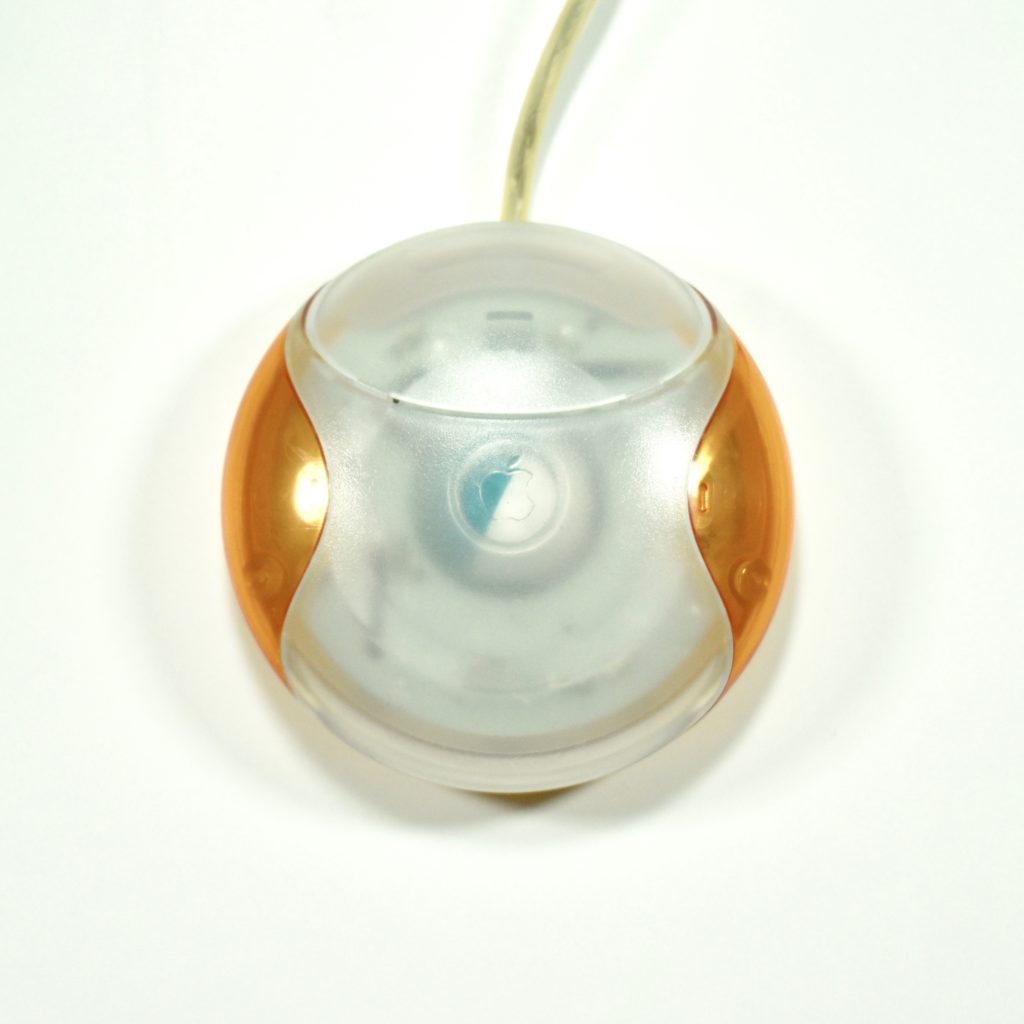
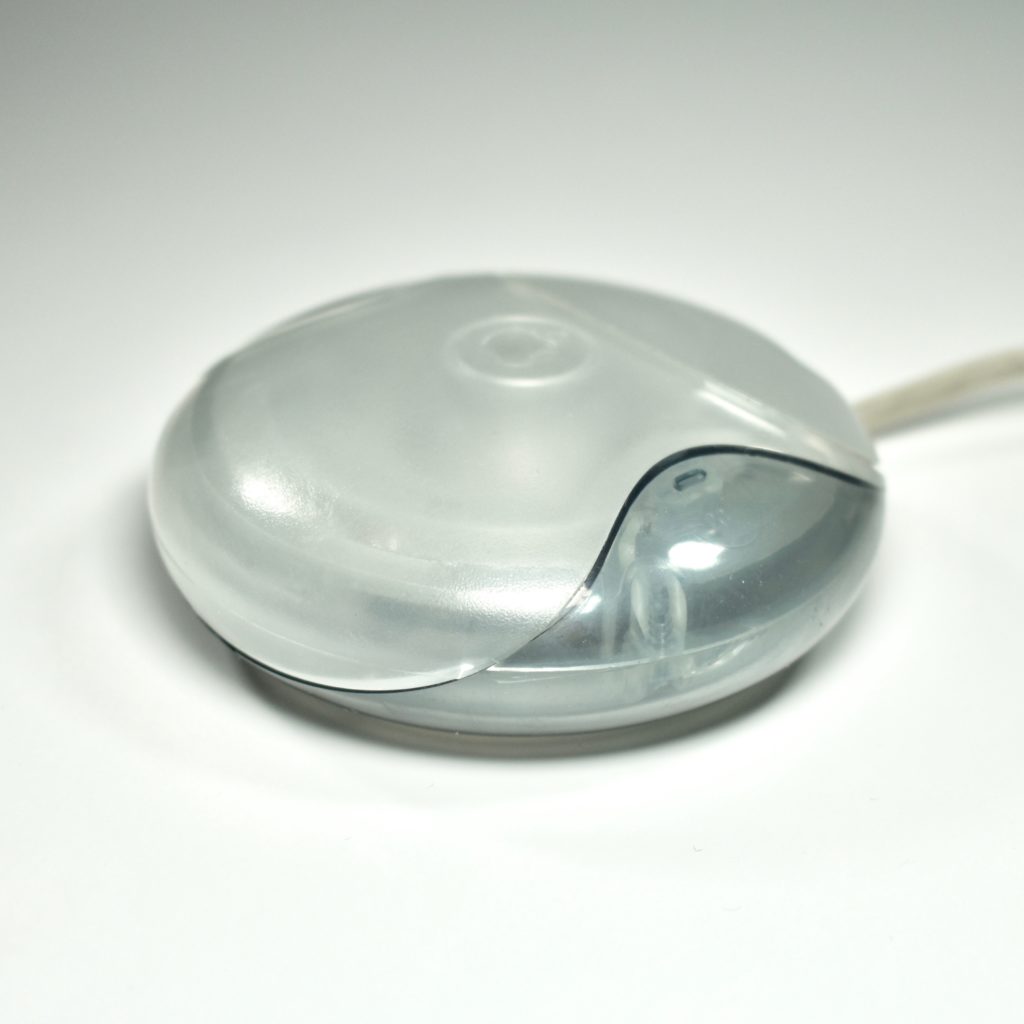
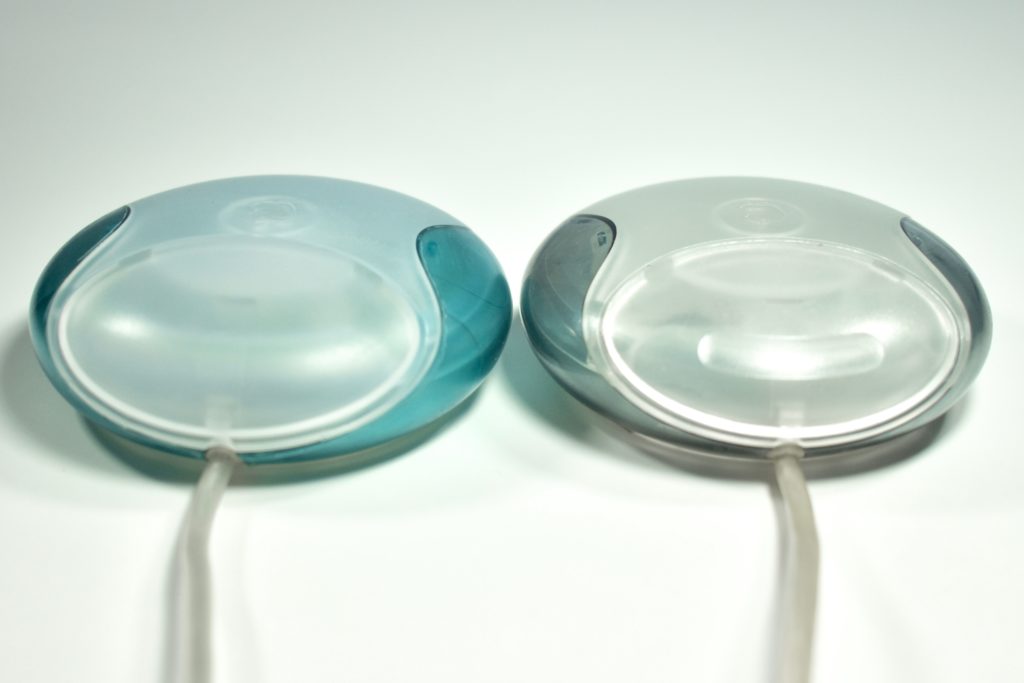
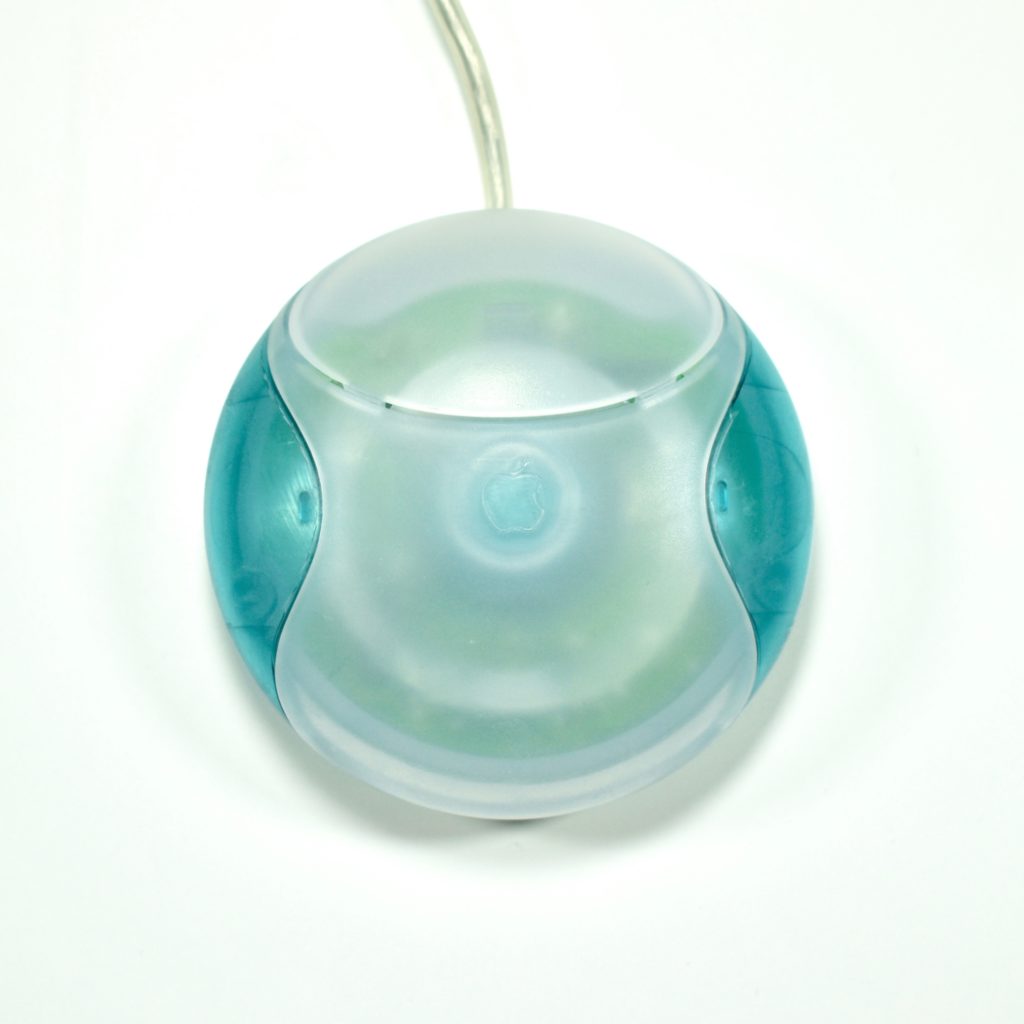
