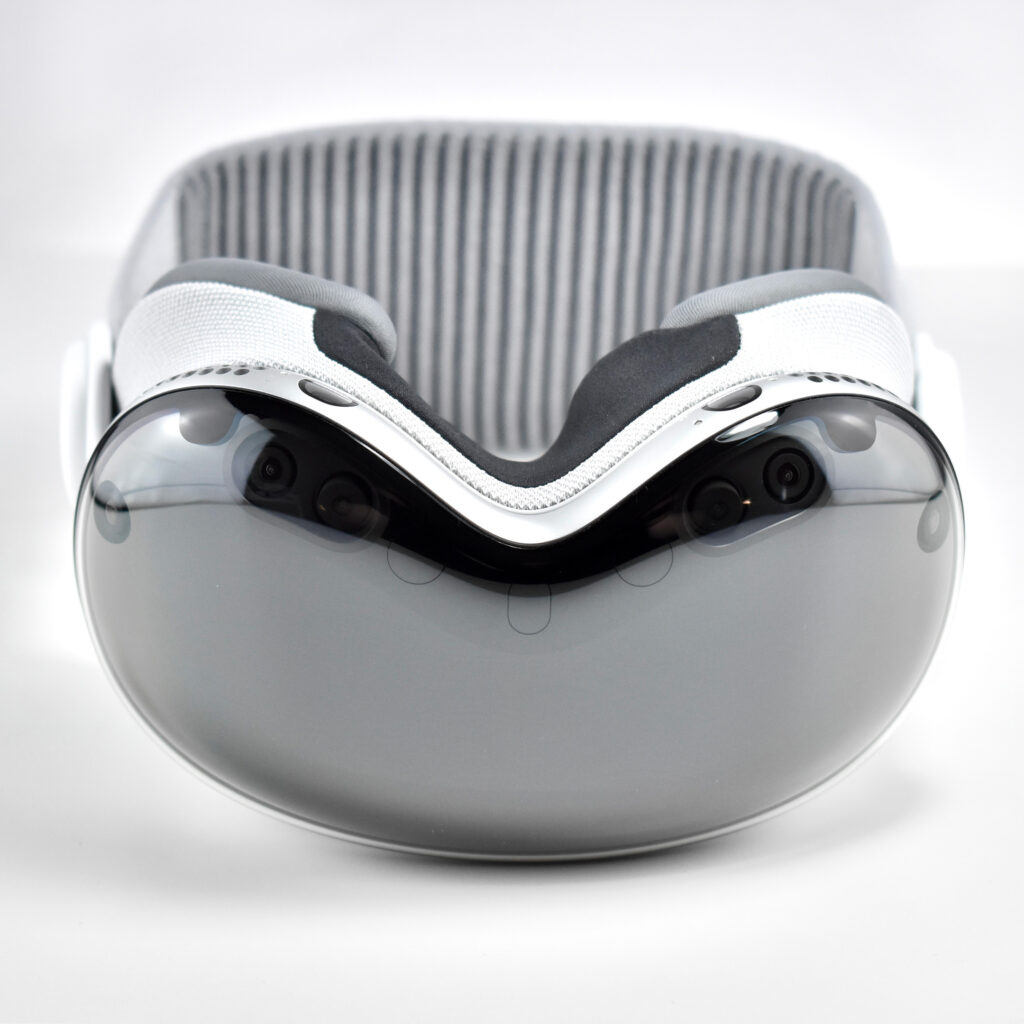
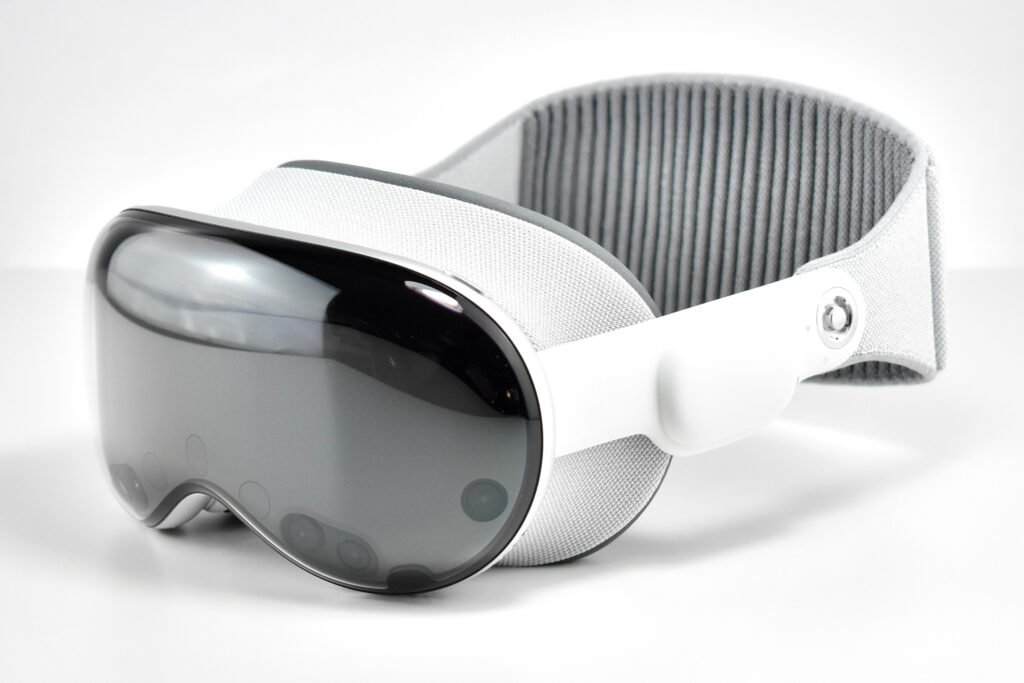
Apple described the “breakthrough design” of the Vision Pro as featuring “an ultra-high-resolution display system that packs 23 million pixels across two displays, and custom Apple silicon in a unique dual-chip design to ensure every experience feels like it’s taking place in front of the user’s eyes in real time.” Mike Rockwell, Apple’s Vice President of the Technology Development Group said that “through a tight integration of hardware and software, we designed a standalone spatial computer in a compact wearable form factor that is the most advanced personal electronics device ever.”
The Apple Vision Pro “can transform any space into a personal movie theater with a screen that feels 100 feet wide.” Internally, the seamless display is accomplished by delivering “more pixels than a 4K display” to each eye.
To add to the visual realism, a new Spatial Audio system is also part of the Apple Vision Pro that Apple called “audio pods.” Apple describes the sound system:
“Dual-driver audio pods positioned next to each ear deliver personalized sound while letting you hear what’s around you. Spatial Audio makes sounds feel like they’re coming from your surroundings. Audio ray tracing analyzes your room’s acoustic properties to adapt and match sound to your space.” I have observed that first-time Vision Pro users are often surprised by the audio experience delivered by the audio pods and ask if others around them can hear the audio. (Others in the room can faintly hear the audio at a low volume level, even if the Vision Pro user has the volume at maximum.)
The Apple Vision Pro is also packed with cameras and sensors that all work together to deliver the overall experience, including:
- 2 high‑resolution main cameras
- 6 world‑facing tracking cameras
- 4 internal eye‑tracking cameras
- TrueDepth camera
- LiDAR Scanner
- 4 inertial measurement units (IMUs)
- Flicker sensor
- Ambient light sensor
Apple described the sensor functionality: “high-resolution cameras transmit over one billion pixels per second to the displays so you can see the world around you clearly. The system also helps deliver precise head and hand tracking and real‑time 3D mapping, all while understanding your hand gestures from a wide range of positions.” Similar to an augmented reality experience, Vision Pro users see the world through live “passthrough” video, and not through a transparent lens.
The original Apple Vision Pro was powered by two chips. Apple’s M2 chip provided an 8‑core CPU with 4 performance cores and 4 efficiency cores, a 10‑core GPU, a 16‑core Neural Engine, and 16 GB unified memory. The Apple R1 chip allowed 12‑millisecond photon‑to‑photon latency using 256 GB/s memory bandwidth.
In addition to the sensor cameras, the Apple Vision Pro could capture Spatial photos and video using the company’s first stereoscopic 3D main camera system. The 18 mm cameras used a ƒ/2.00 aperture and could capture 6.5 stereo megapixels. Upon release of the Apple Vision Pro, the iPhone 15 Pro, iPhone 15 Pro Max, and all iPhone 16 models could capture Spatial video using two cameras on each of those iPhone models (single-camera iPhones cannot capture Spatial video).
Inputs built in to the Apple Vision Pro included hand, eye, and voice. In addition, supported input accessories included keyboards, trackpads, game controllers, Bluetooth mouse support, and other third-party accessories such as the Logitech Muse pen (not released until 2025).
