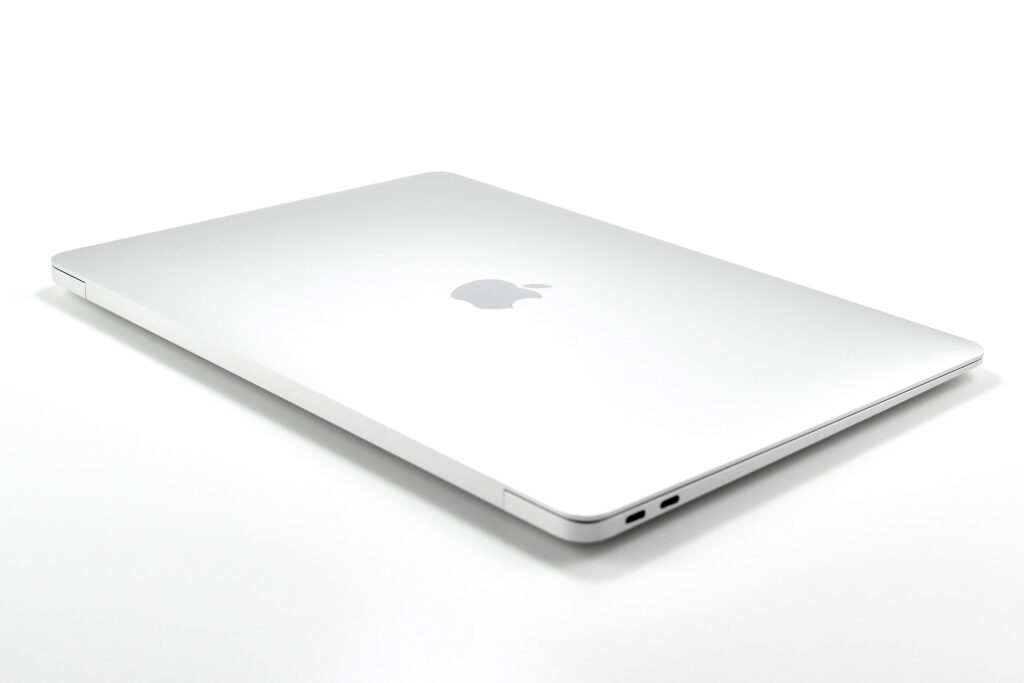
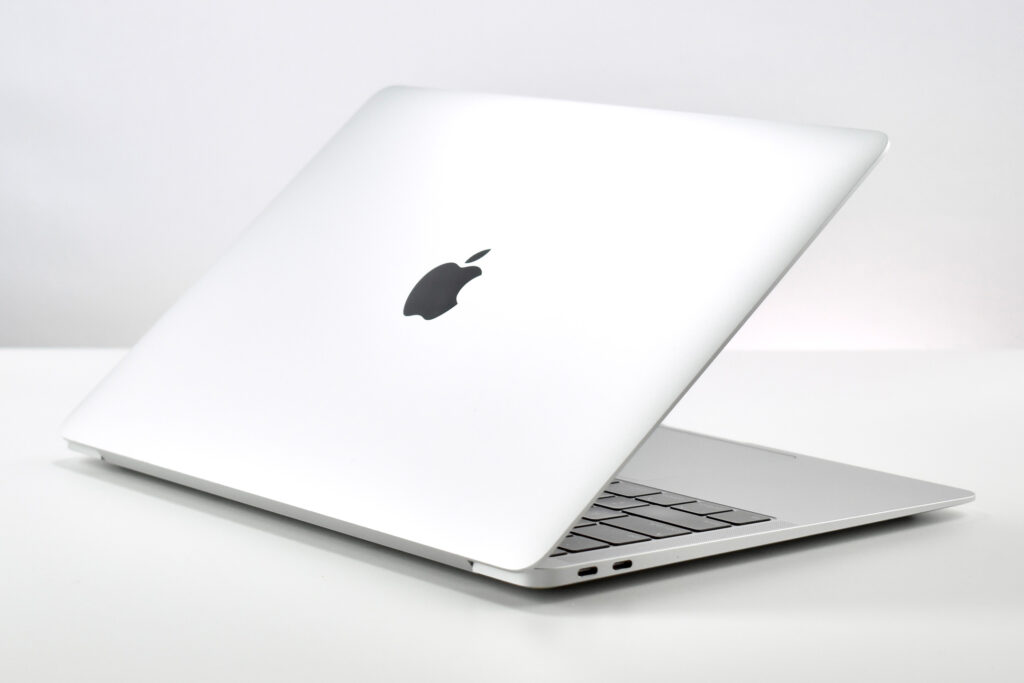
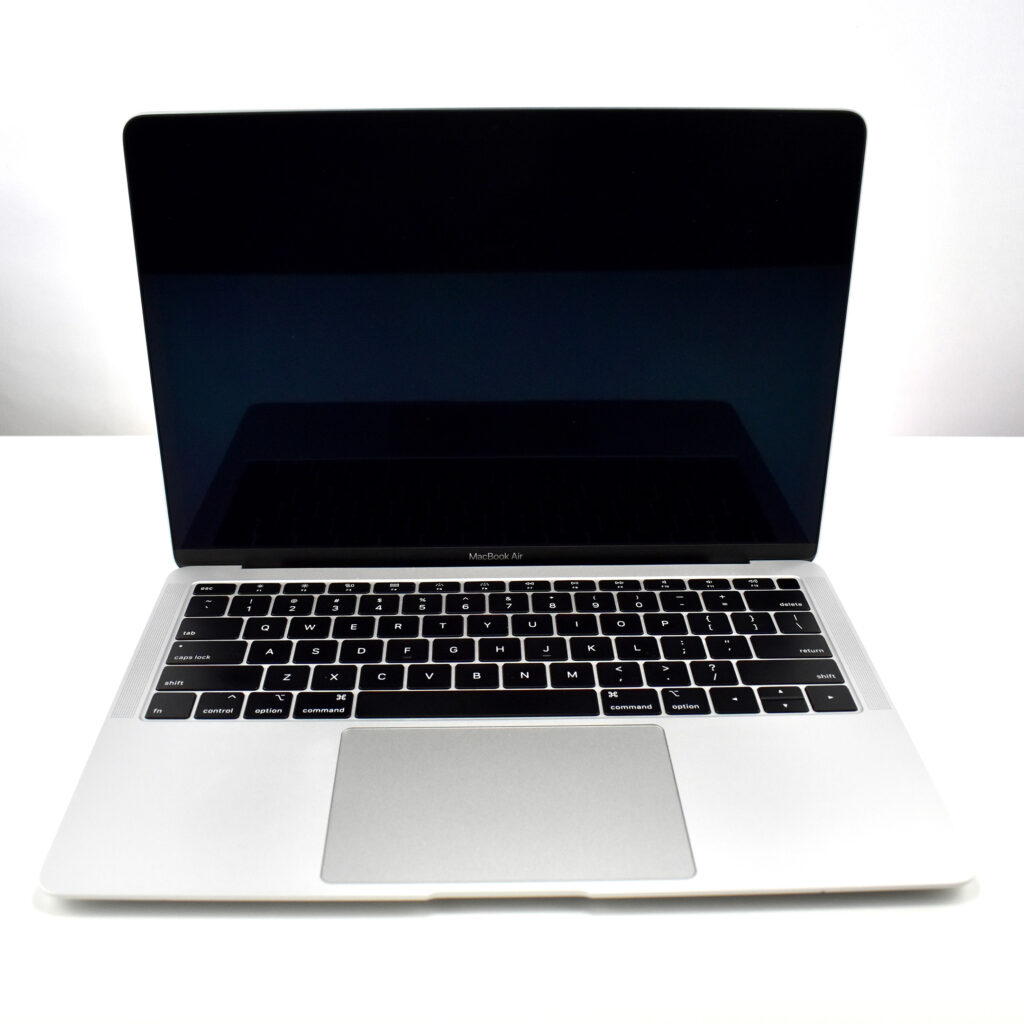
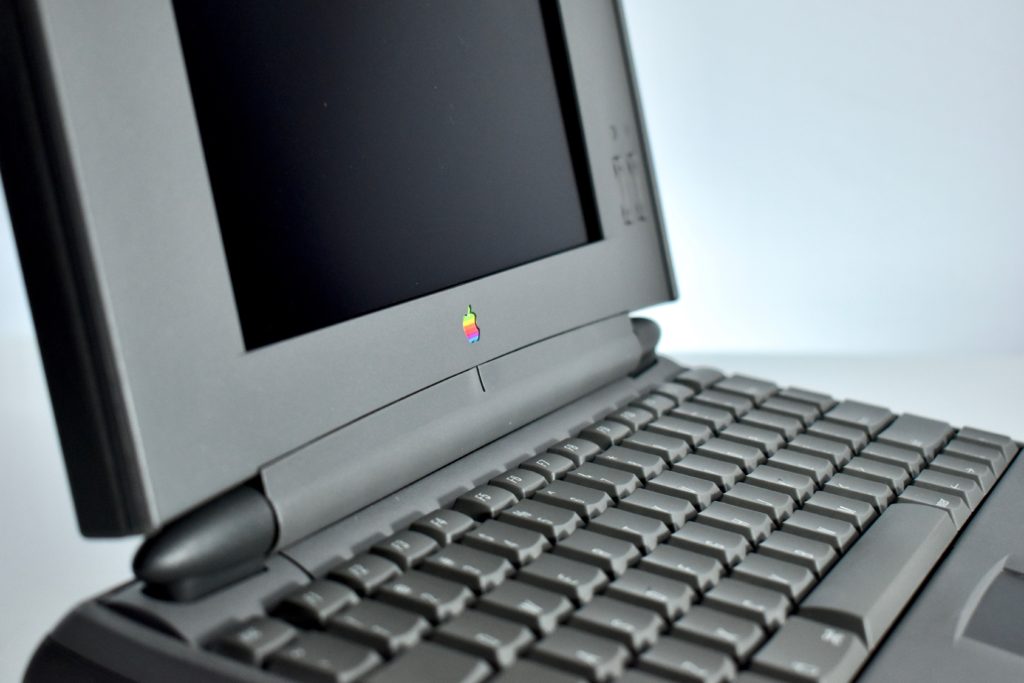
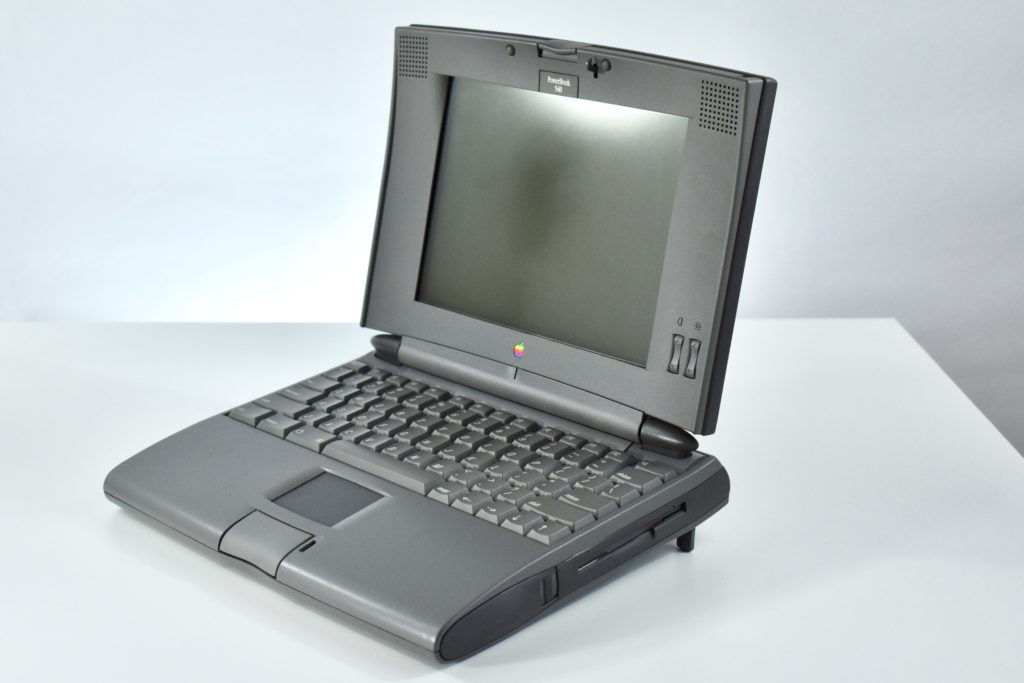
On October 18, 2018, Apple introduced an all-new MacBook Air model:
