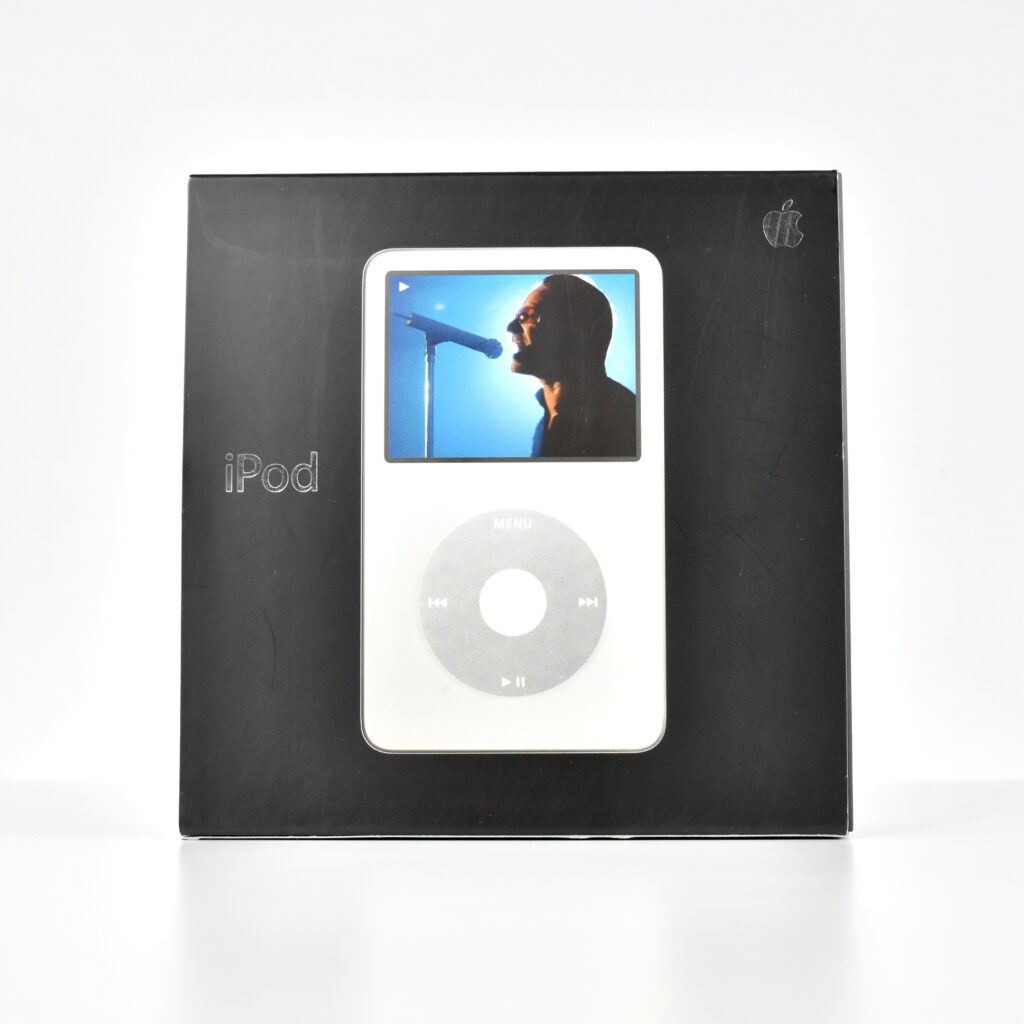
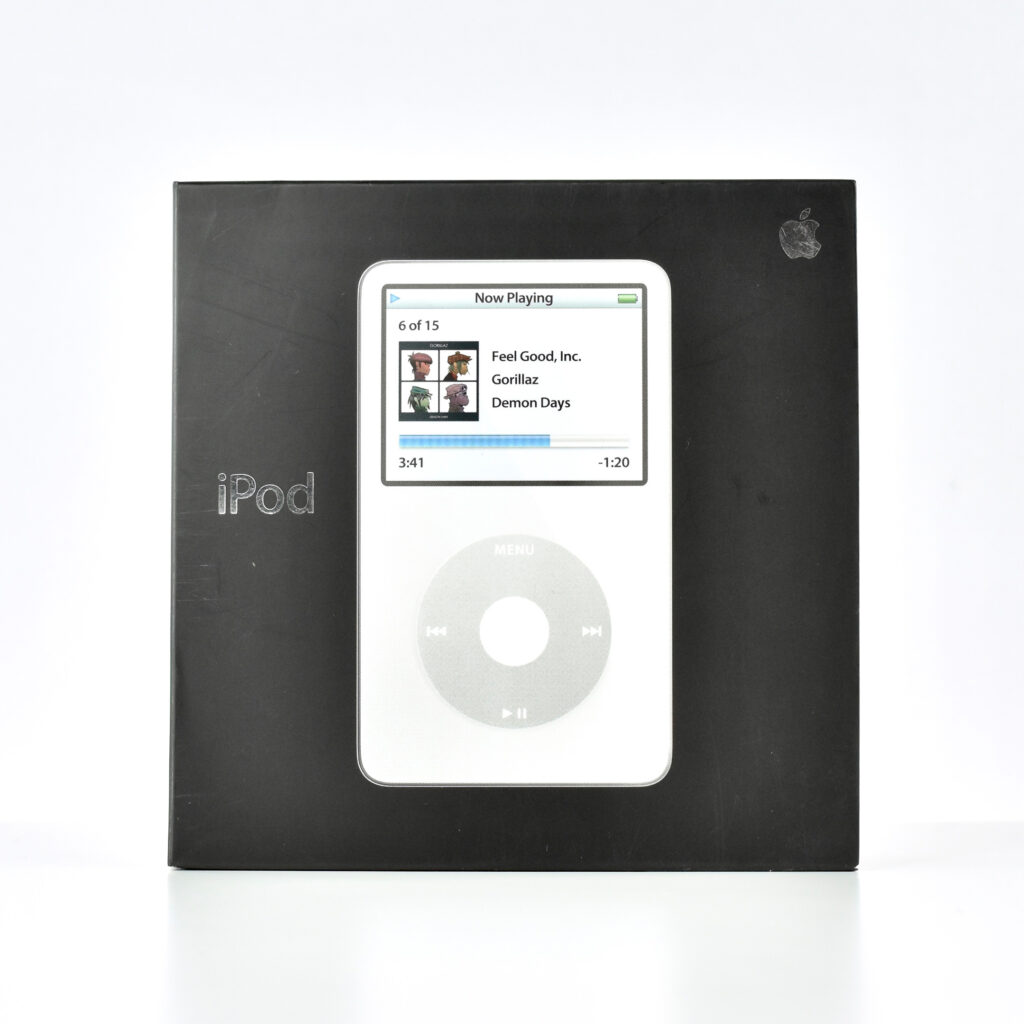
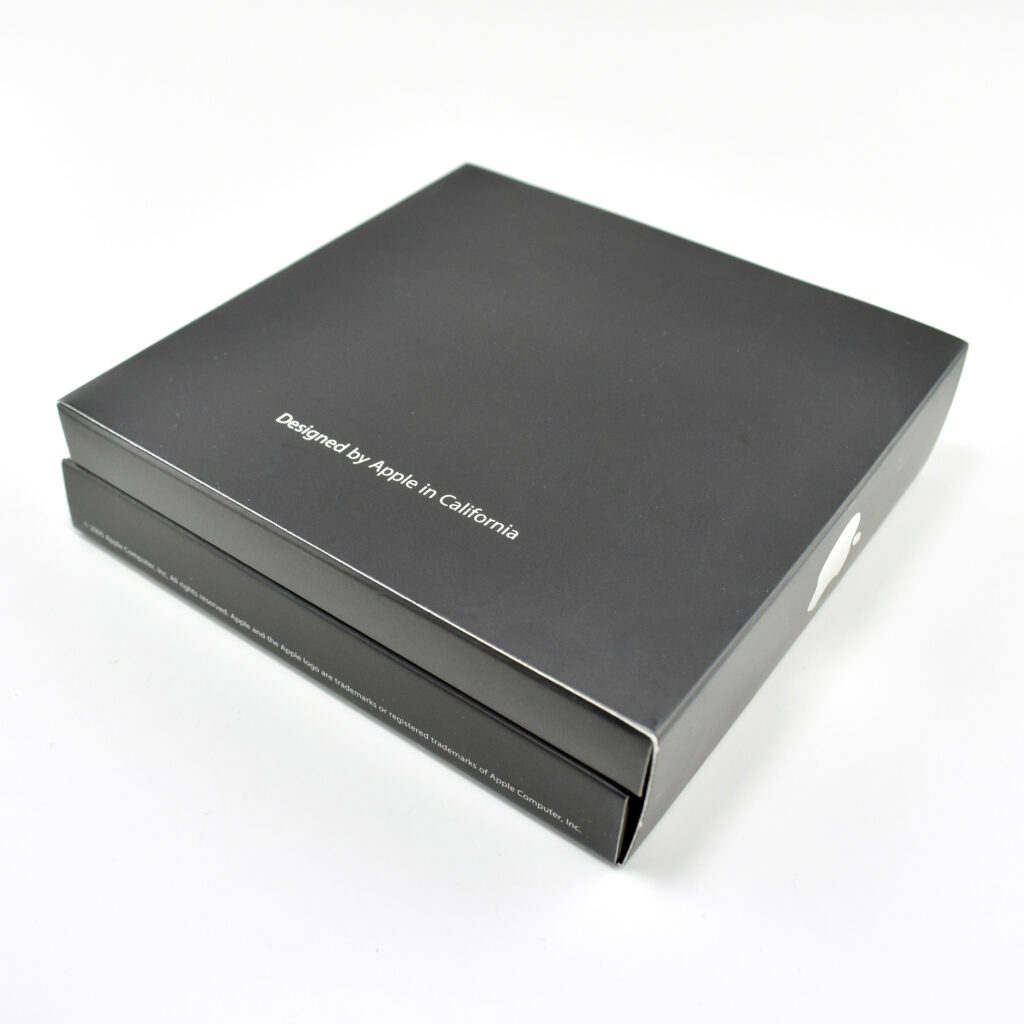
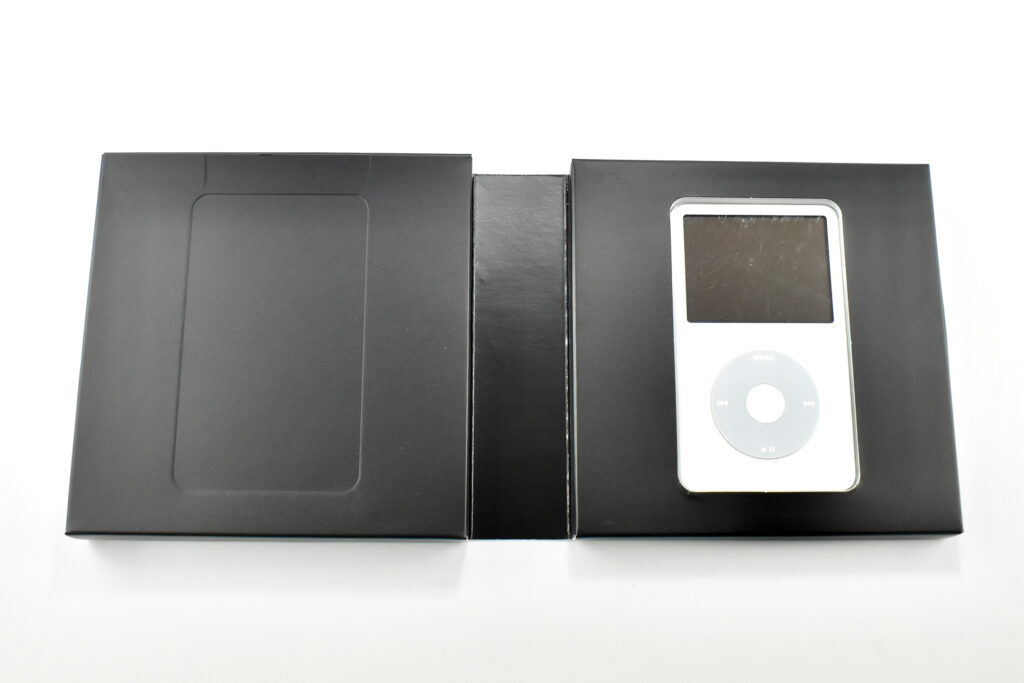
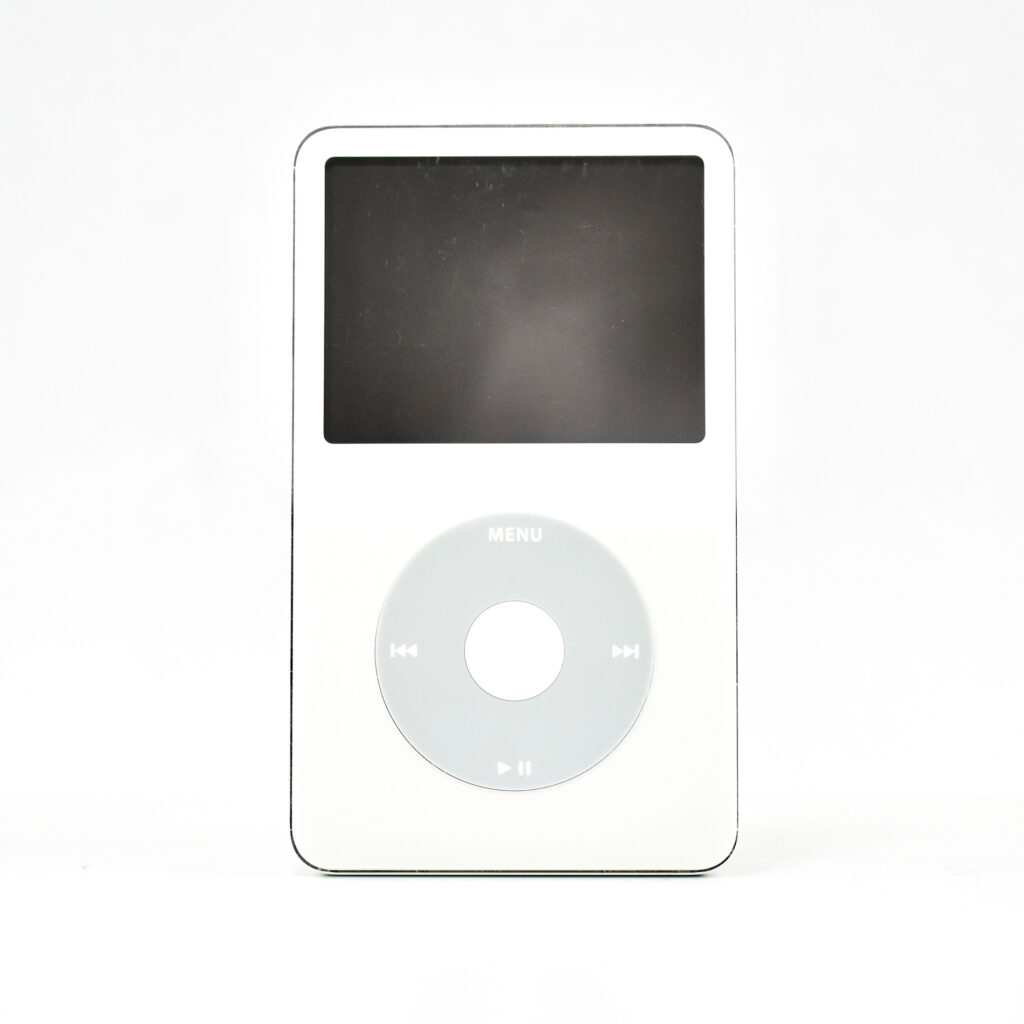
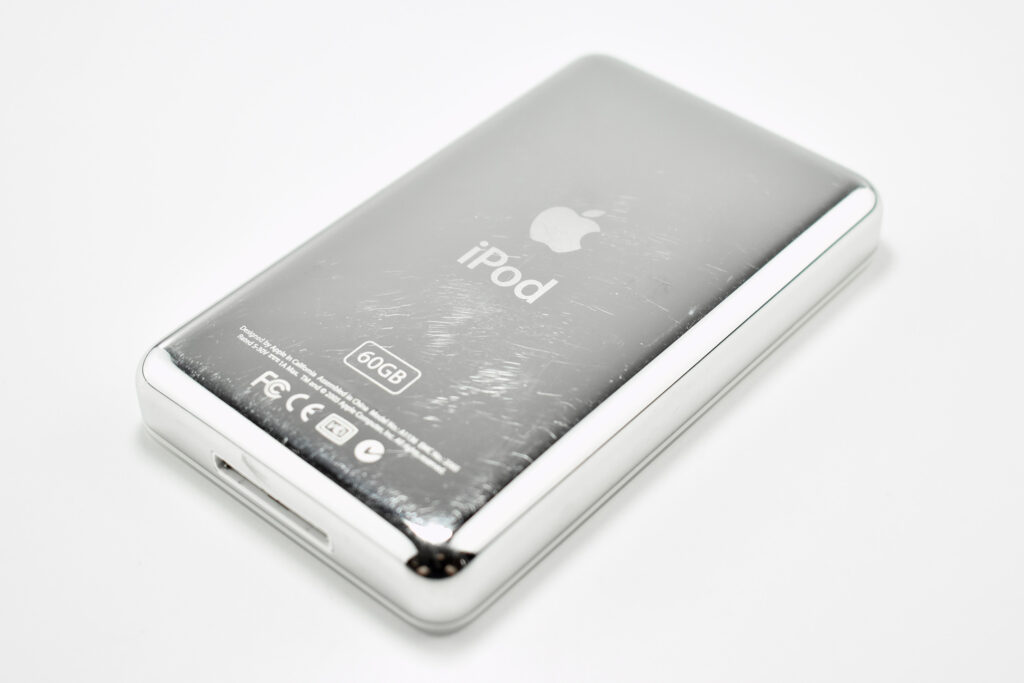
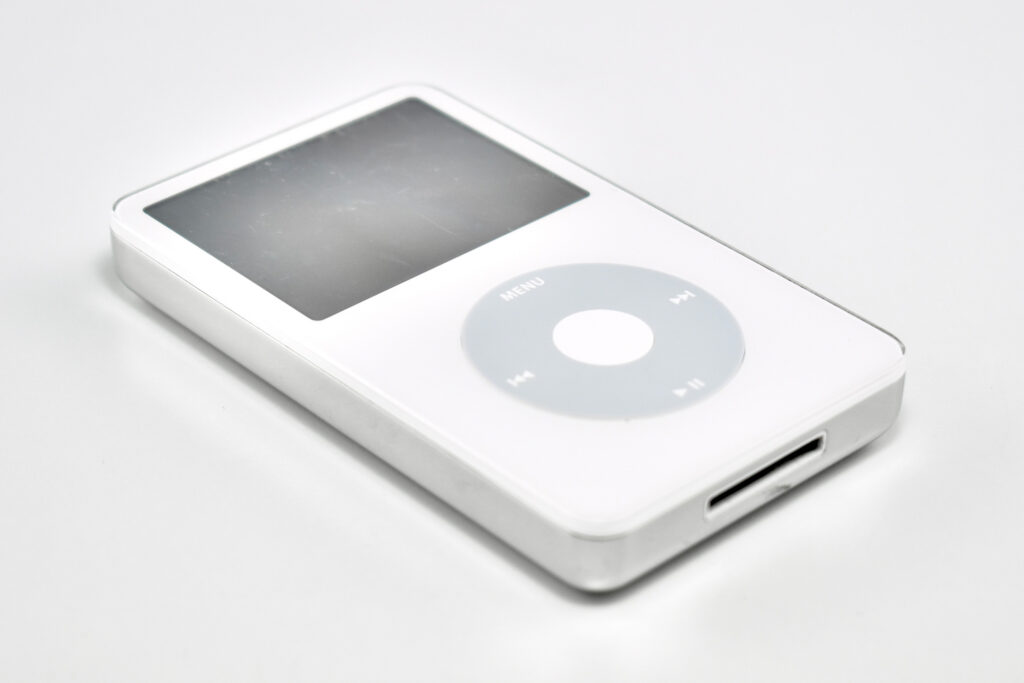
