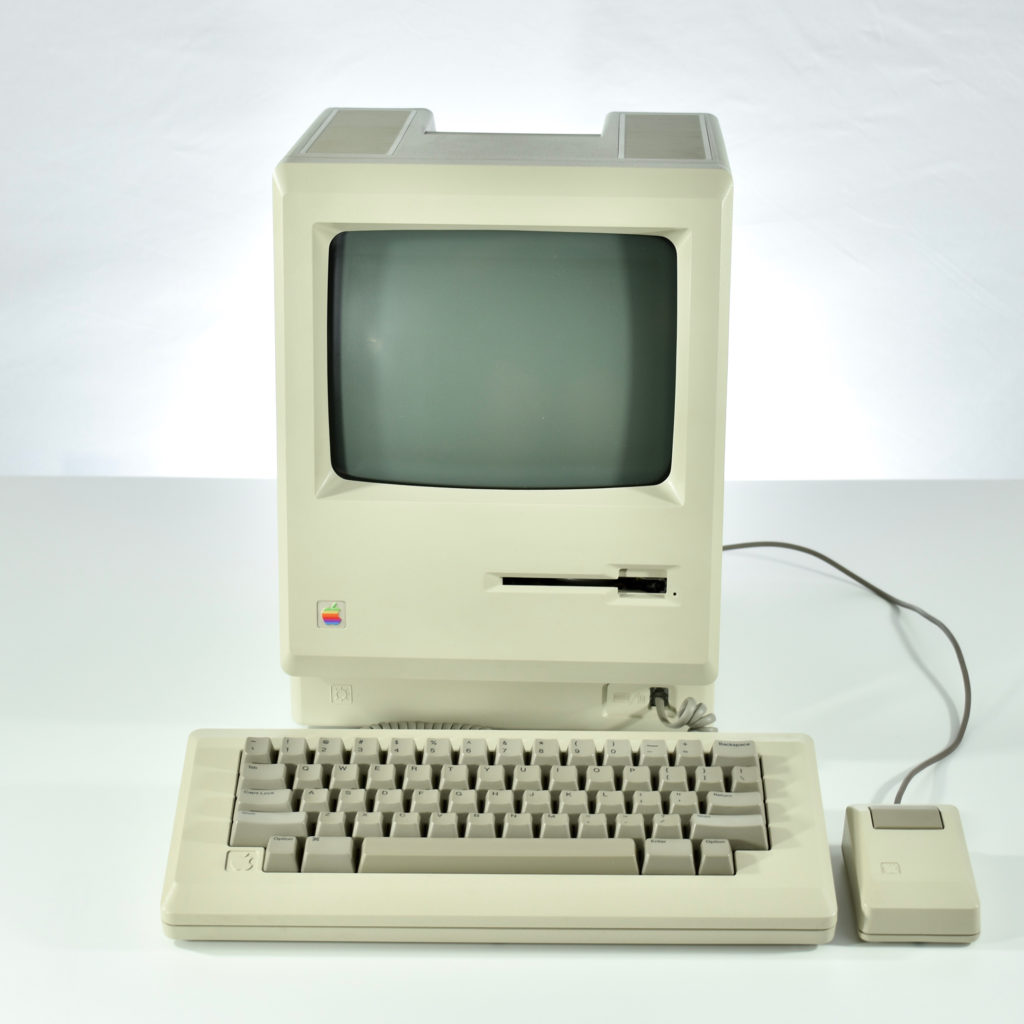
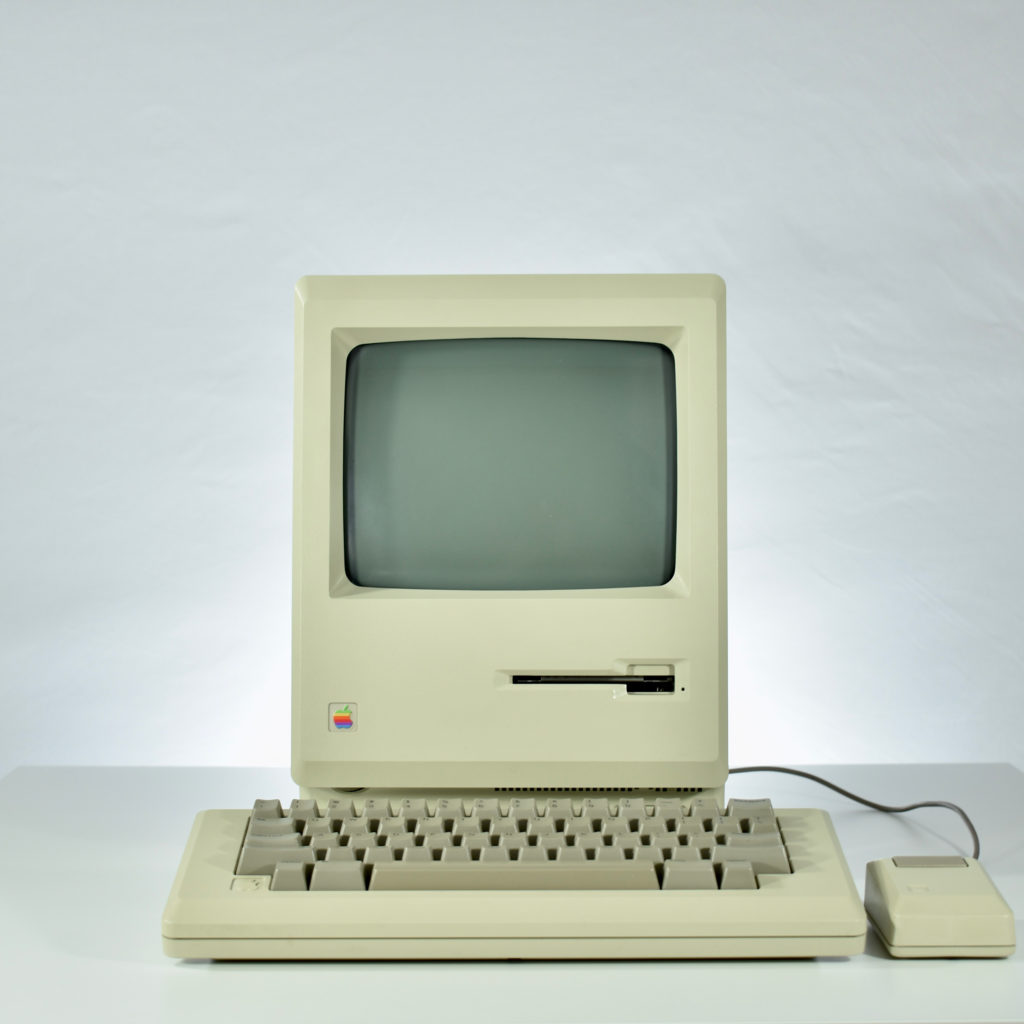
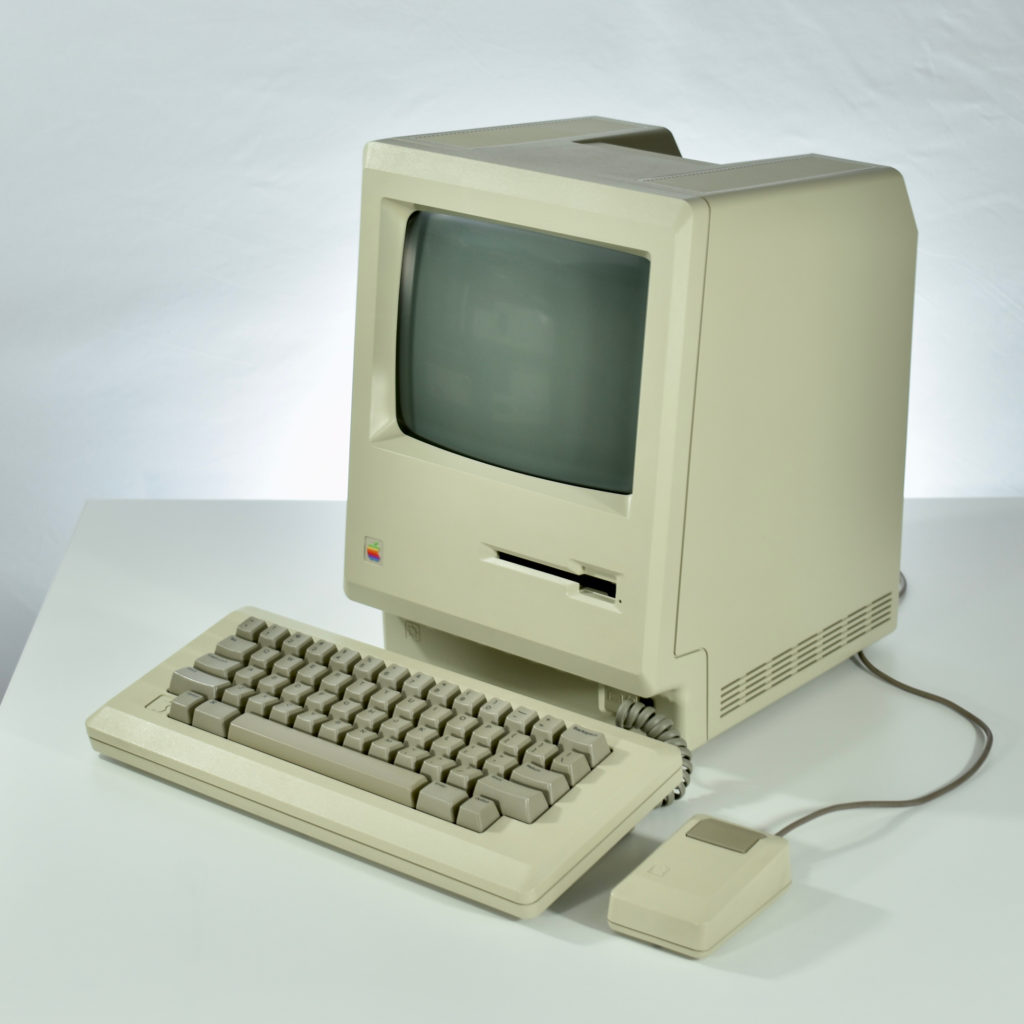
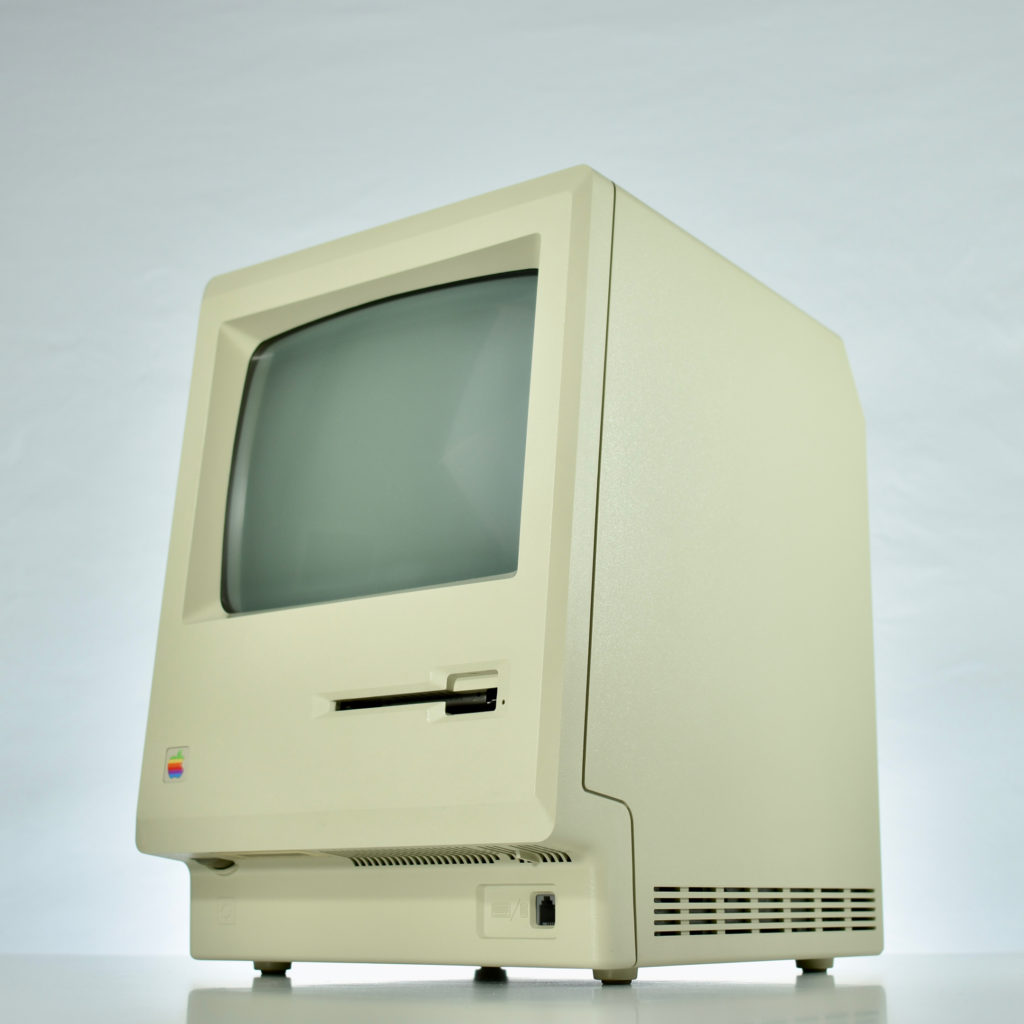
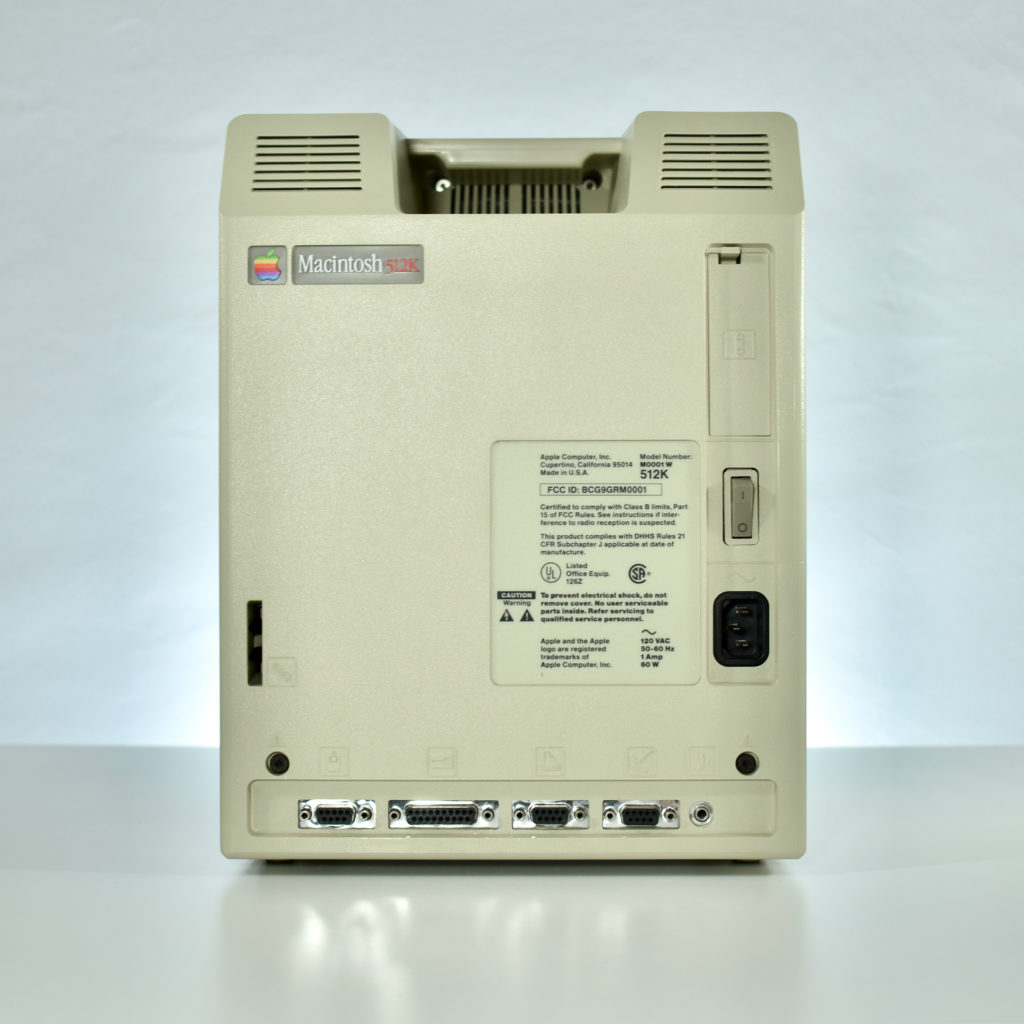