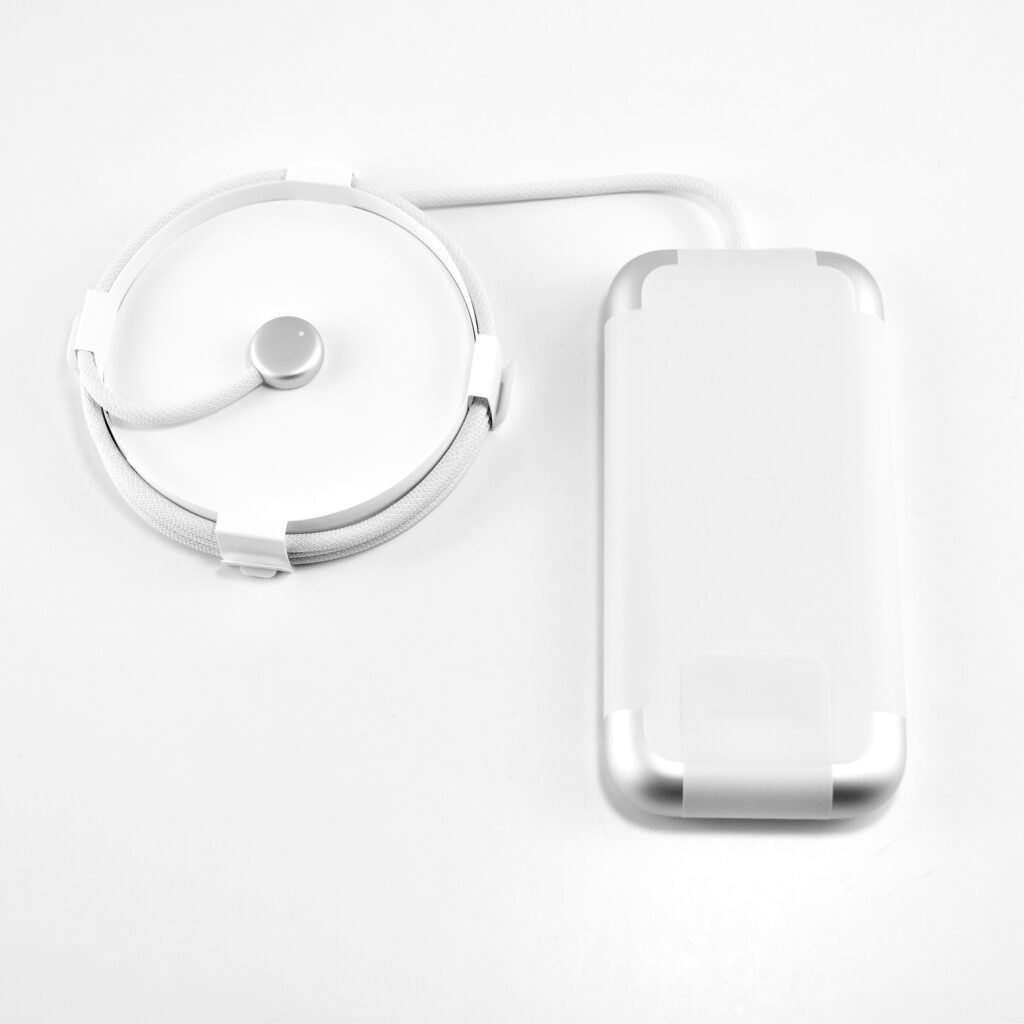
The Apple Vision Pro used a battery pack that delivered “up to 2 hours of general use” or up to 2.5 hours while watching videos. However, the device could also be used with the USB-C port plugged into power while charging the battery.
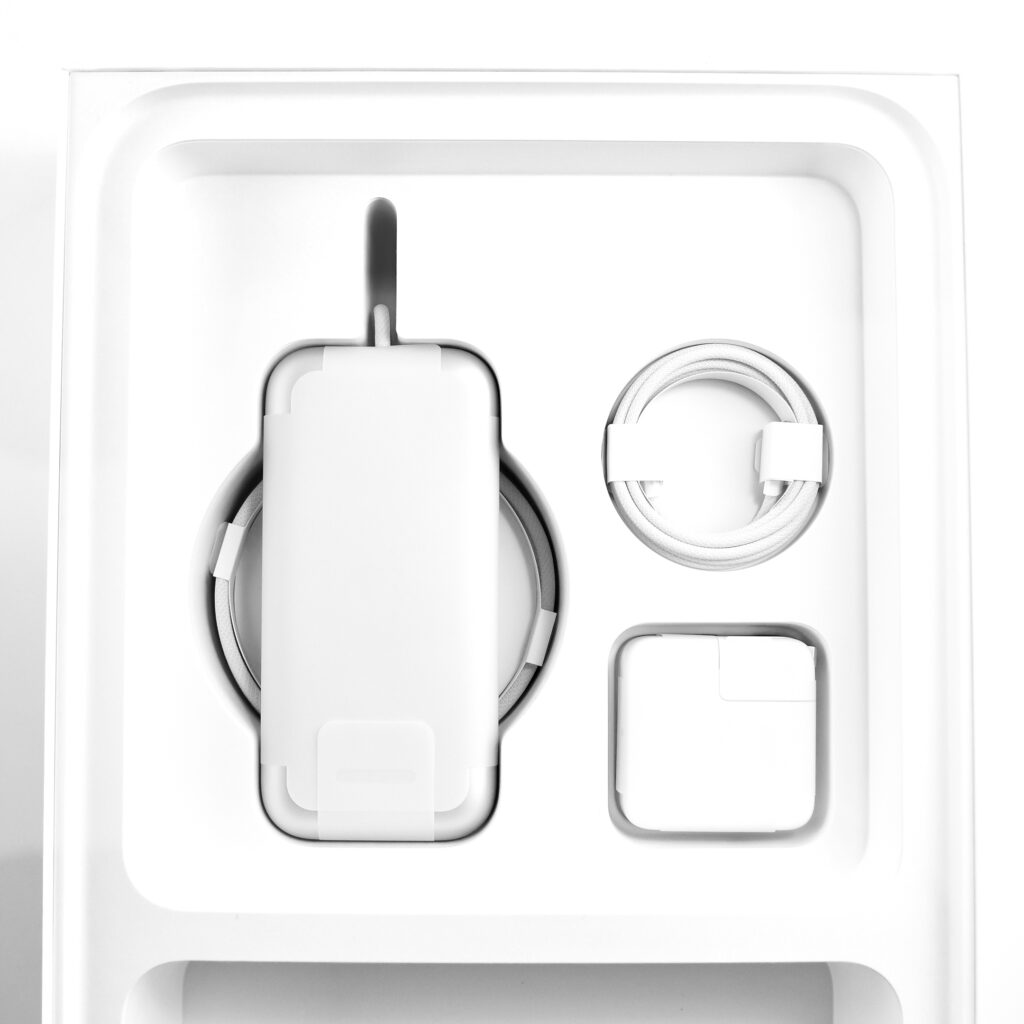
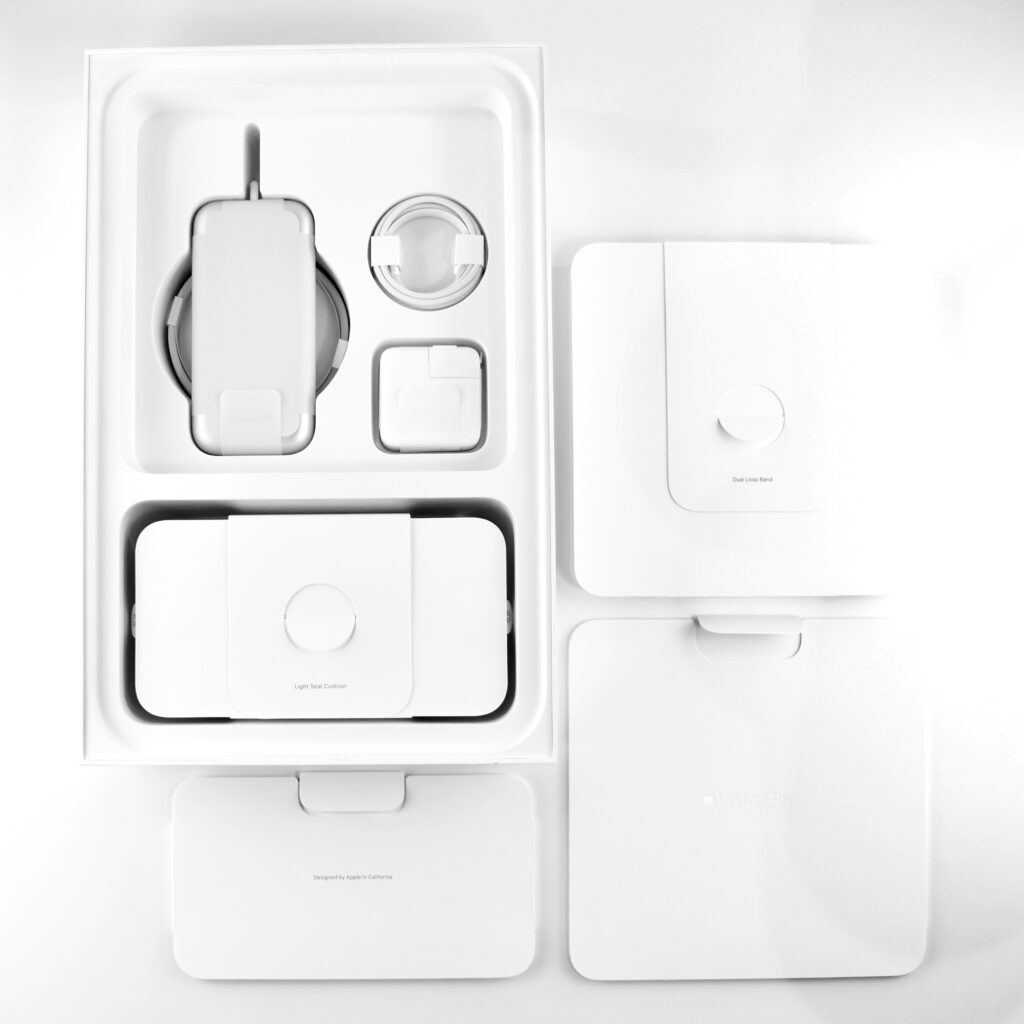
The Apple Vision Pro shipped with many accessories and custom-sized parts compared to Apple’s other devices. The following accessories were included with each Apple Vision Pro:
- Light Seal
- Light Seal Cushions (2 sizes)
- Solo Knit Band
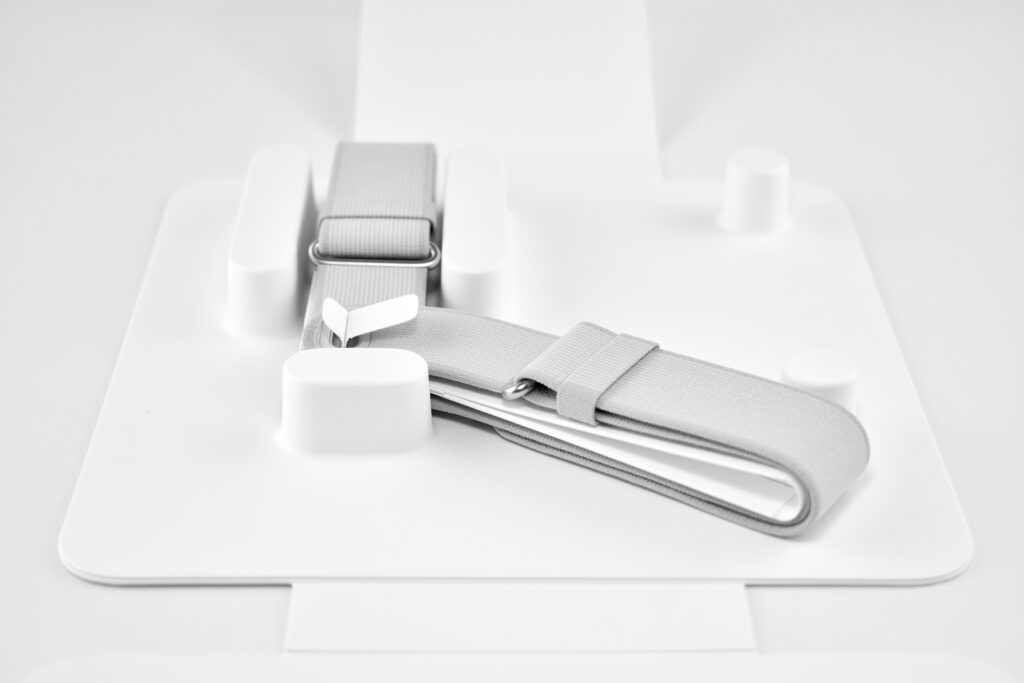
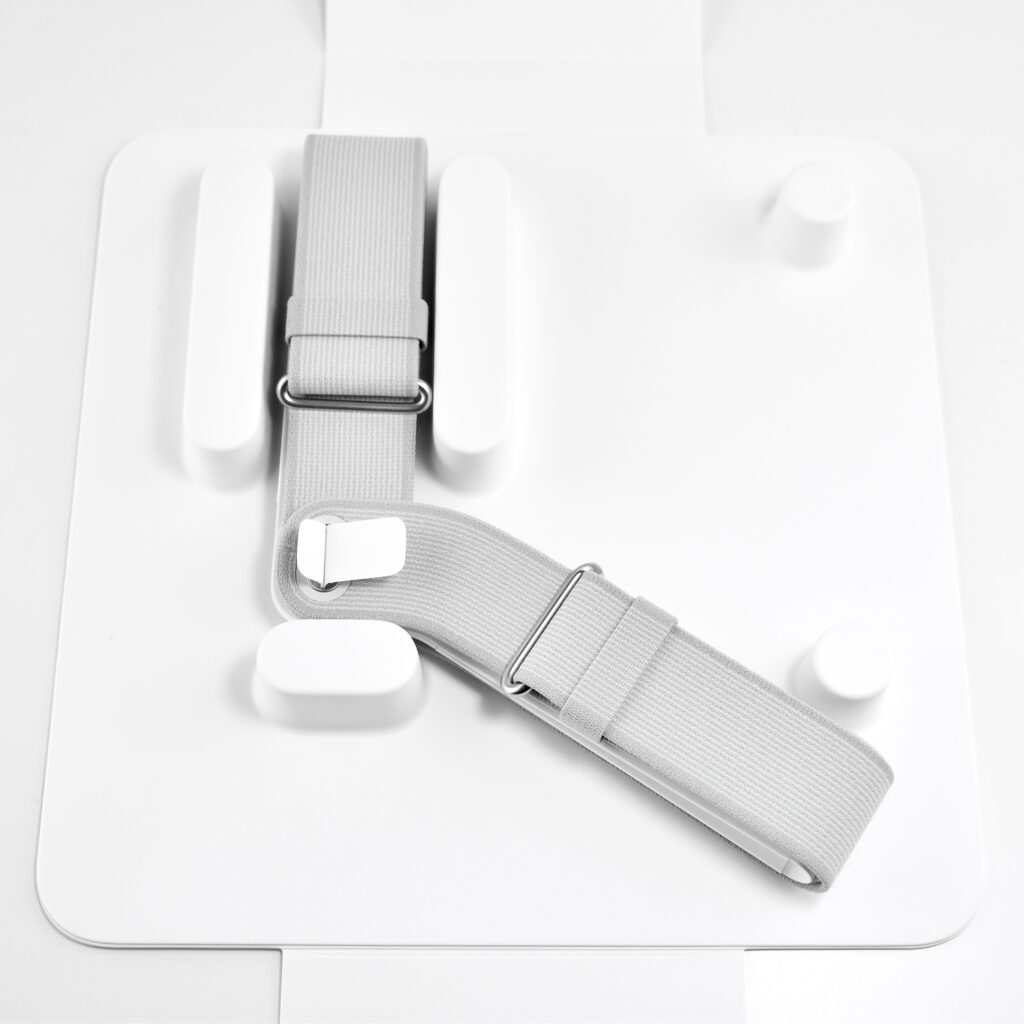
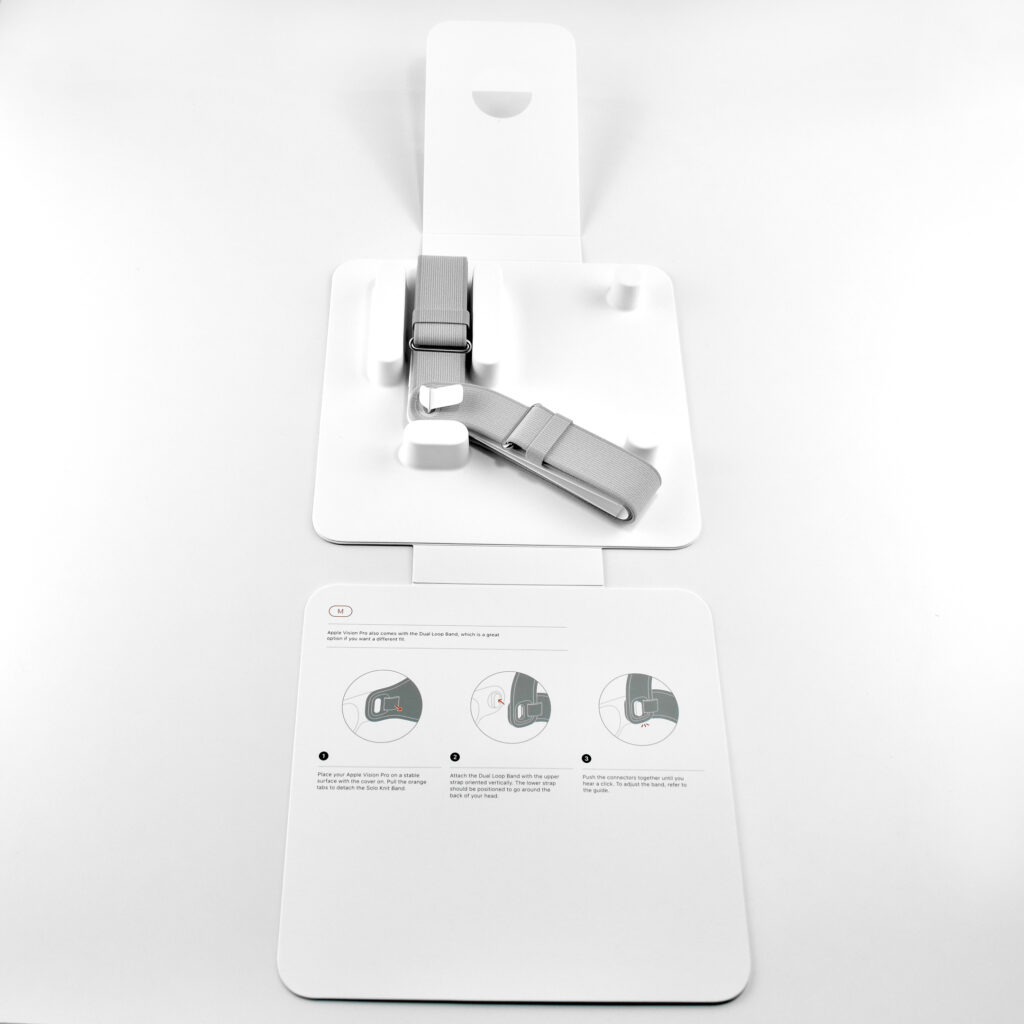
- Dual Loop Band
- Battery pack
- Cover
- 30W USB-C Power Adapter
- USB-C Charge Cable
Several of the parts and accessories that shipped with the Apple Vision Pro were impressive design innovations on their own, even if they were not often mentioned in reviews—or even by Apple. Some examples from my perspective included:
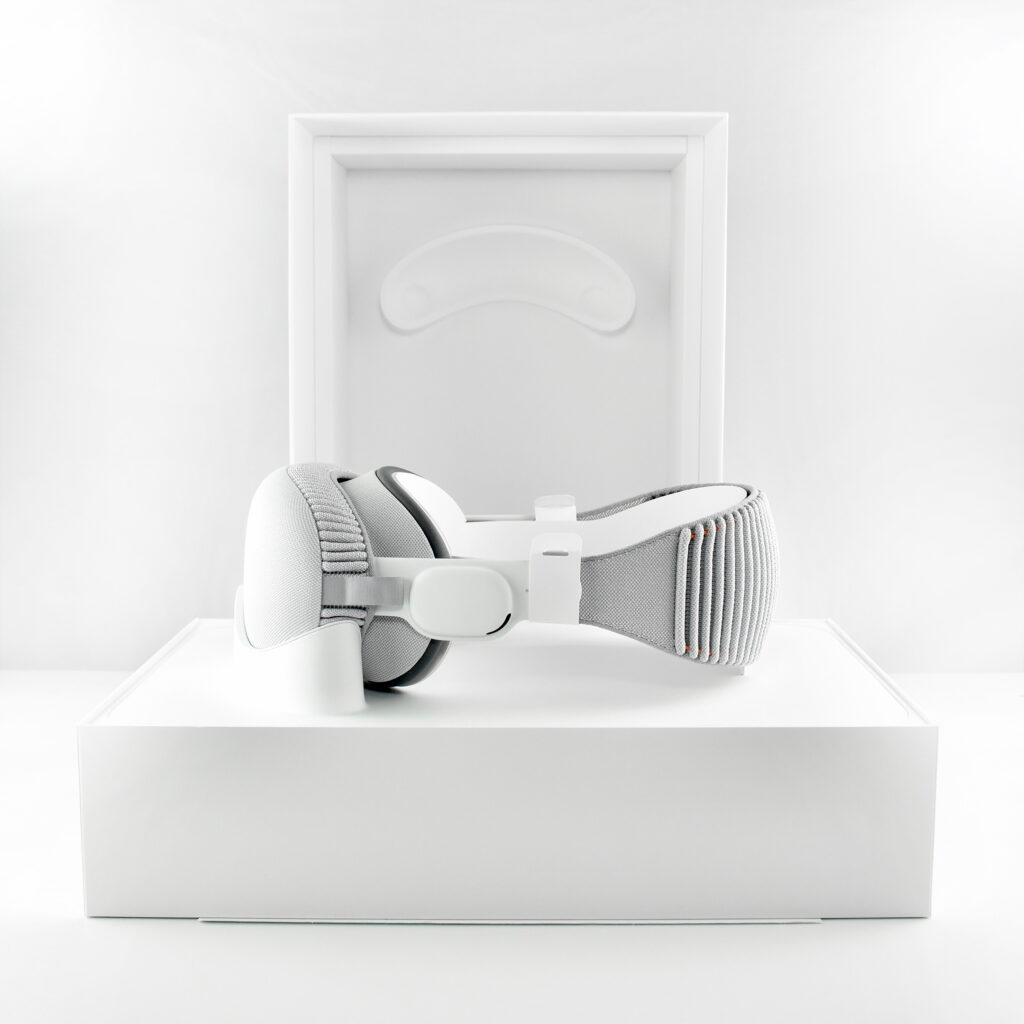