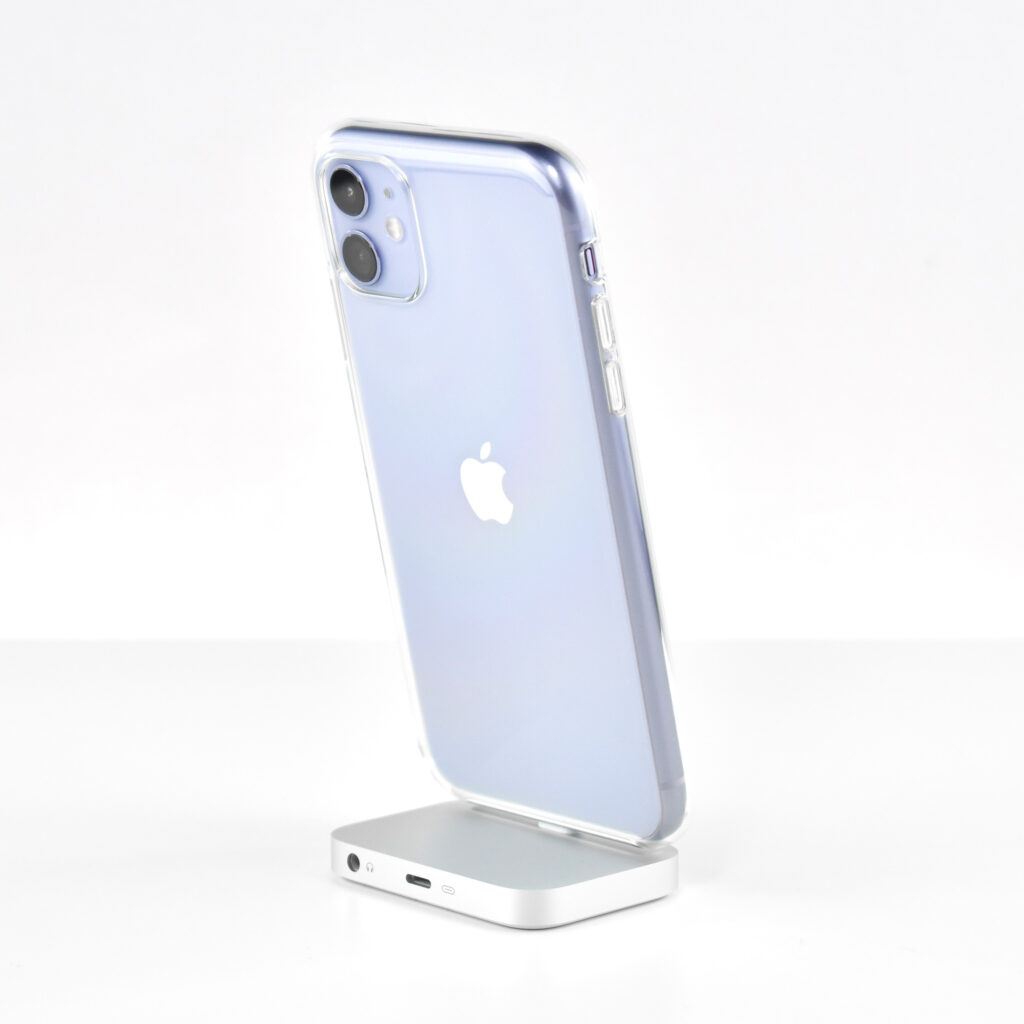
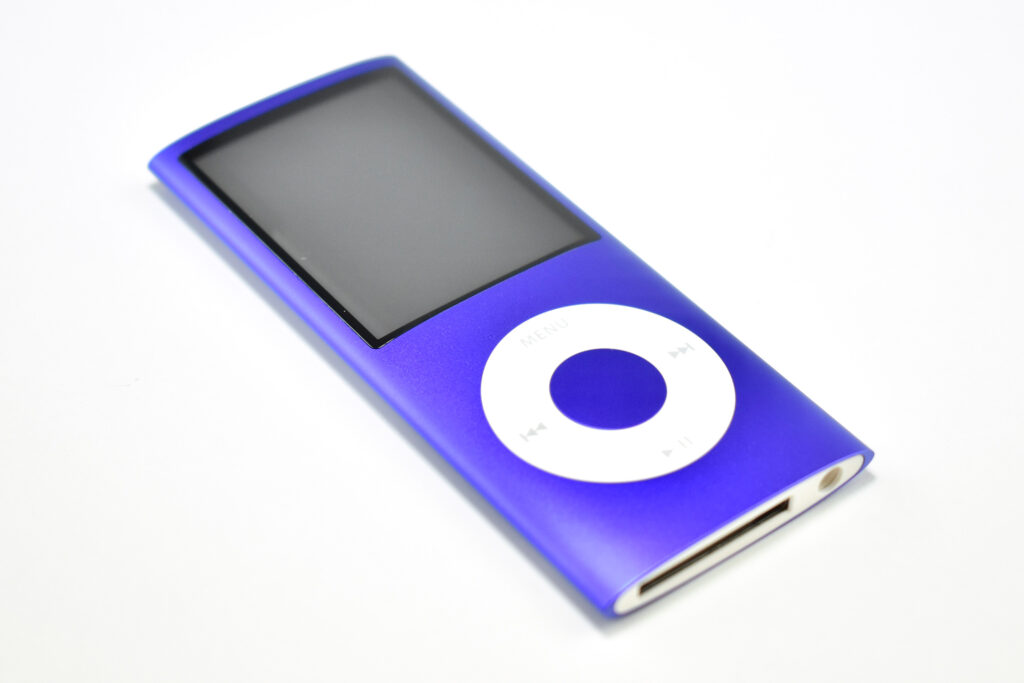
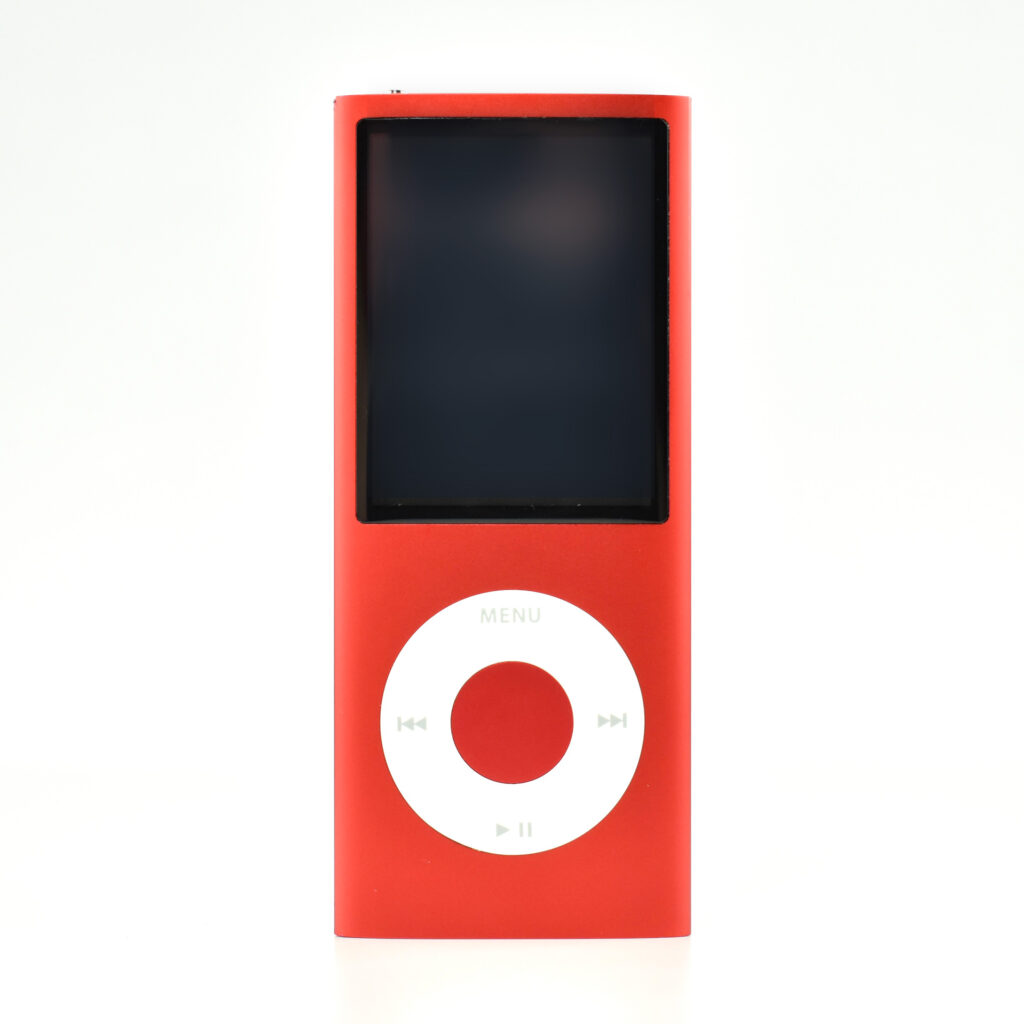
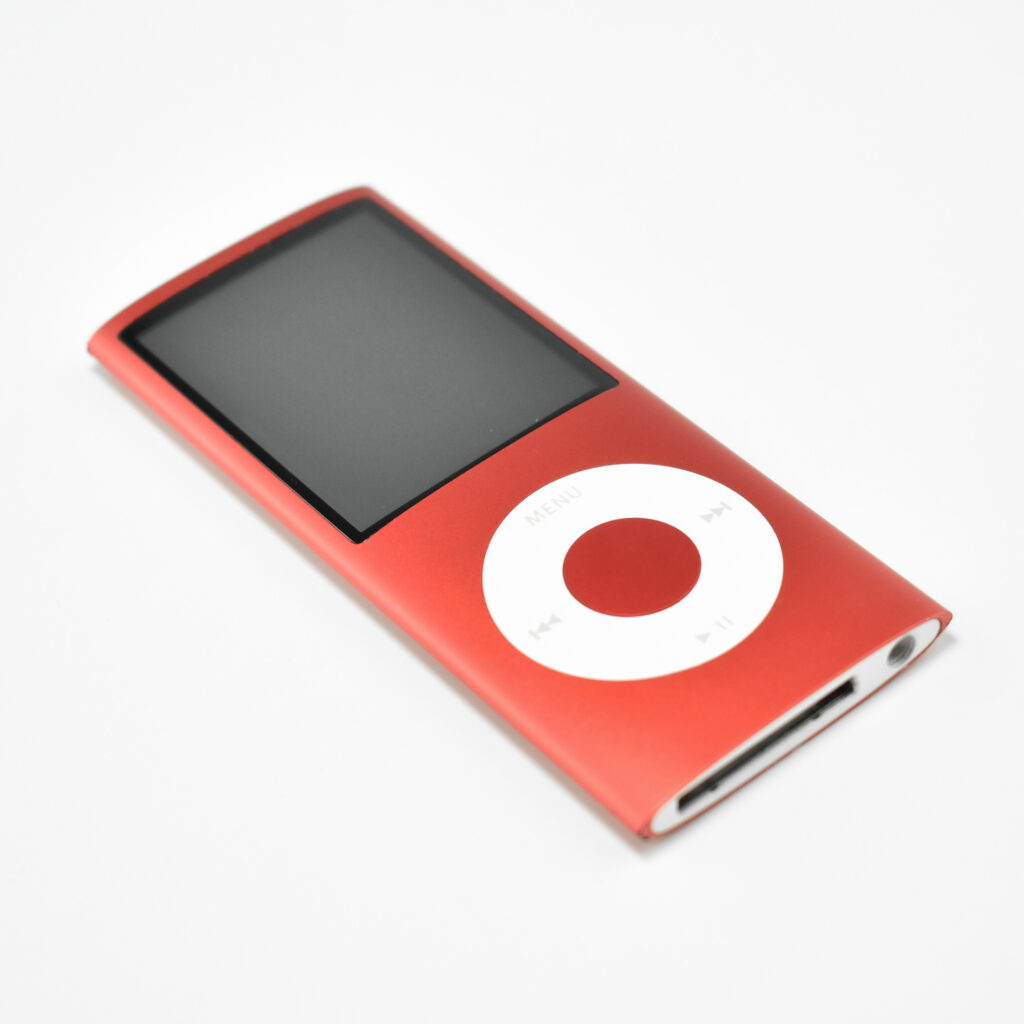
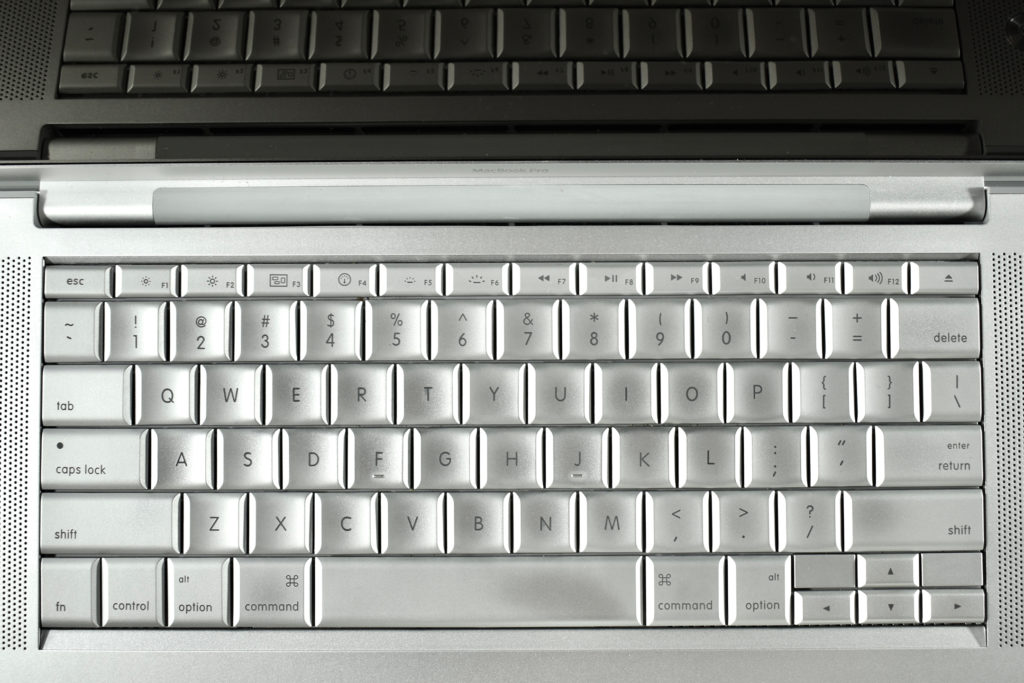
The iPod Generation 5, also known as iPod with video, was the first iPod model capable of displaying