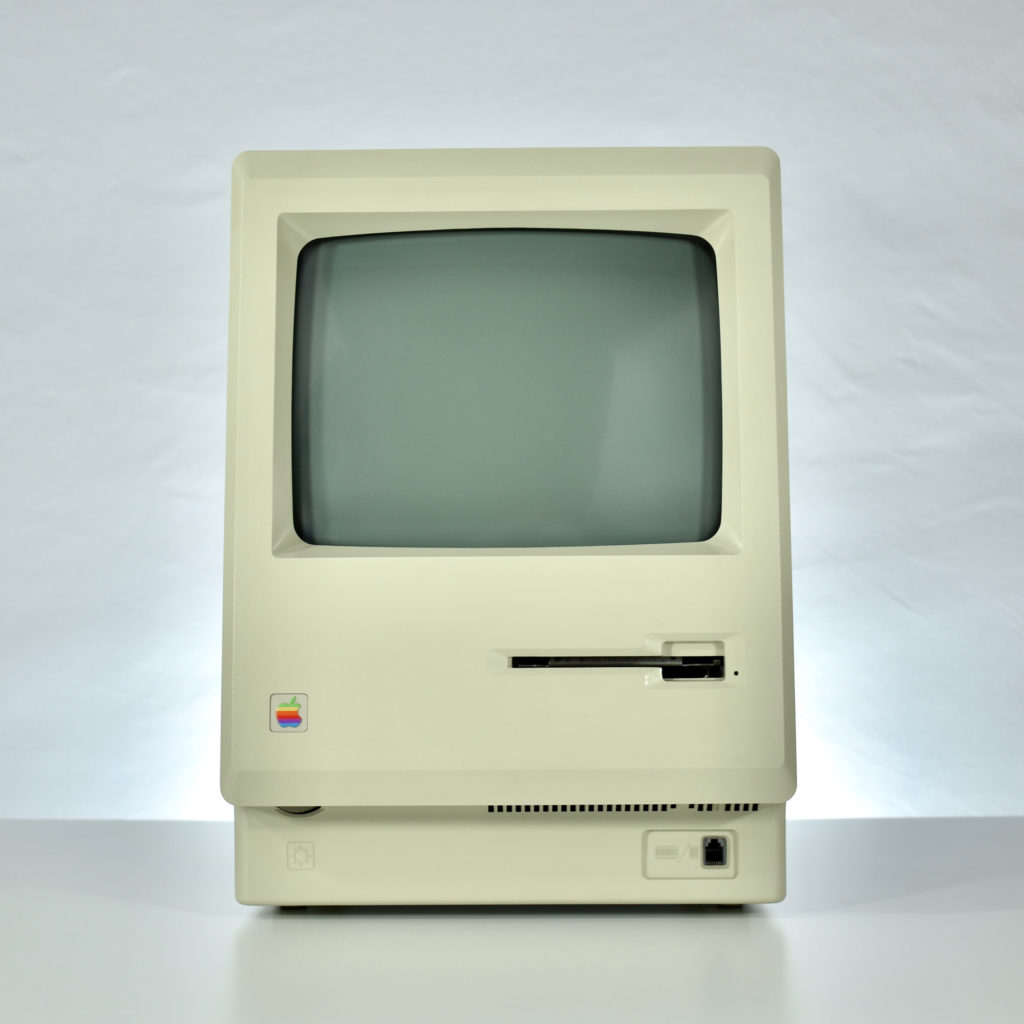
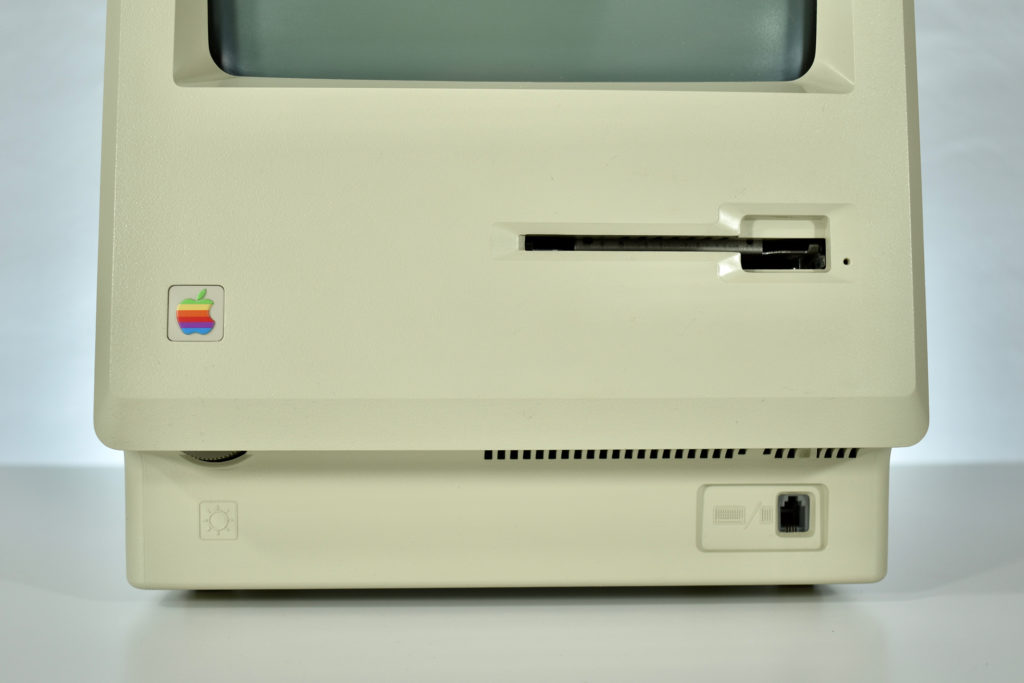
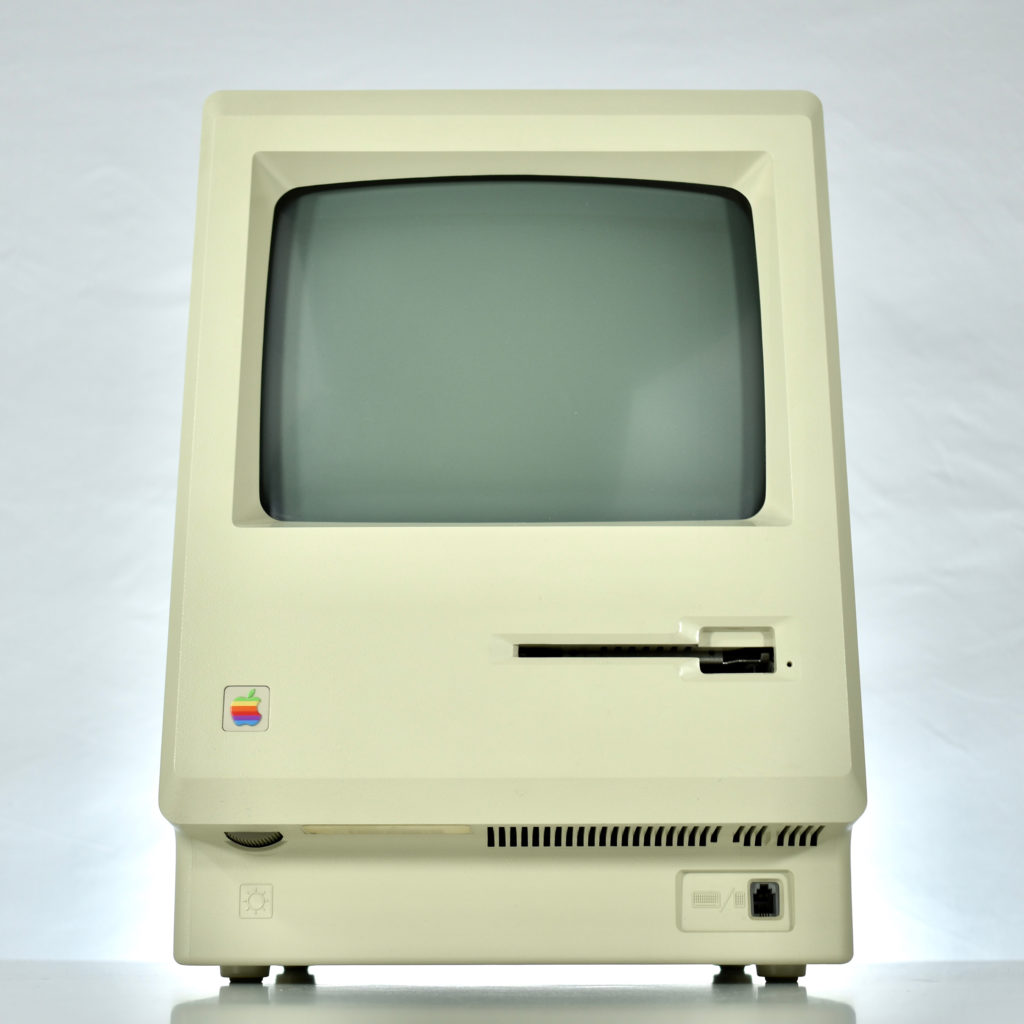
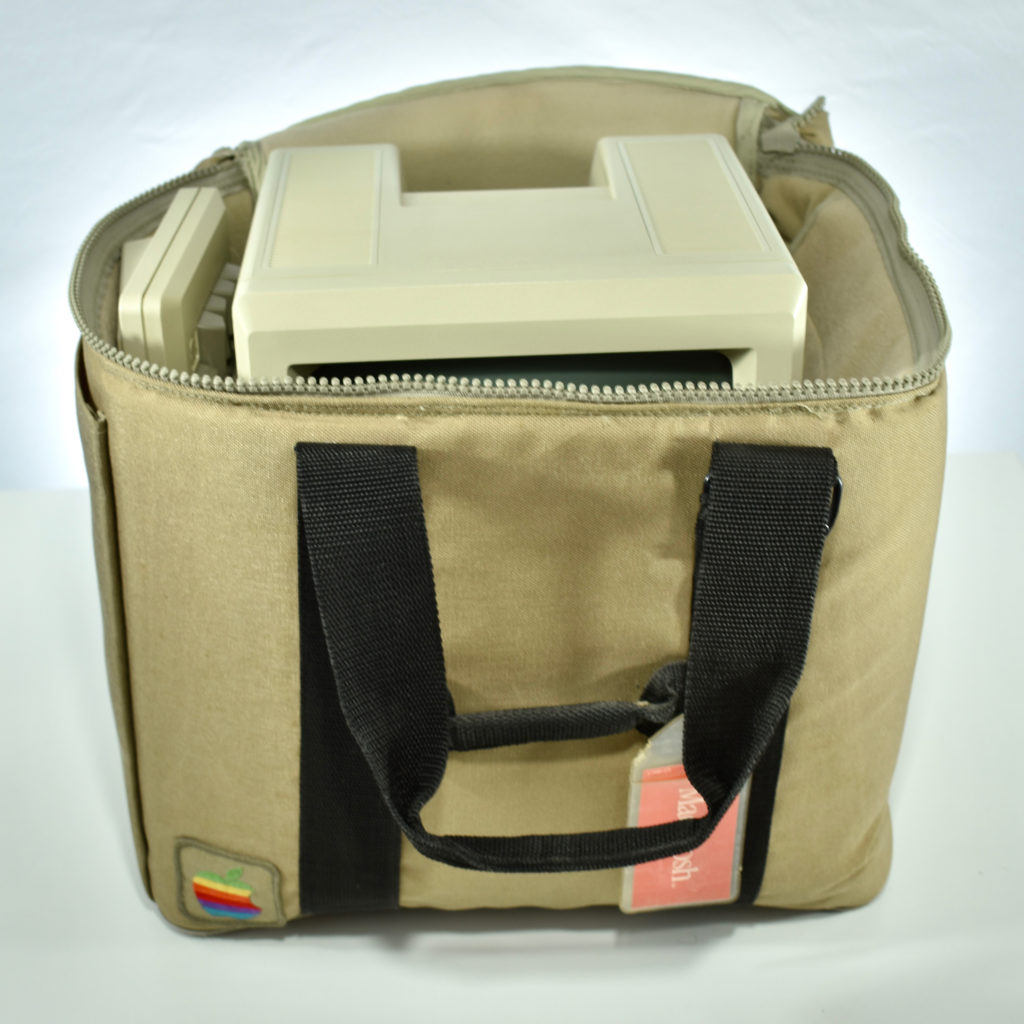
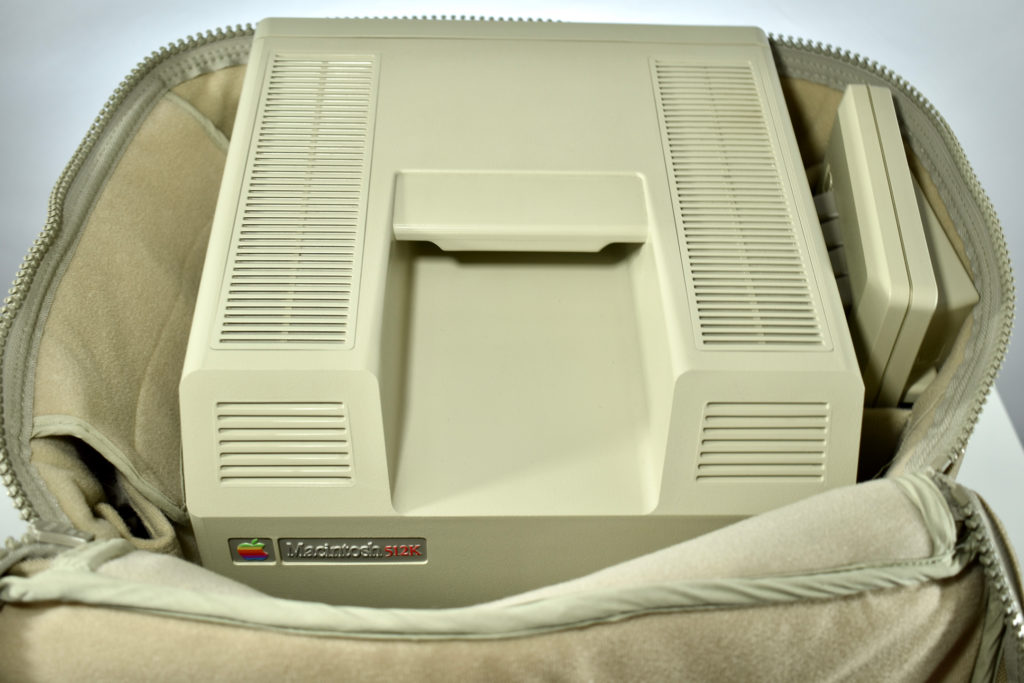
Upon release of the Macintosh 512K, a slightly redesigned Macintosh with the specs as the original Macintosh was introduced as the Macintosh 128K. Thus, the Macintosh 512K was technically the third Macintosh to be released since the new 128K model differed from the original Macintosh.
The Macintosh 512K had the same 512×342 monochrome display as the original Macintosh, but its memory was quadrupled. The name Macintosh 512K refers to its 512 kilobytes (kB) of internal RAM. The computer was not designed to be upgraded with additional RAM or further expanded, although a few third-party add-ons made available (such as a $2,195 “HyperDrive” hard drive by General Computer Corporation).
The Macintosh 512K was bundled with software including MacPaint and MacWrite, but many additional titles were soon available, including MacDraw, MacProject, Macintosh Pascal, and Microsoft Excel (requiring 512 kB of RAM to run). The increased memory also allowed the Macintosh 512K to handle larger word processing files, file sharing using Apple’s AppleShare local file sharing abilities, and generally faster performance of the graphical user interface (GUI).
Sources: Wikipedia (Macintosh 512K, GCC), EveryMac