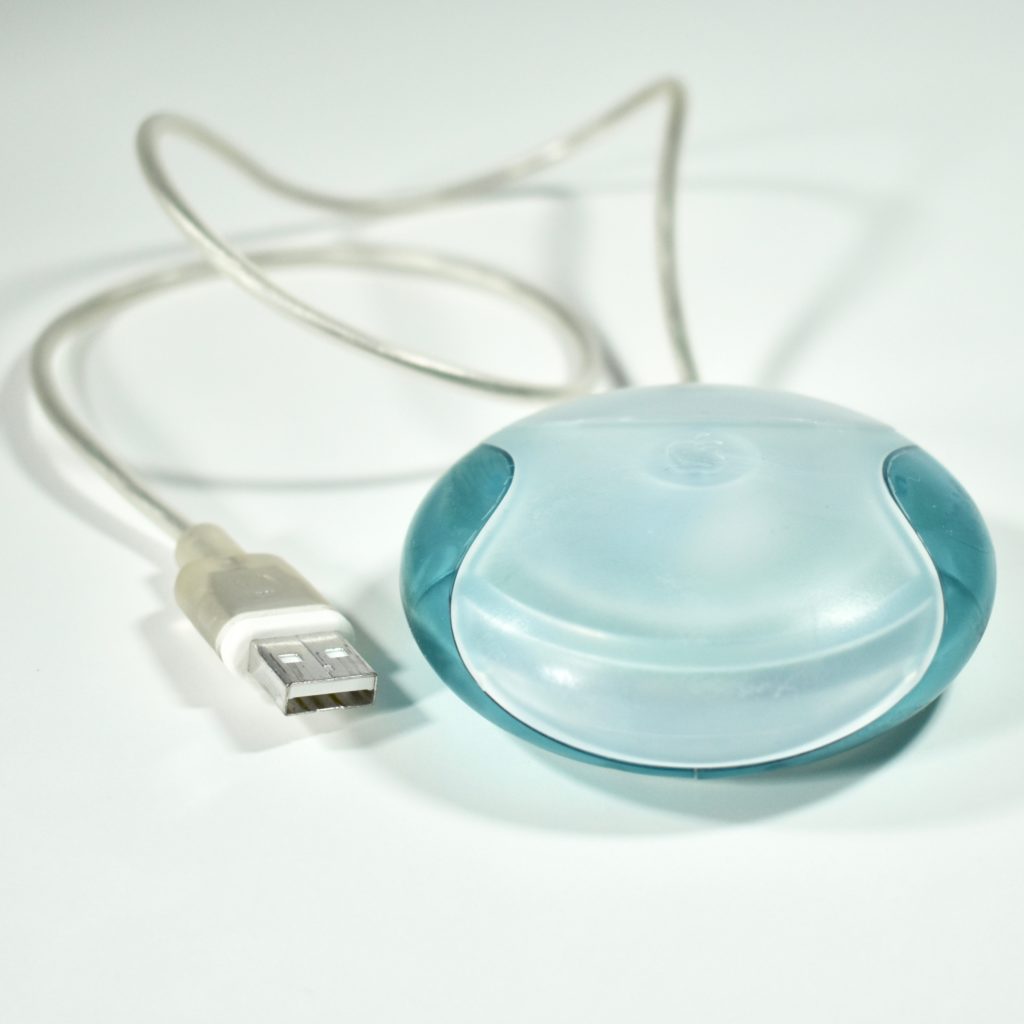
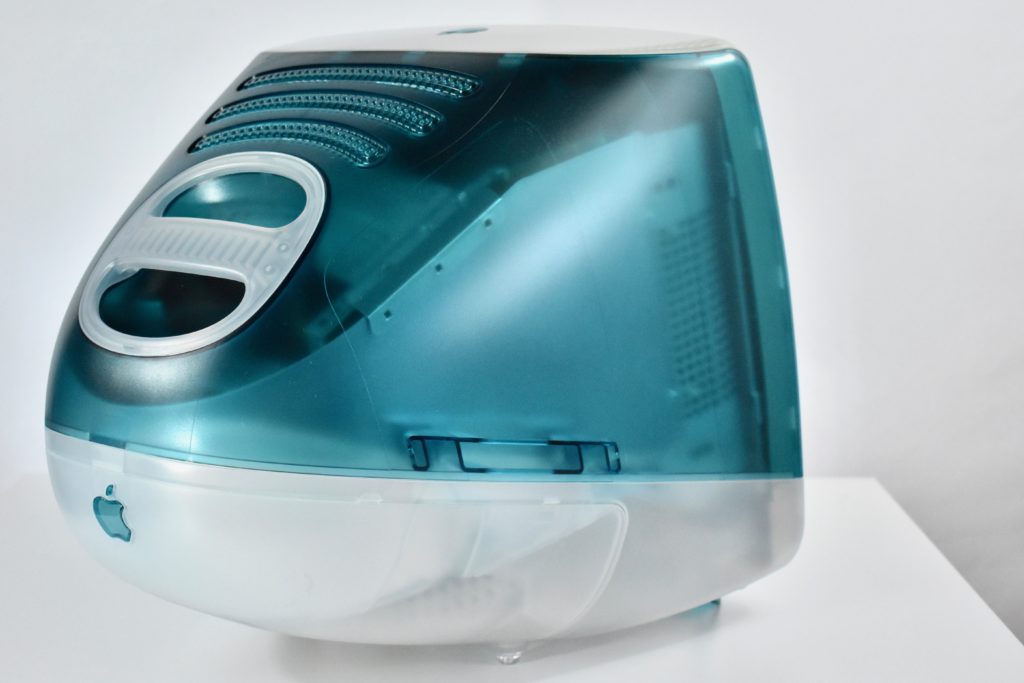
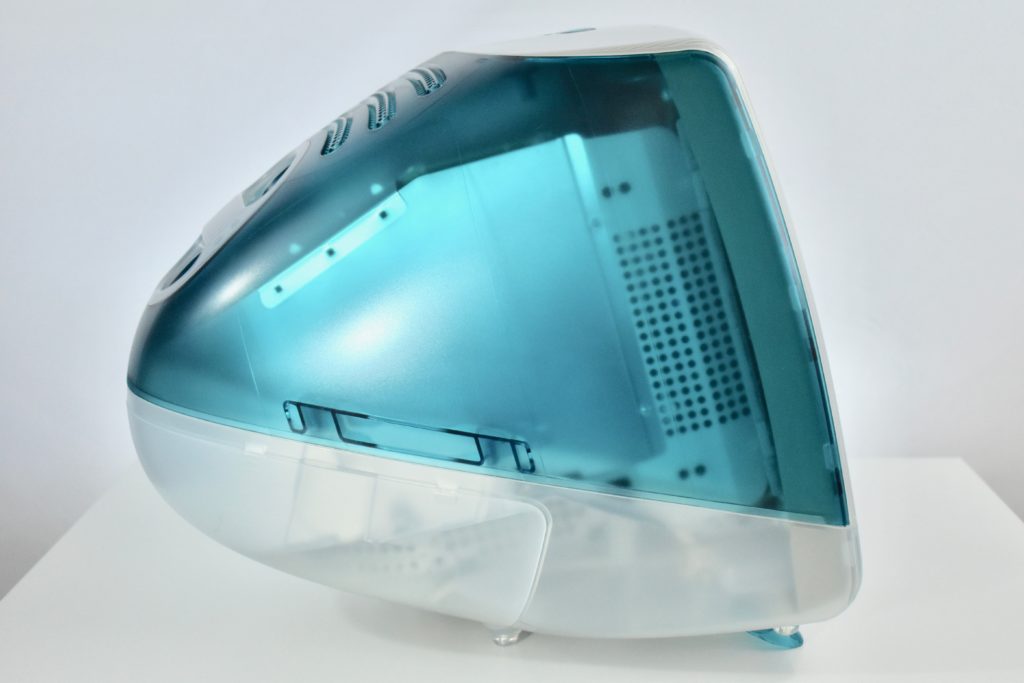
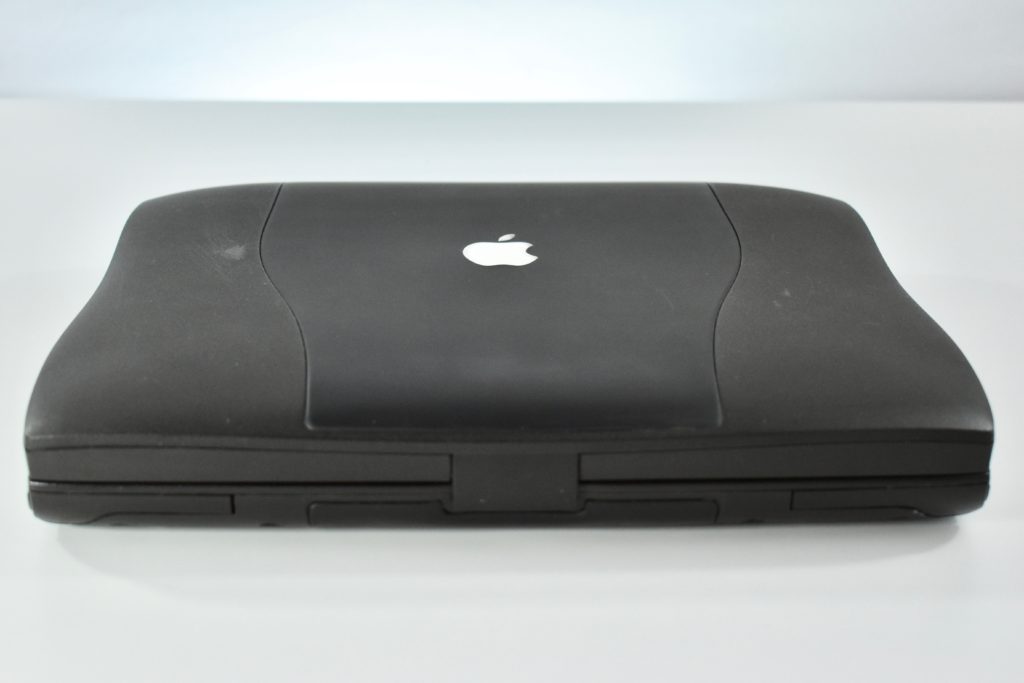
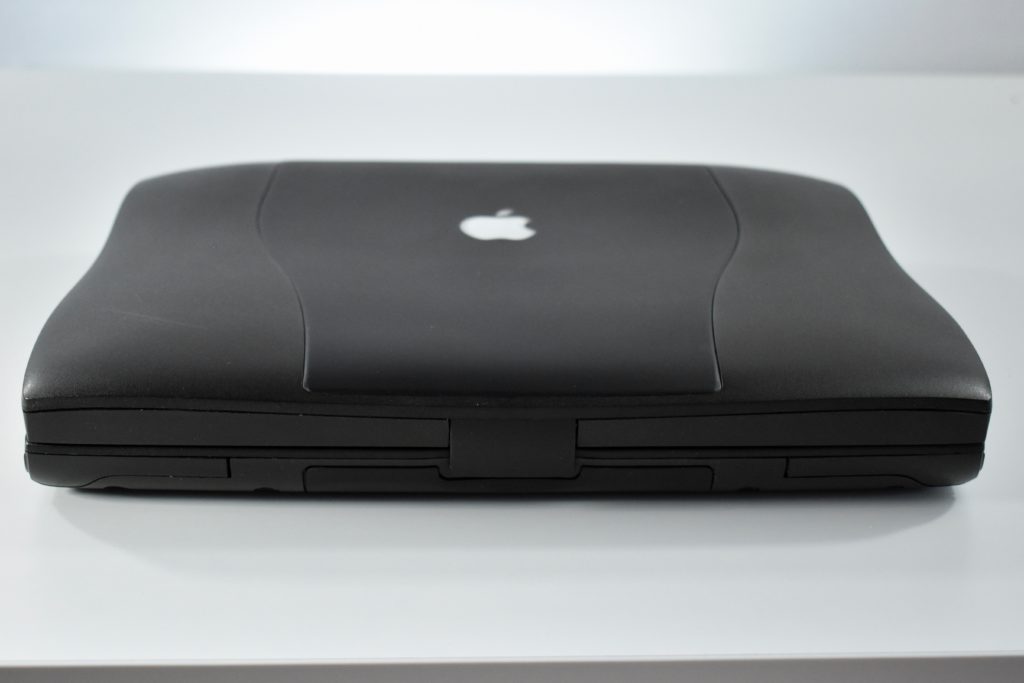