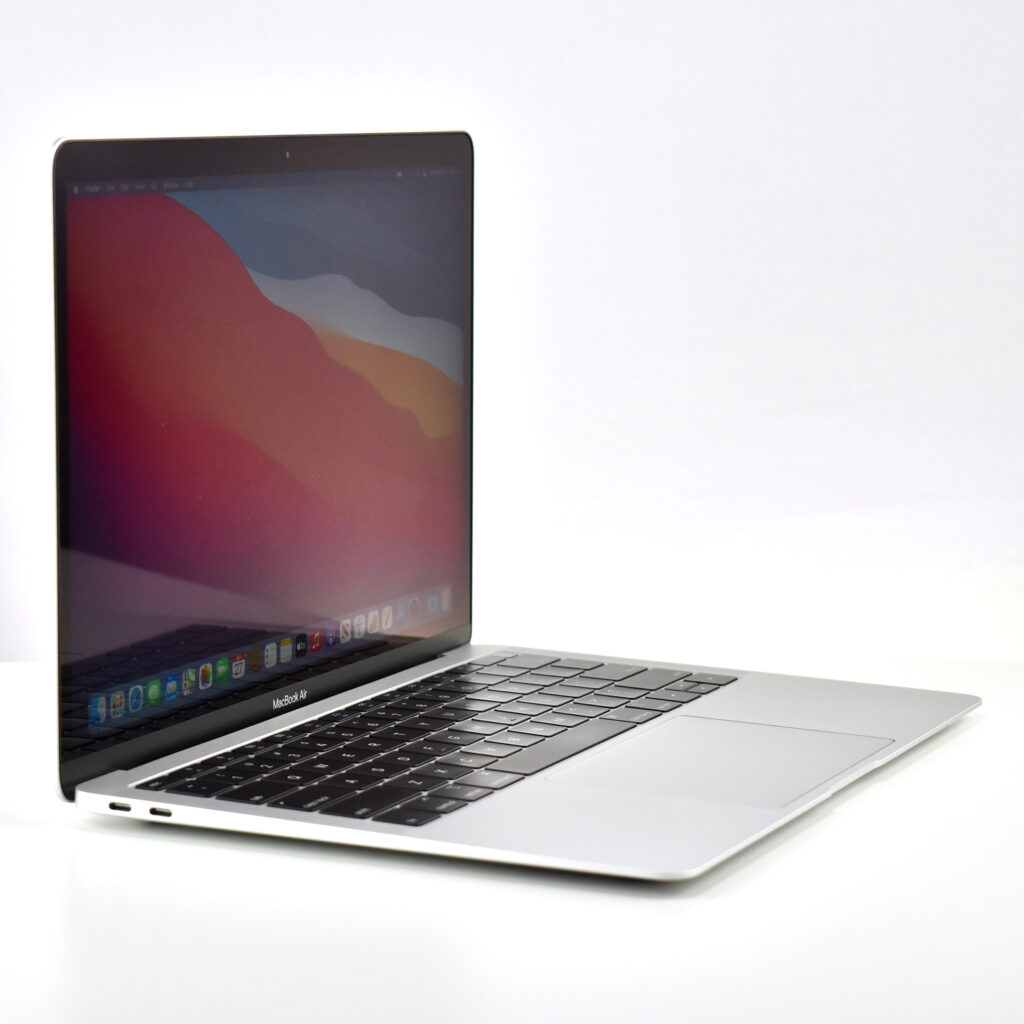
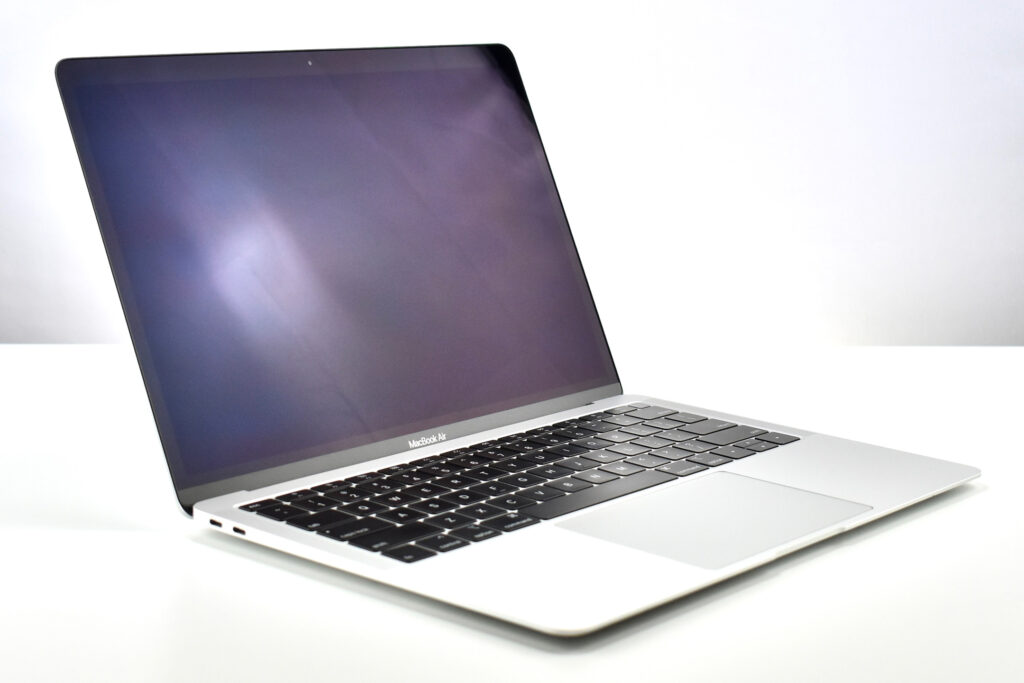
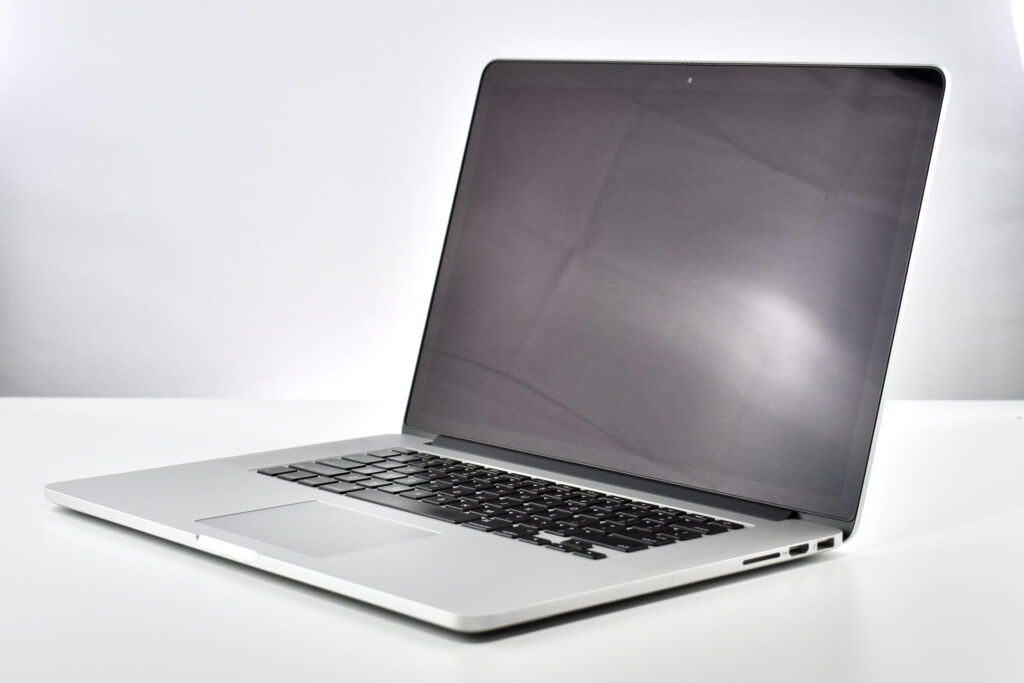
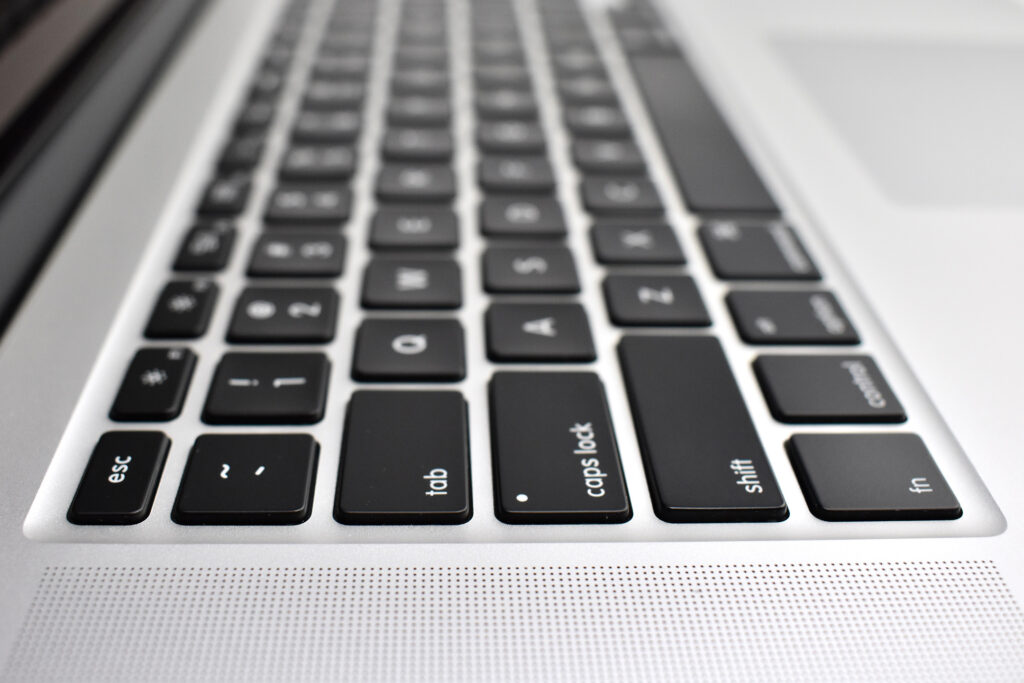
“Apple today introduced an all-new MacBook Air, bringing a stunning 13-inch Retina display, Touch ID, the latest processors and an even more portable design to the world’s most loved notebook. Delivering the all-day battery life it’s known for, the new MacBook Air is available in three gorgeous finishes — gold, space gray and silver. The most affordable Retina-display Mac ever also includes an Apple-designed keyboard, a spacious Force Touch trackpad, faster SSDs, wide stereo sound, the Apple T2 Security Chip and Thunderbolt 3, making the new MacBook Air the perfect notebook to take with you everywhere you go.”