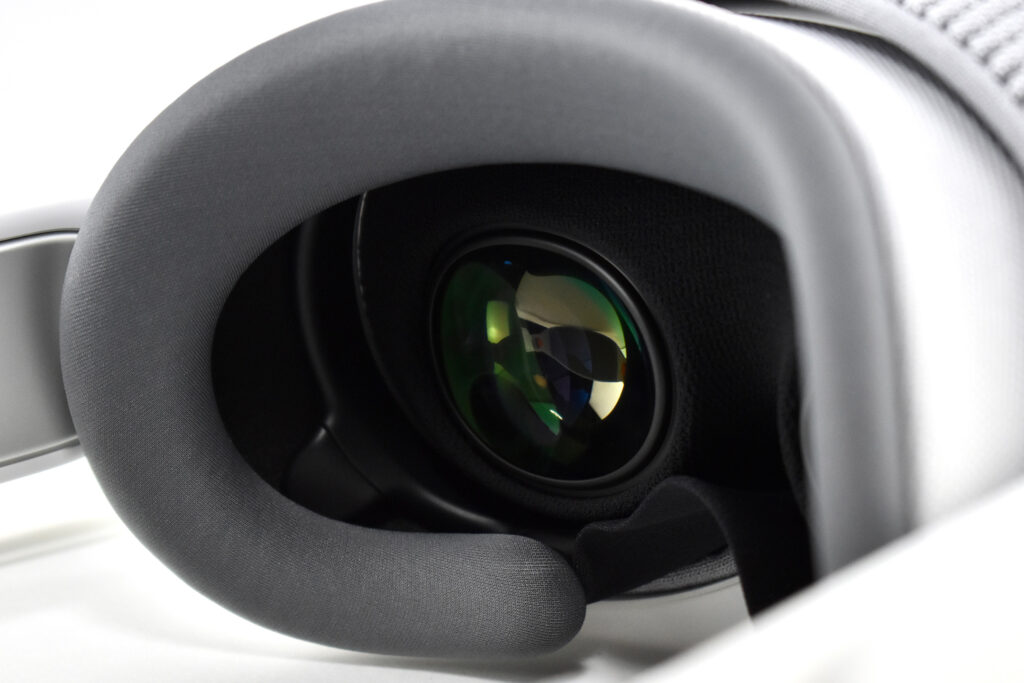
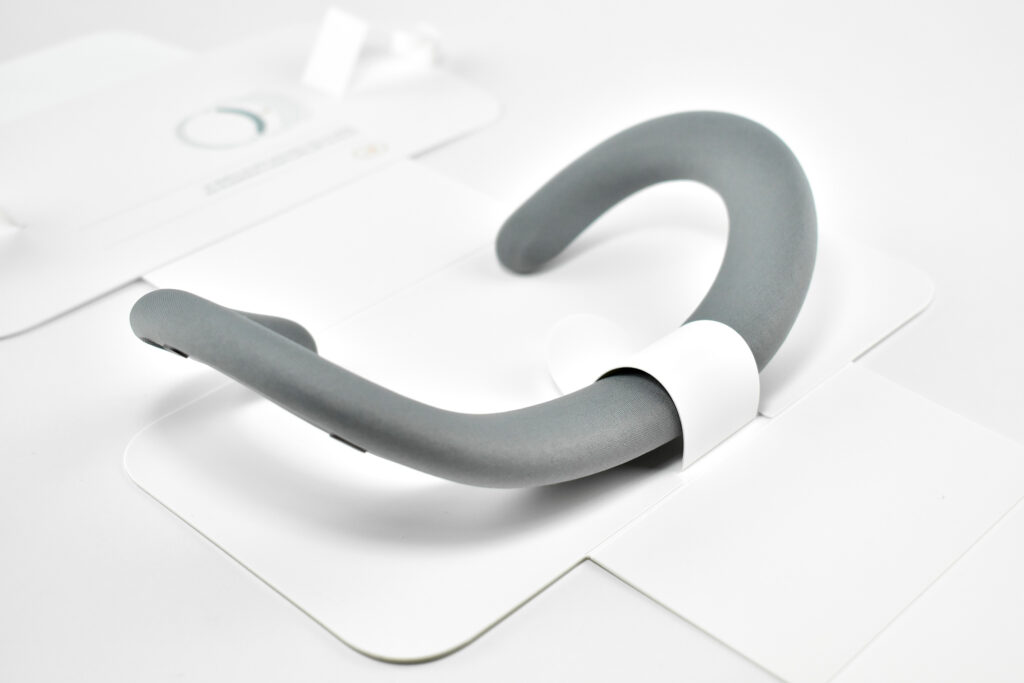
Light Seal—The light seal came in multiple sizes that were matched to the user through a custom app that scanned a user’s face to calculate the appropriate size. The light seal attached magnetically to the main body of the Apple Vision Pro.
Light Seal Cushions—The light seal cushion was also sized for the user and attached with magnets to the light seal to provide a custom fit so light would not “leak” into the space around the eyes.