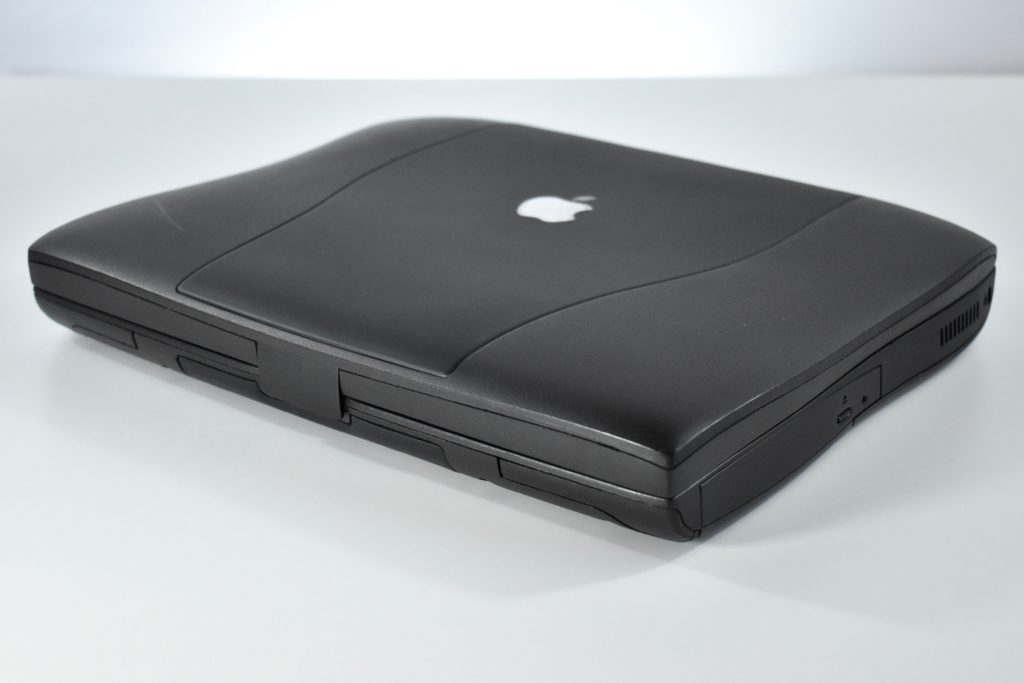
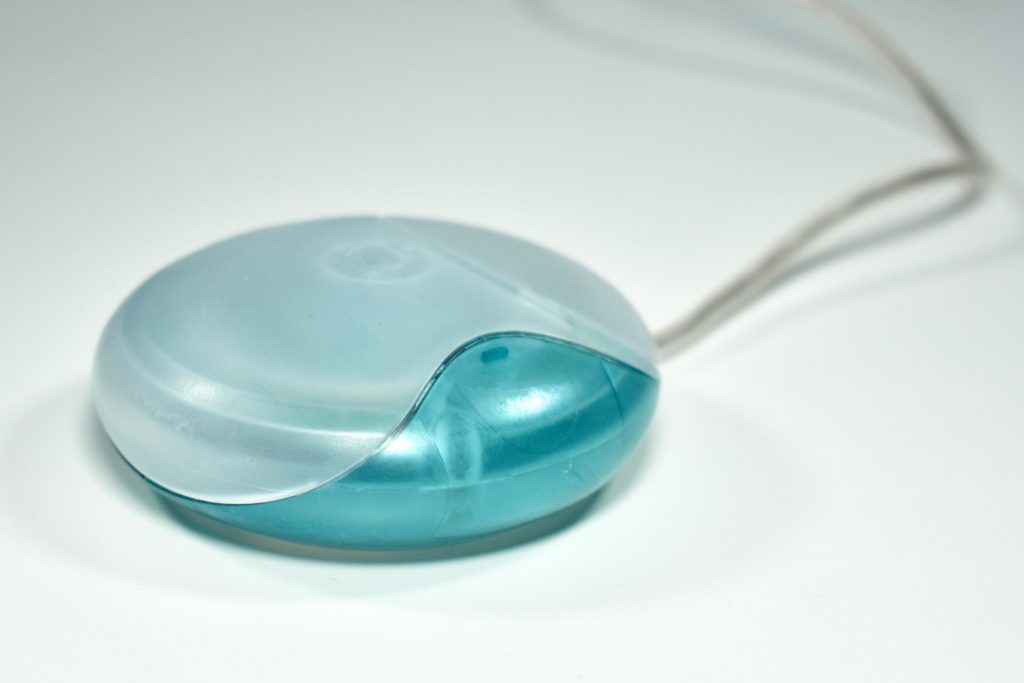
The Apple USB Mouse was first released with the original iMac. The mouse was translucent white and accented in translucent Bondi blue, the same colors as the original iMac. The mouse was round and often referred to as the “hockey puck” mouse. Like previous Apple mouse designs, the USB mouse used a single button and a rubber ball for tracking. However, the rubber ball was two-toned to add design interest by capitalizing on the translucent case.
The mouse has been described as a rare design mistake for Apple because its round shape made it difficult to feel the top of the device, making tracking difficult. Soon after its release, Apple added a dimple in the graphite version of the mouse at the top above the button. The dimple remained on all subsequent versions of the USB Mouse, including this example.