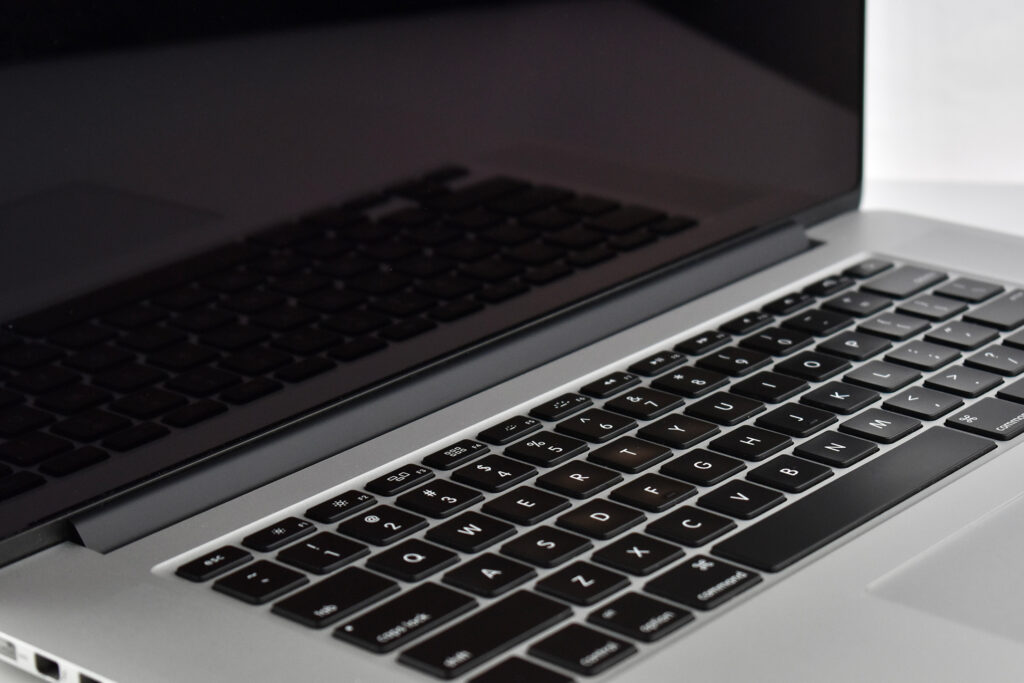
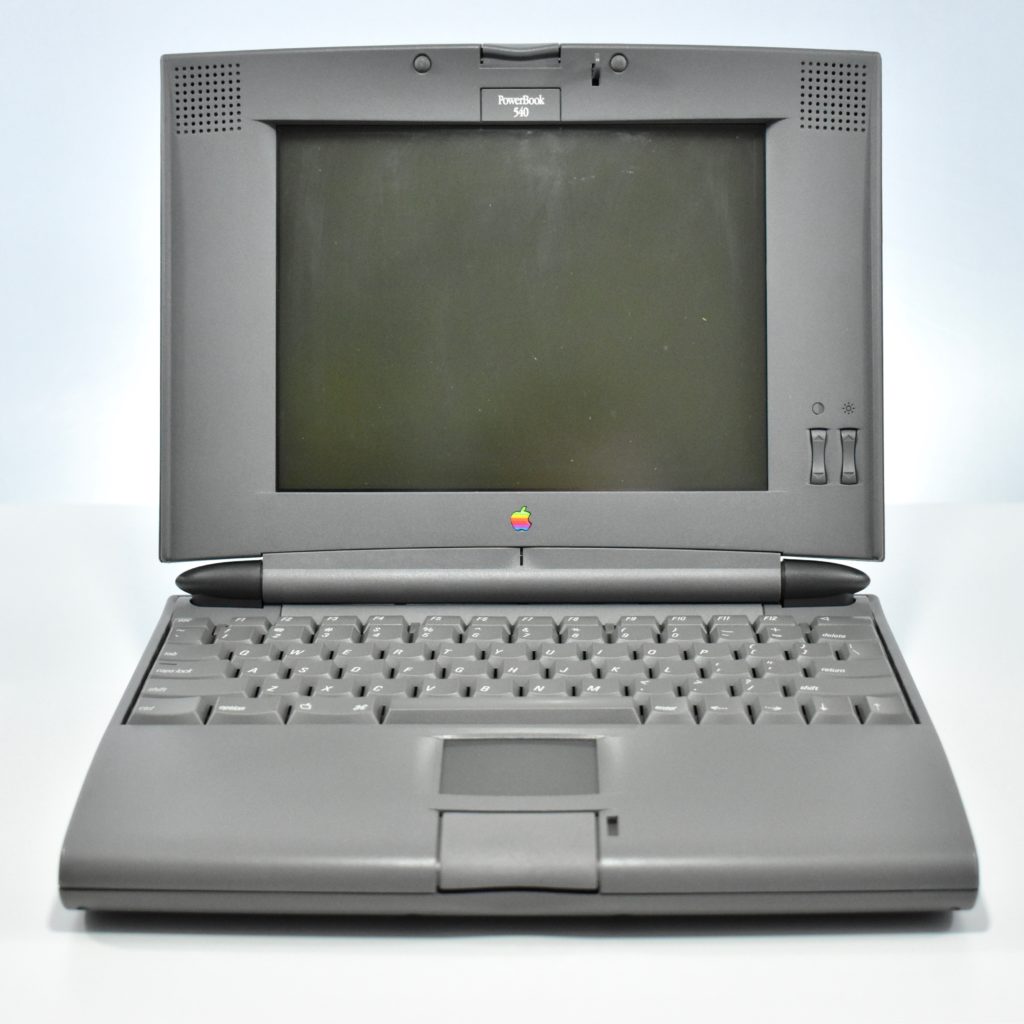
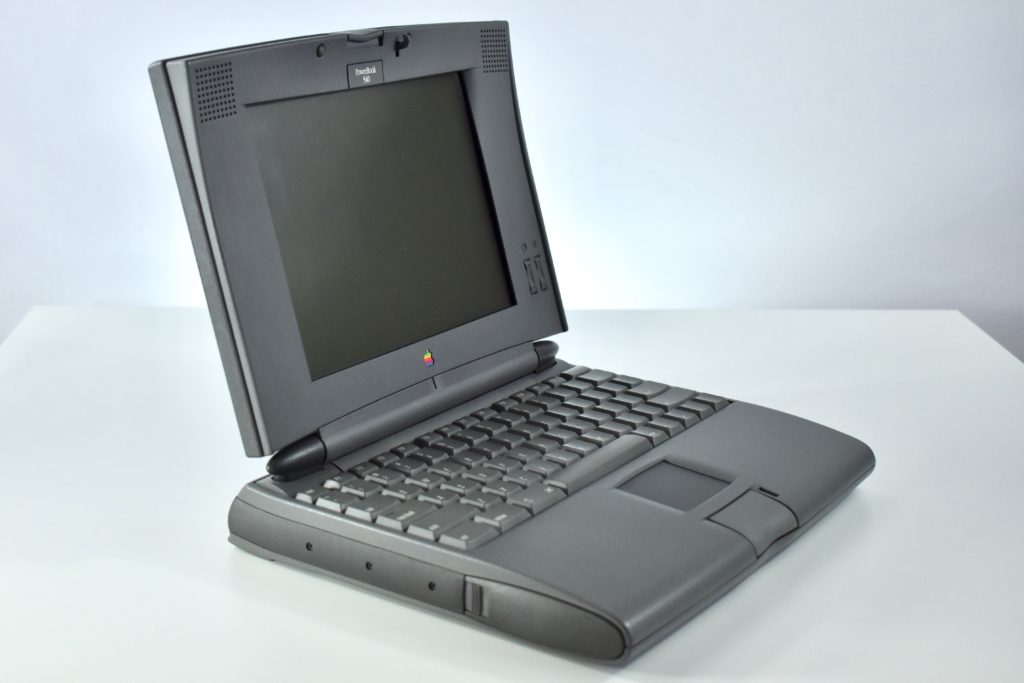
The 13.3-inch Retina display was 2560 x 1600 (at 227ppi)—a 16:10 aspect ratio. It used a 1.6GHz dual-core Intel Core i5, and offered many storage options: 128GB, 256GB, 512GB, or 1.5TB SSD. RAM options included 8GB or 16GB.