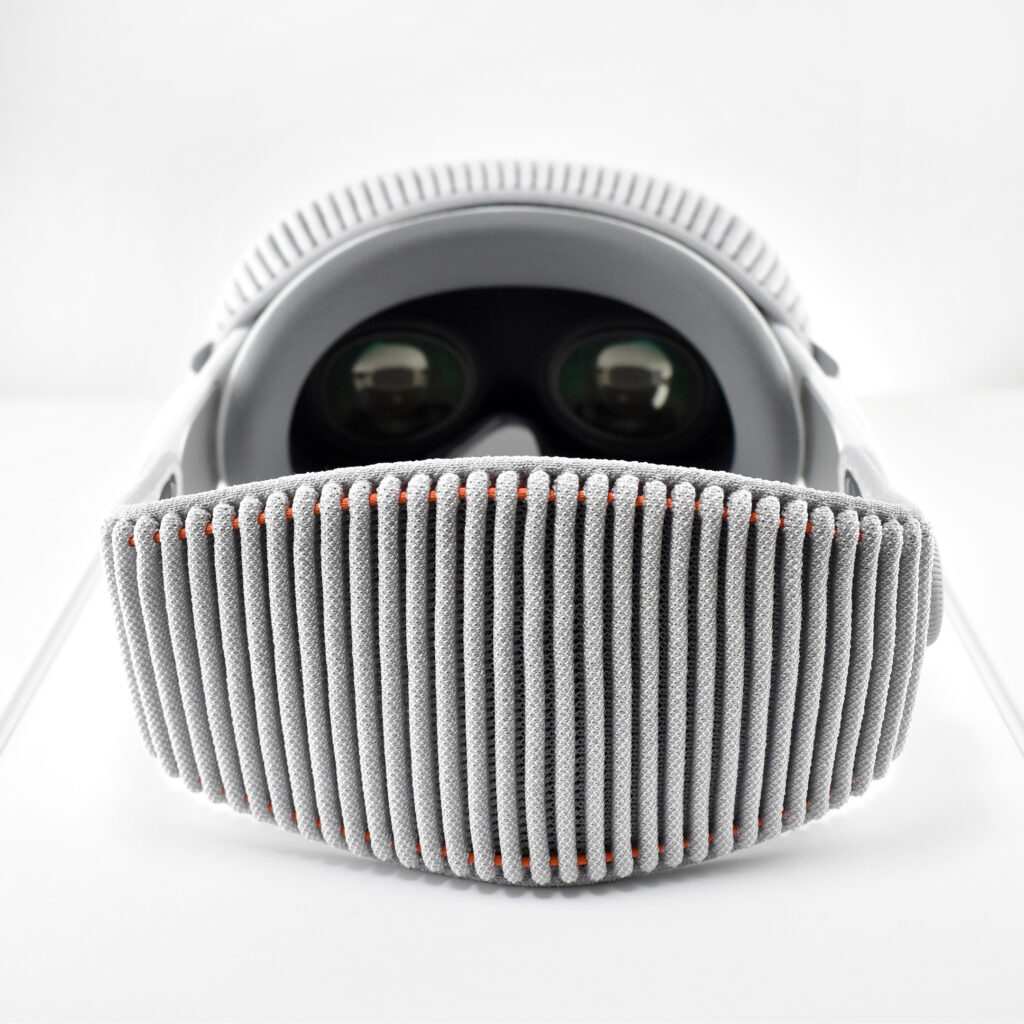
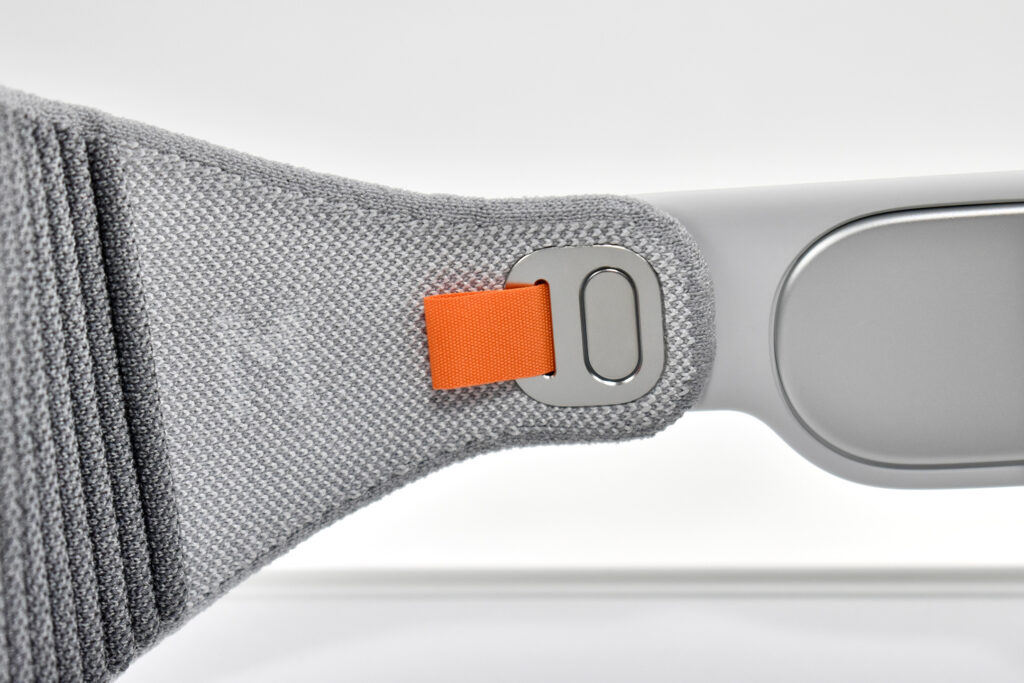
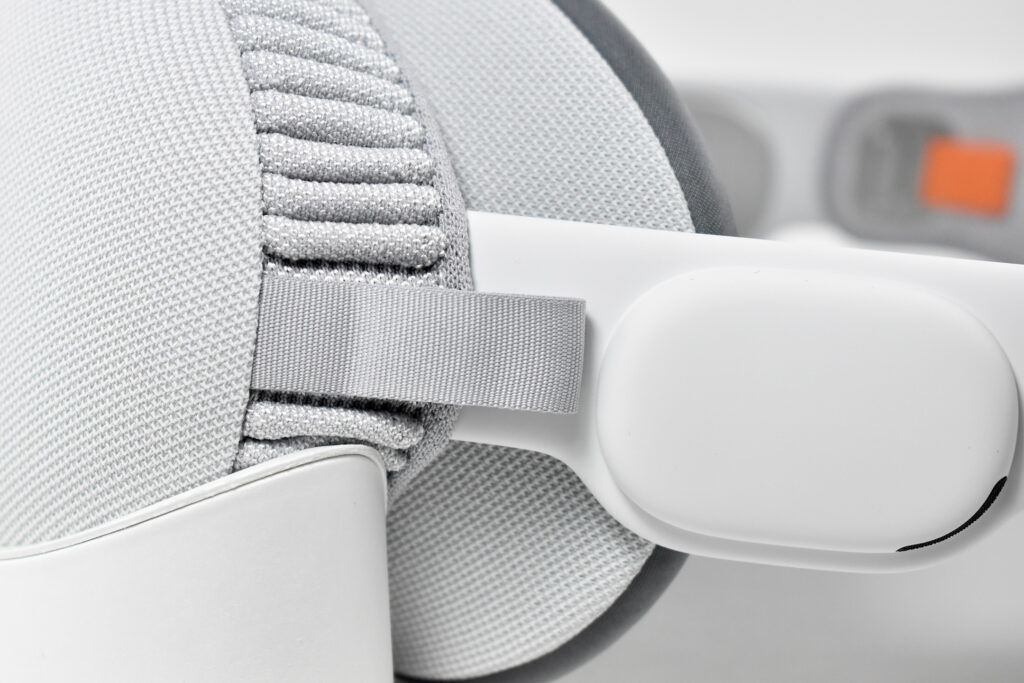
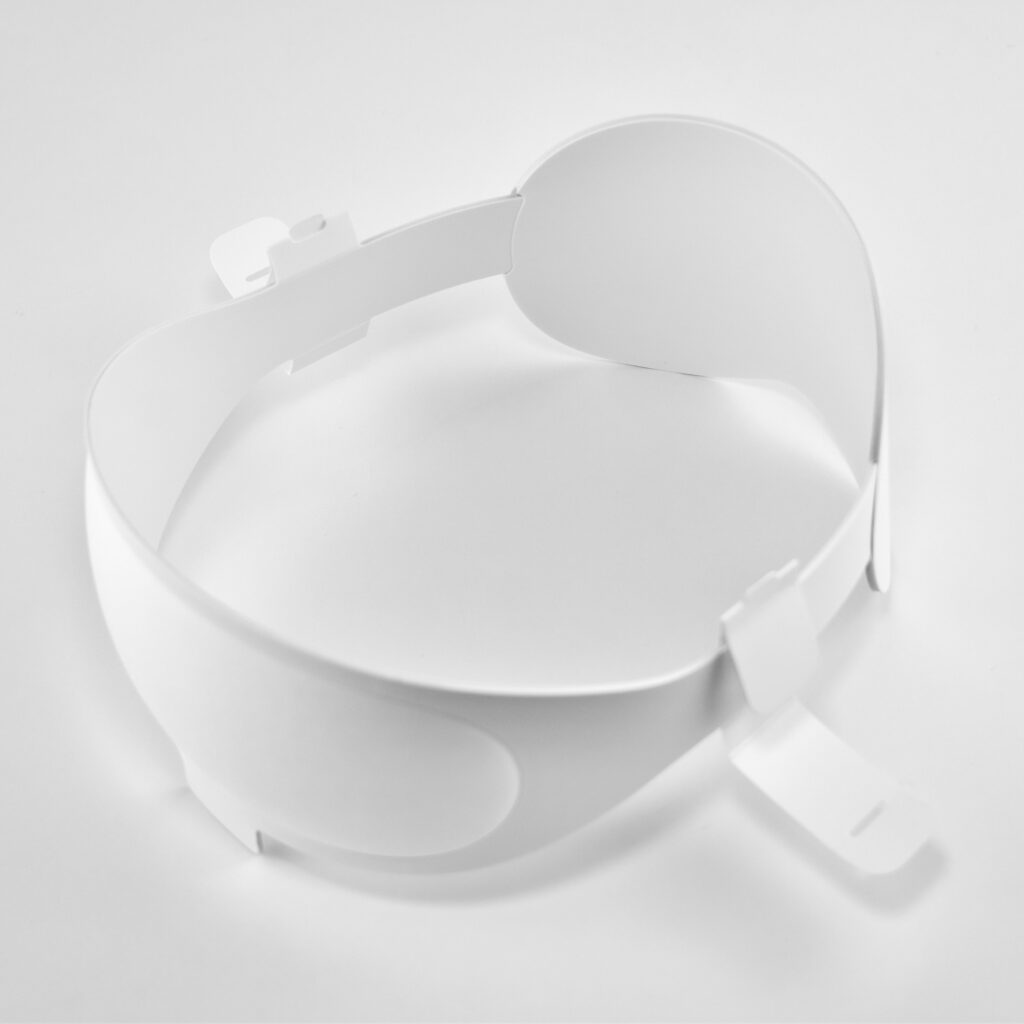
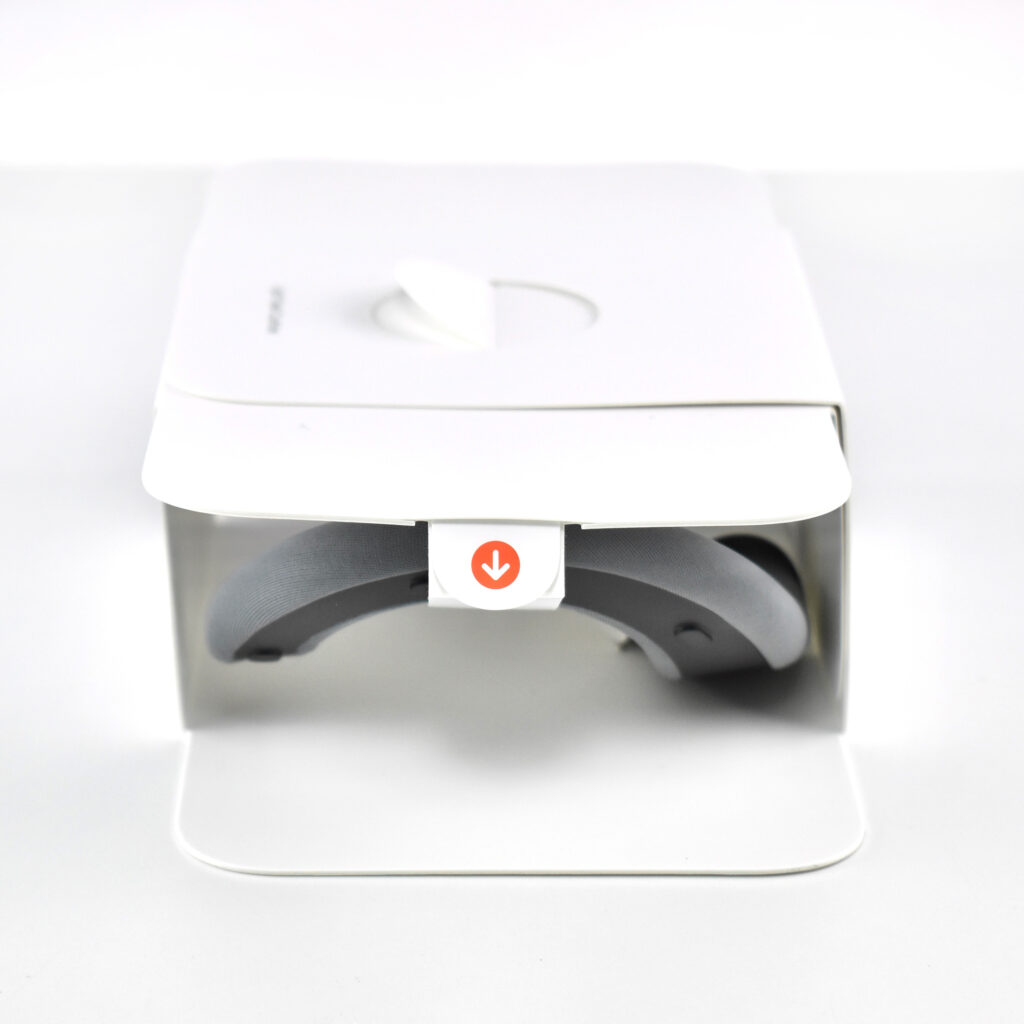
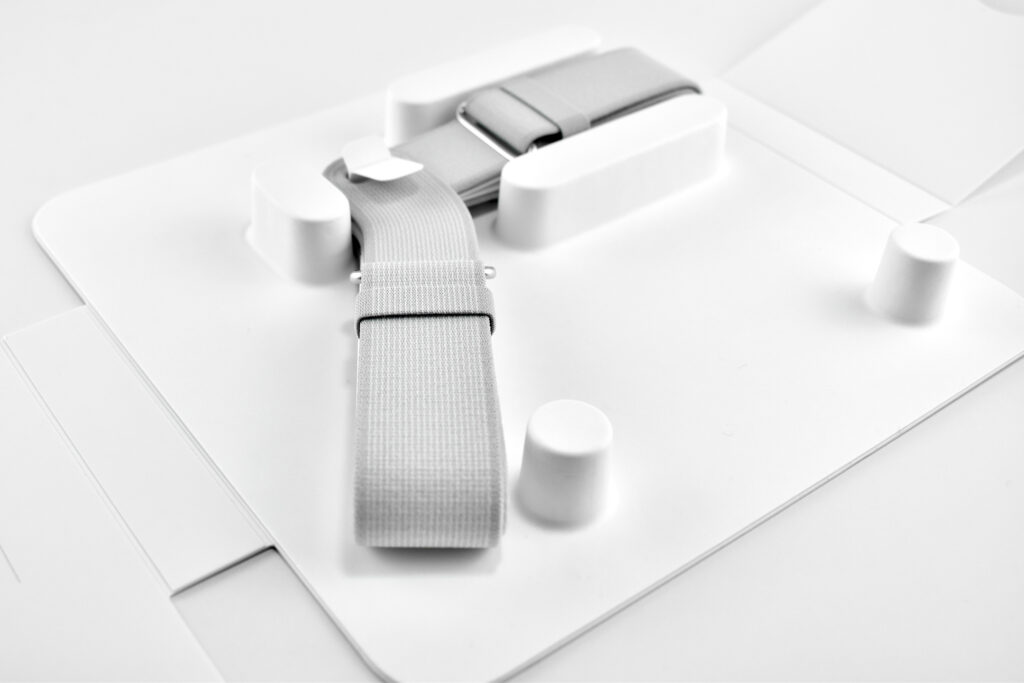
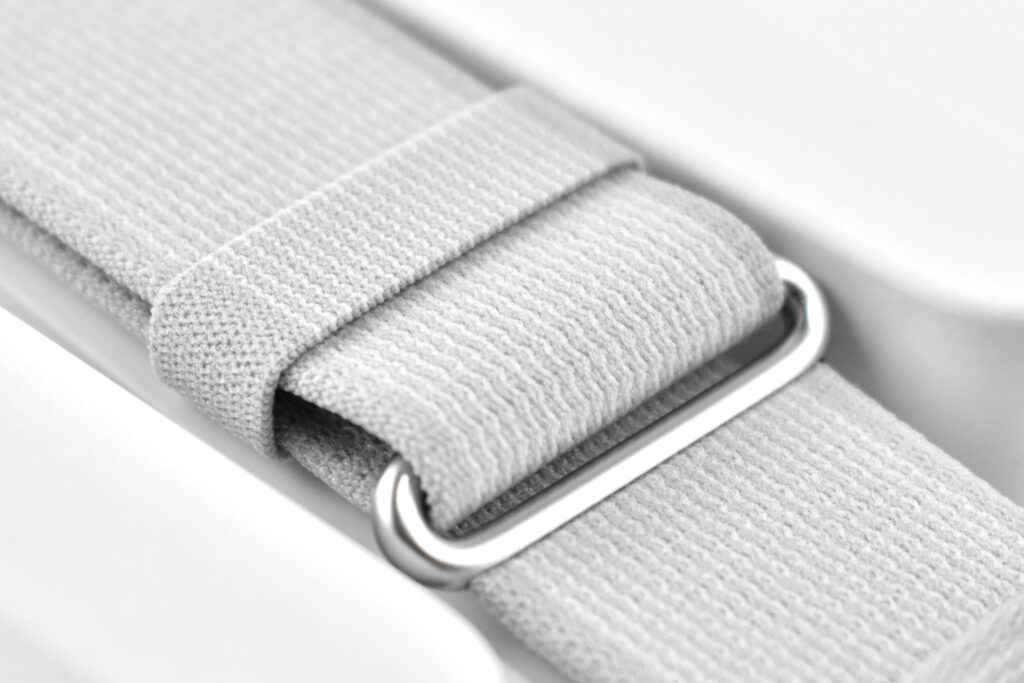
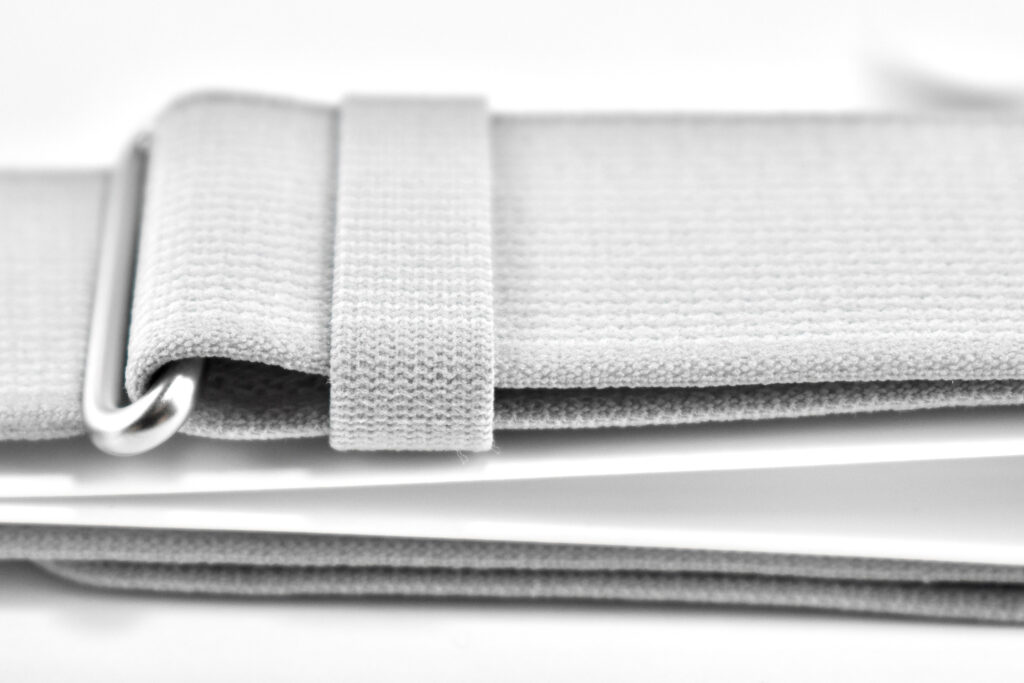
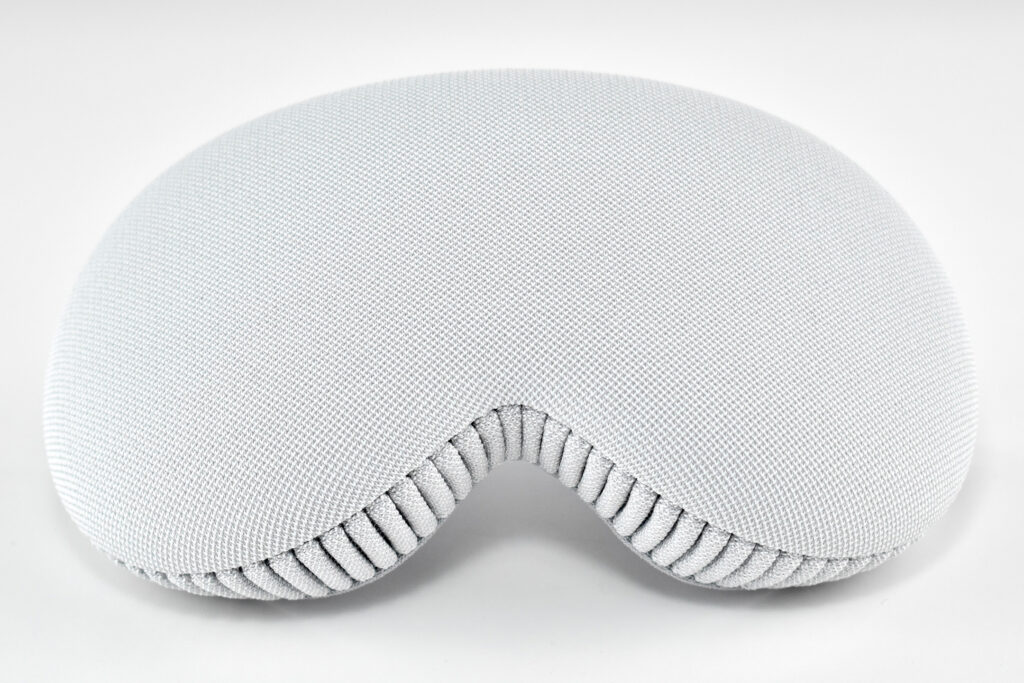
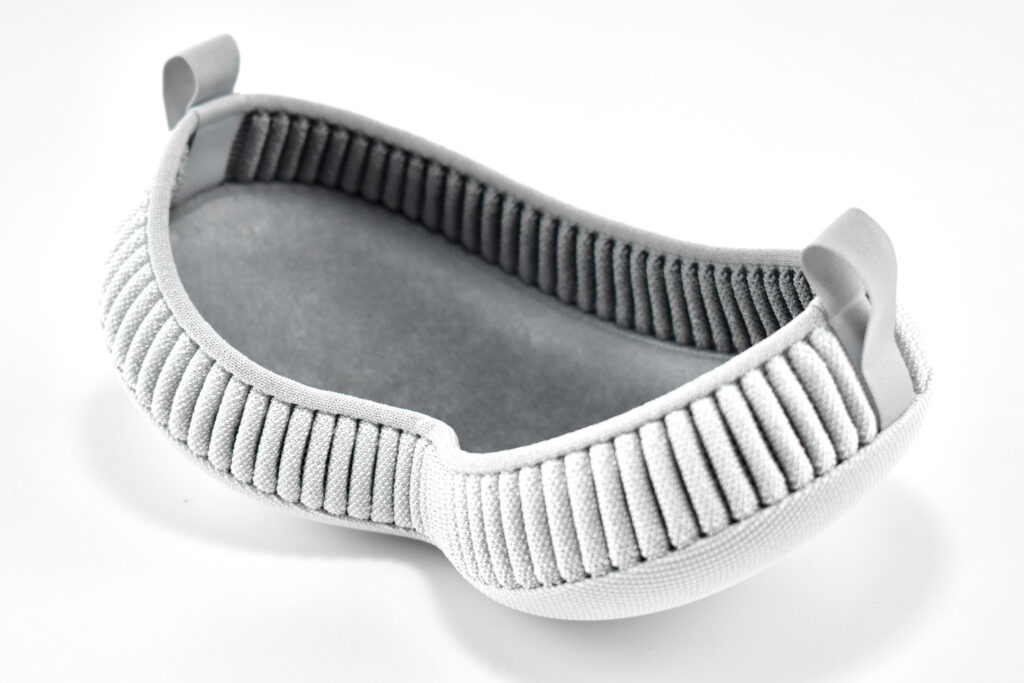
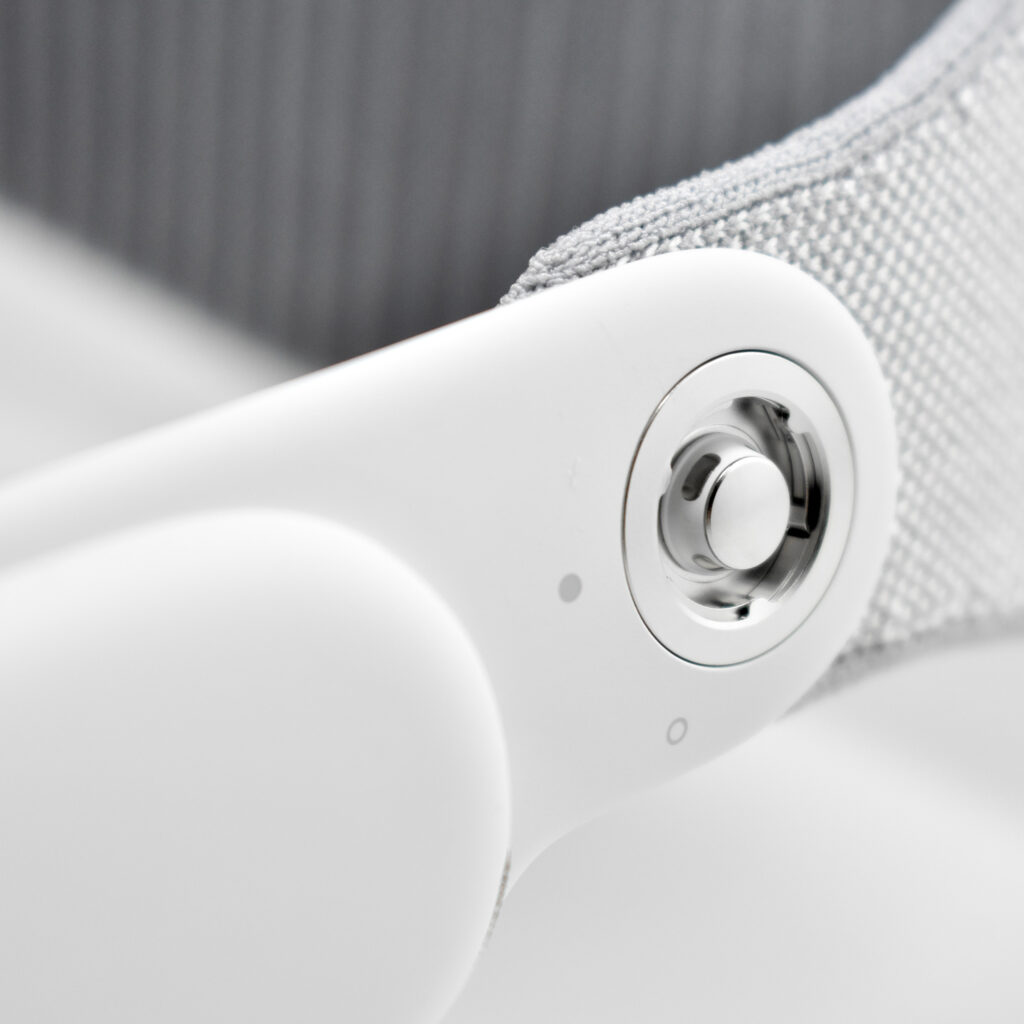
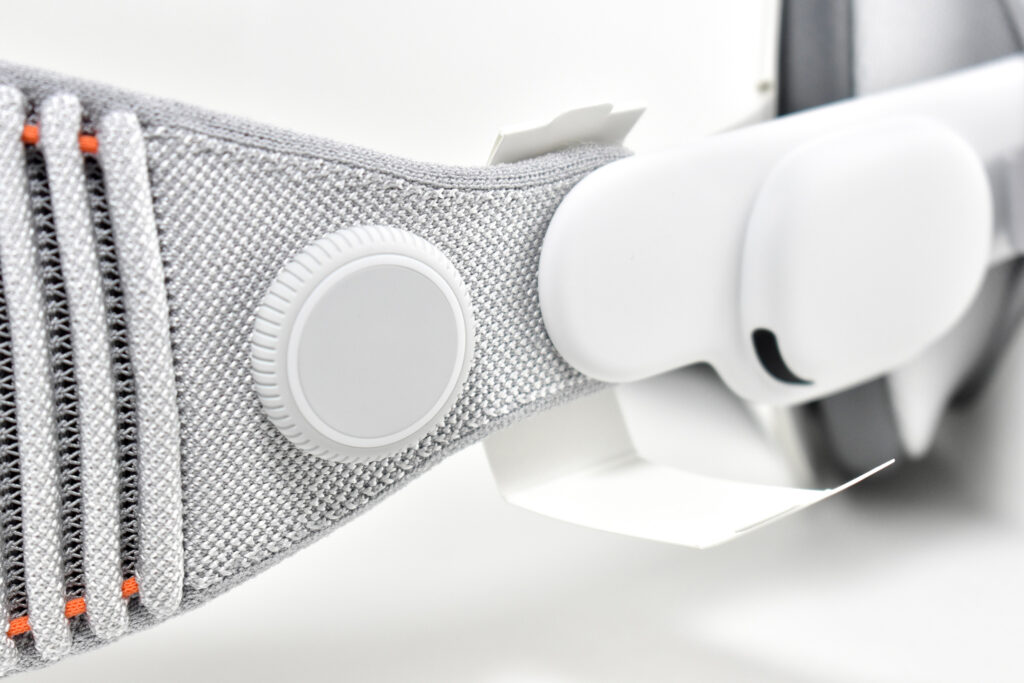
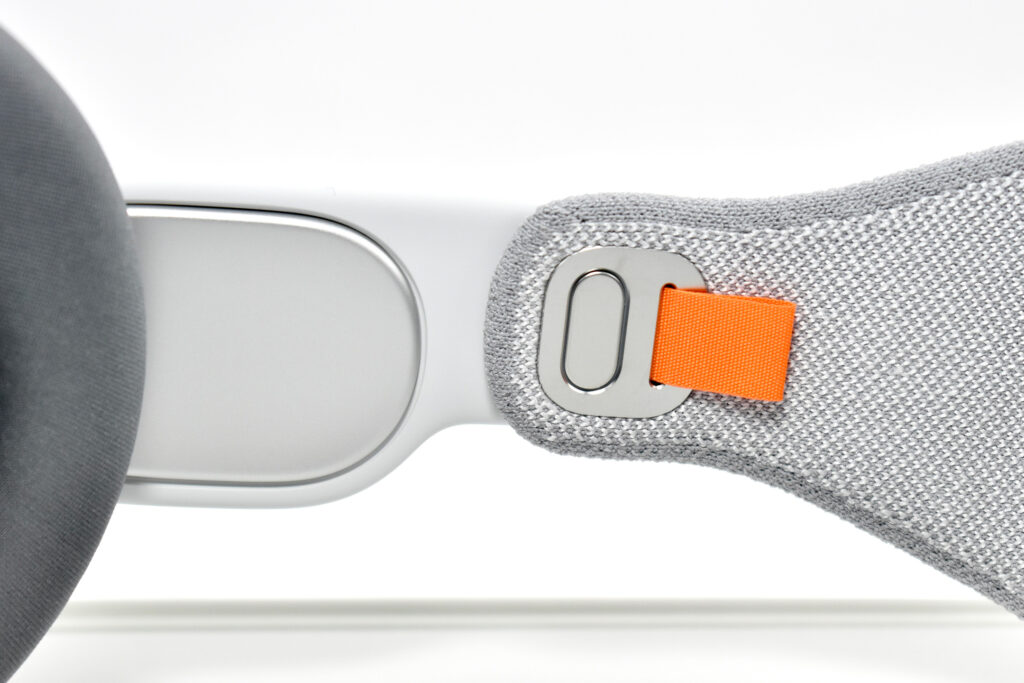
Dual Loop Band and Solo Knit Band—The two bands that shipped each represented impressive engineering and design to fit the 22.9 ounce (1.43 pounds) device to the head and provide relative comfort and support during use. The Dual Loop Band provided a 2-strap system that supported the device around the back and over the top of the head with adjustable velcro closures. The Solo Knit Band was a single