video. This device’s part number is MA003LL/A, and its model number is A1136. Apple describes this iPod:
“The iPod (5th generation) is a hard drive-based iPod featuring a large, widescreen color display, a Click Wheel, and the capability of displaying photos and videos. It uses USB for syncing.”
According to EveryMac:
“It uses a 30 GB or 60 GB 4200 RPM ATA-66 hard drive, capable of supporting up to 7,500 songs or up to 15,000 songs in 128-Kbps AAC format. Additionally, Apple reports that the 30 and 60 GB drives, respectively, can hold over 1000 or 2000 4-minute videos in H.264…”
Apple described the color of this iPod as “iBook white” (after its laptop sold at the same time), or “jet black” for the U2 version of this iPod. All iPod Generation 5 models had a chrome stainless steel back. The 30GB model of the Generation 5 iPod was 31% thinner than the 30GB Generation 4, and the 60GB model of the Generation 5 iPod was 12% thinner than the 60GB Generation 4.
This iPod had a 2.5-inch (diagonal) QVGA transflective color LCD display (at 320×240) capable of displaying over 260,000 colors. The backlight was both larger and higher-resolution than earlier iPod models.
EveryMac reported that:
“The iPod 5G can immediately display many types of photos transferred directly from a digital camera using the iPod Camera Connector (US$29), and can display photo slide shows on the internal display or a television using the included AV cable (S-video, data and audio output, and a variable line output port are provided by the optional Universal Dock (US$39) that also provides support for the Apple Remote (US$29). Unlike earlier iPod models, it also supports video playback on the internal display or on a television (at a maximum resolution of 480×480).”
Source: Apple (Identify Your iPod), EveryMac