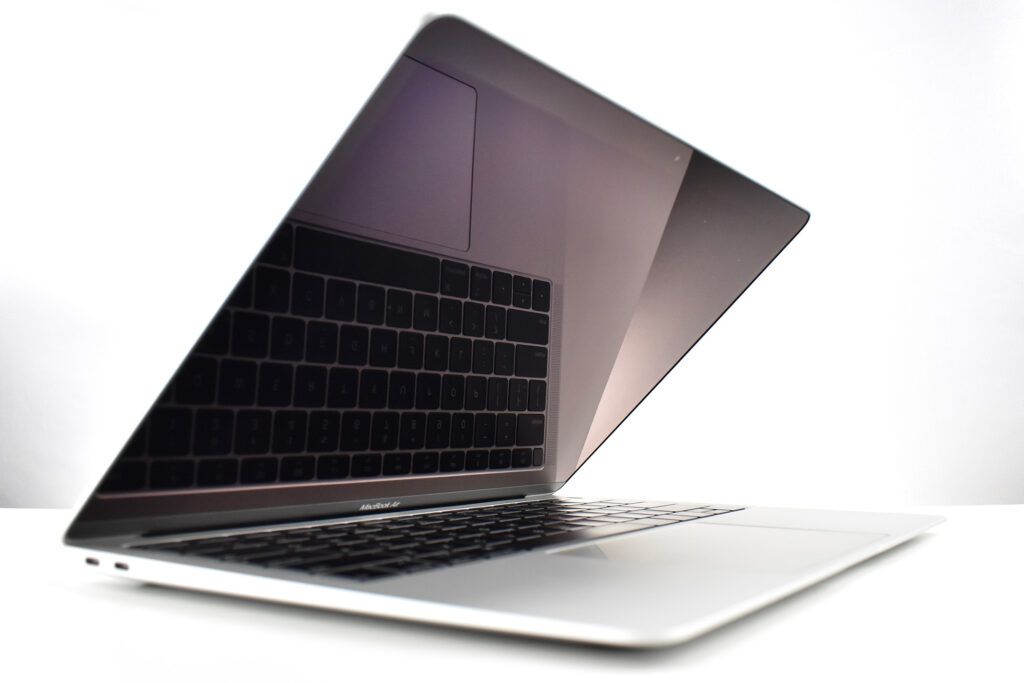
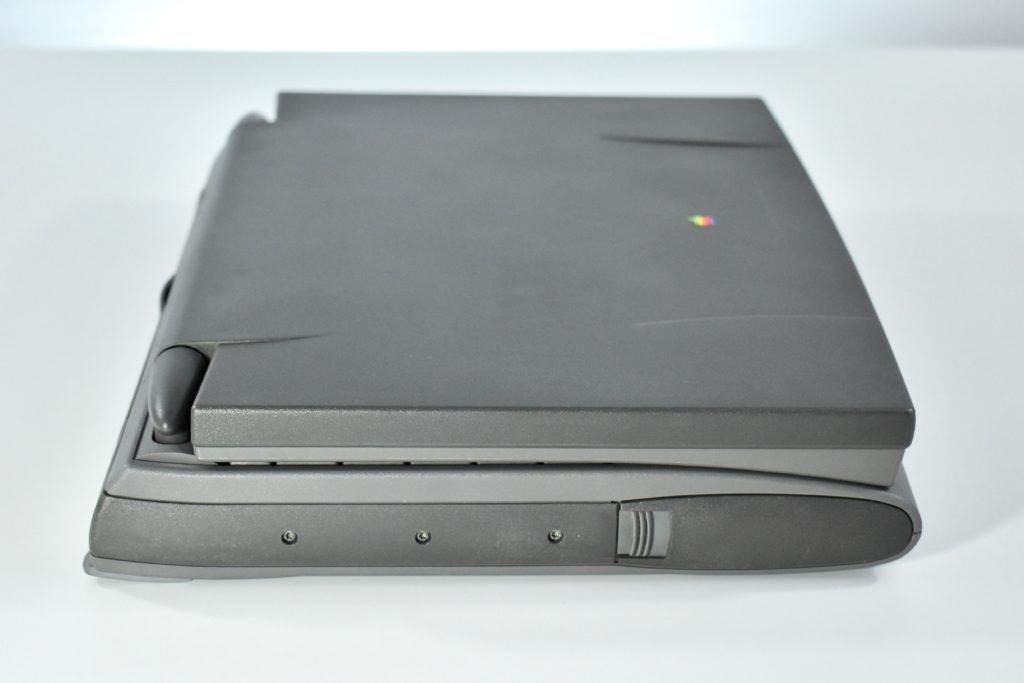
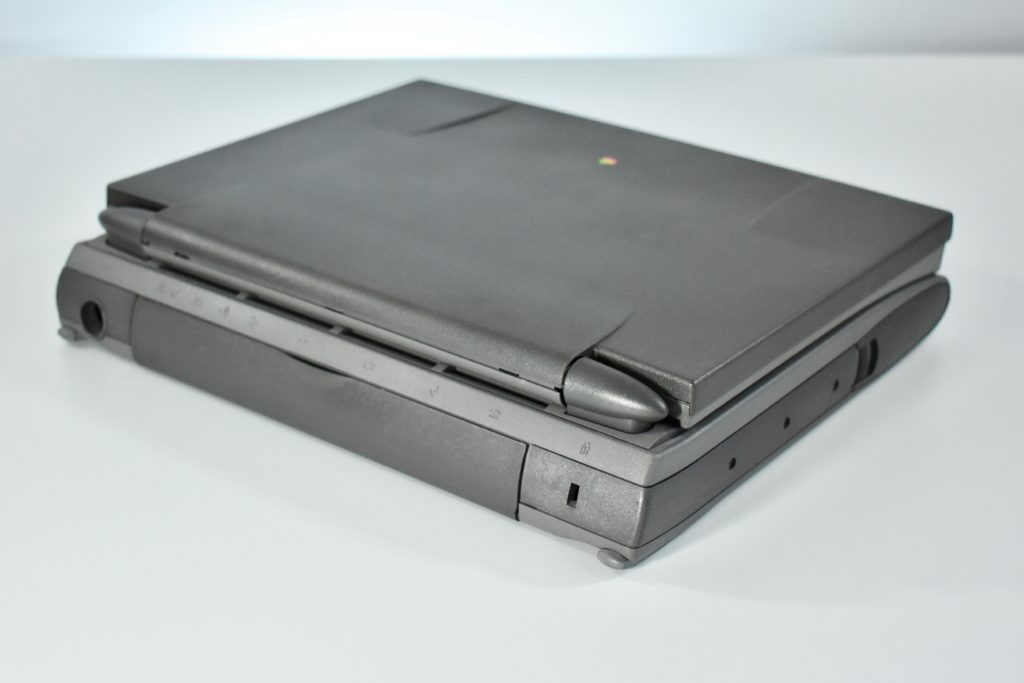
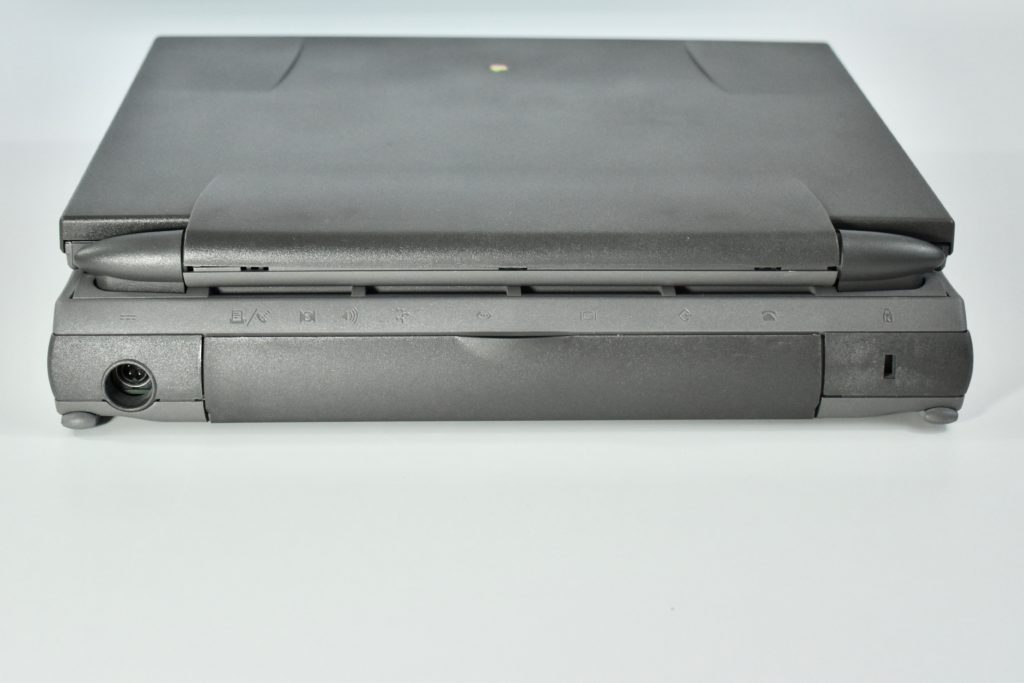
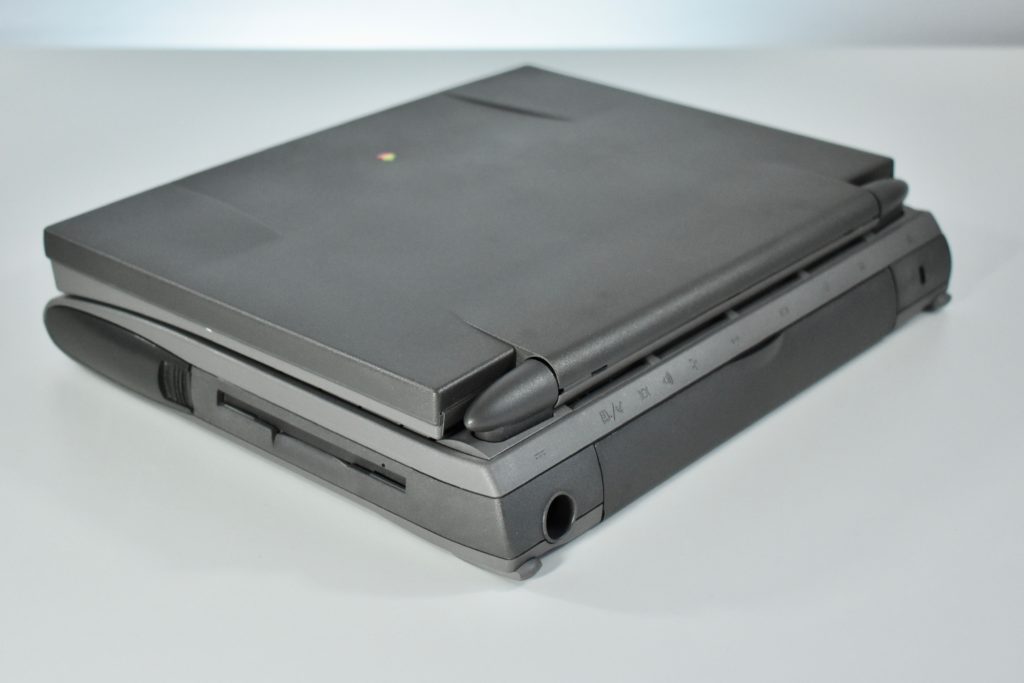