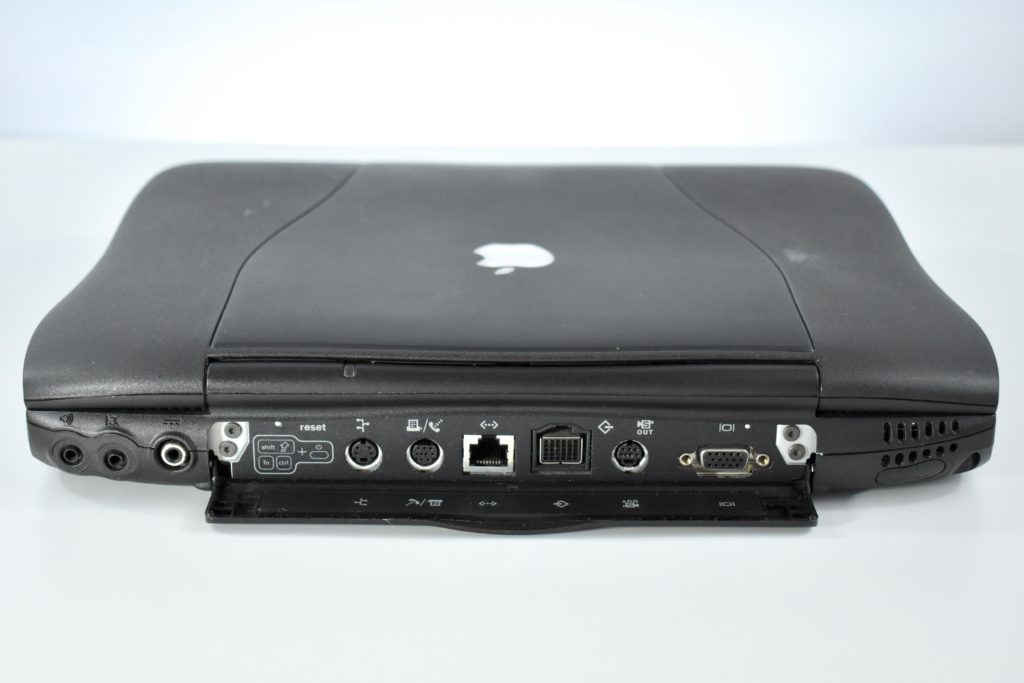
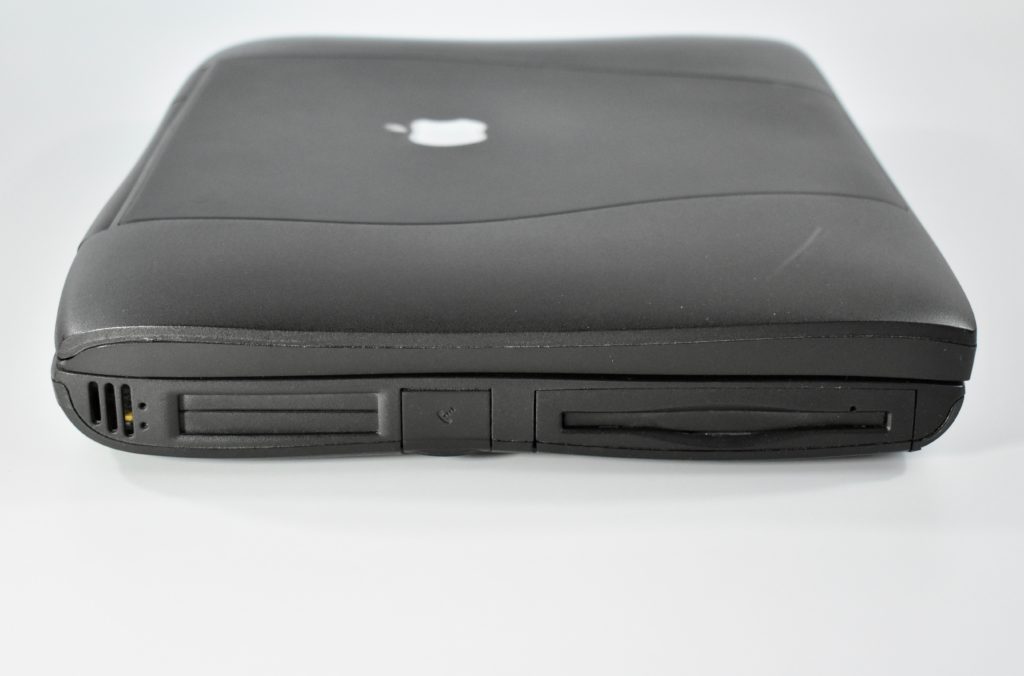
The mouse also had a short cord. Although the cord worked well when plugged into the USB port on a matching iMac keyboard, the cord was too short to use (for right-handed users) with Mac laptops at the time since USB ports were located on the left side.
Source: Wikipedia.com