thicker band that was “3D knitted as a single piece to create a unique rib structure that provides cushioning, breathability, and stretch. It has an easy-to-reach Fit Dial to let you adjust Apple Vision Pro to your head and enables microadjustments during use.” I personally prefer the Solo Knit Band.
Further, the Solo Knit Band was noted by journalists and reviewers as looking fashionable, especially compared to the utilitarian straps provided by other AR/VR headsets. One 9to5Mac author noted, “I just think the Solo Knit Band looks cooler, and comfort just hasn’t been an issue for me.”
Cover—Even the lowly knit cover was an impressive piece of design in my opinion. The cover itself had knit edges, but allowed the Apple Vision Pro device to be effortlessly lowered into the accessory with a perfect fit that fully protected the glass front. Tabs on the edges also allowed it to be easily removed.
ZEISS Optical Inserts—For those of us who require vision correction and do not wear contact lenses, Prescription ZEISS Optical Inserts were available to be custom-made to an exact prescription. The inserts easily snapped in with magnets and were “recognized” by an Apple Vision Pro device by selecting the user’s account settings.
Although this entry is not intended as a review of the Apple Vision Pro, as a user I can attest that the device is extremely difficult to describe to someone who has not used it first-hand. In my experiences, the device and visionOS functioned seamlessly from the original visionOS through visionOS 2. In my Apple-user-experience lifetime (since the early-1980s), I have never experienced a more mature operating system for a brand new device—especially one with so many brand new user interface elements.
After a lifetime of keyboard typing, mouse clicking, and most recently touch-based interfaces, the Apple Vision Pro required a user to make the leap to looking at virtual interface elements (through eye tracking) and interacting though hand gestures (pinches, pulls, and a 2-hand pinch/pull motions). Having coached about 50 first-time users through using the Apple Vision Pro as of this writing, I have observed that every user was able to understand these UI paradigms within the first 5–10 minutes of using the device (most adapted more quickly).
Finally, I wrote a series of education-focused articles about my first impressions of the Apple Vision Pro after the device was first released. They are available on a separate blog at Blogger:
- Unpacking, Photographing, Setup, and First Impressions
- Reviewing the Reviews
- New Terms Introduced with the Apple Vision Pro
- Focus on Foveated Rendering
Sources: Simon Greenwold (2003), FastCompany (2024), Apple (product page, Newsroom, Tech Specs, Solo Knit Band, gestures and controls), 9to5Mac