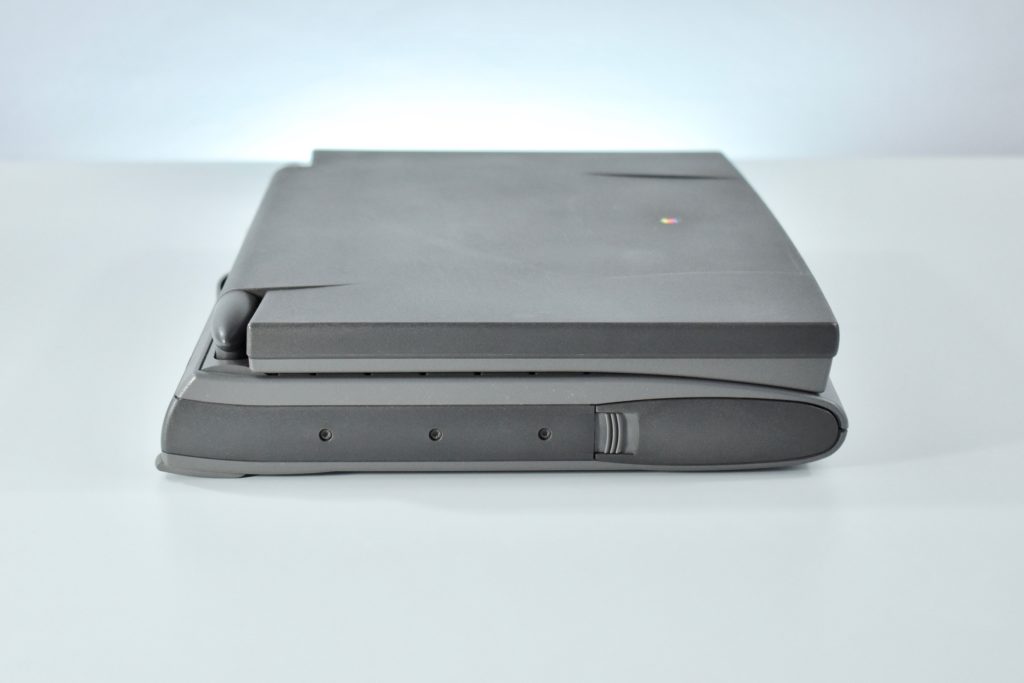
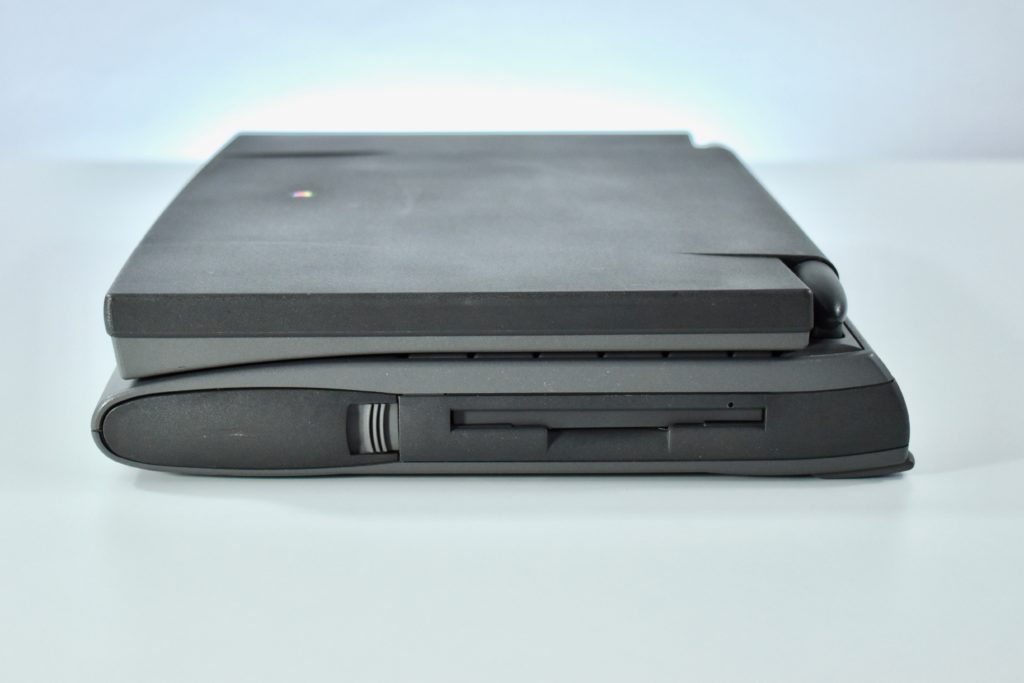
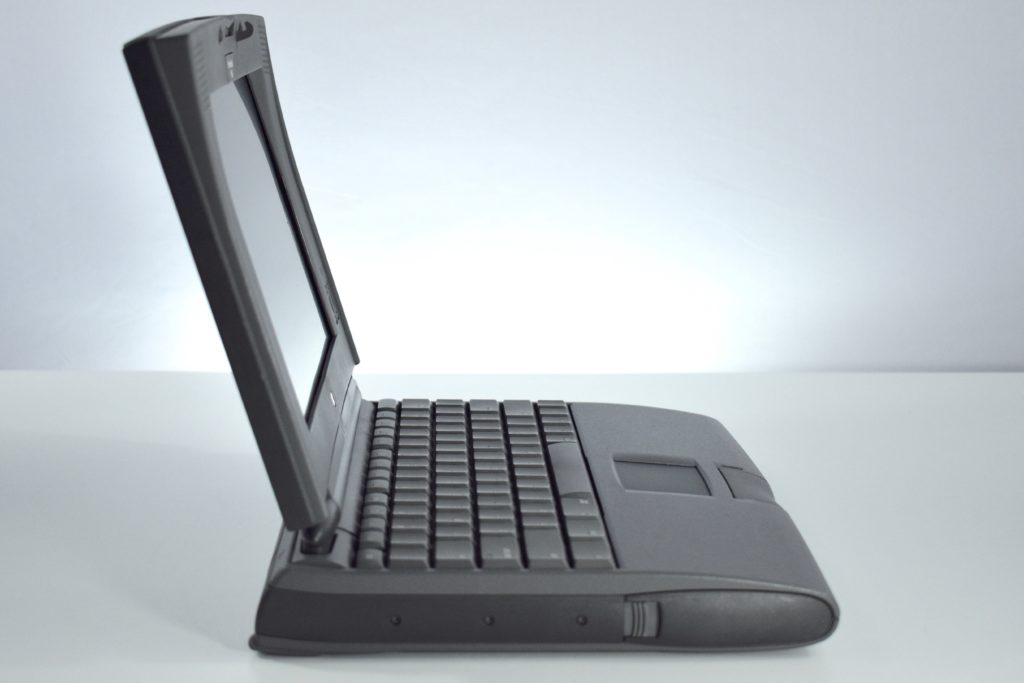
Like all previous MacBook Air models, this version used a tapered body design. It measured 0.16 inch in front to 0.61 inch in back (0.41–1.56 cm) thick, and was 11.97 inches (30.41 cm) wide and 8.36 inches (21.24 cm) deep. It weighed 2.75 pounds (1.25 kg).
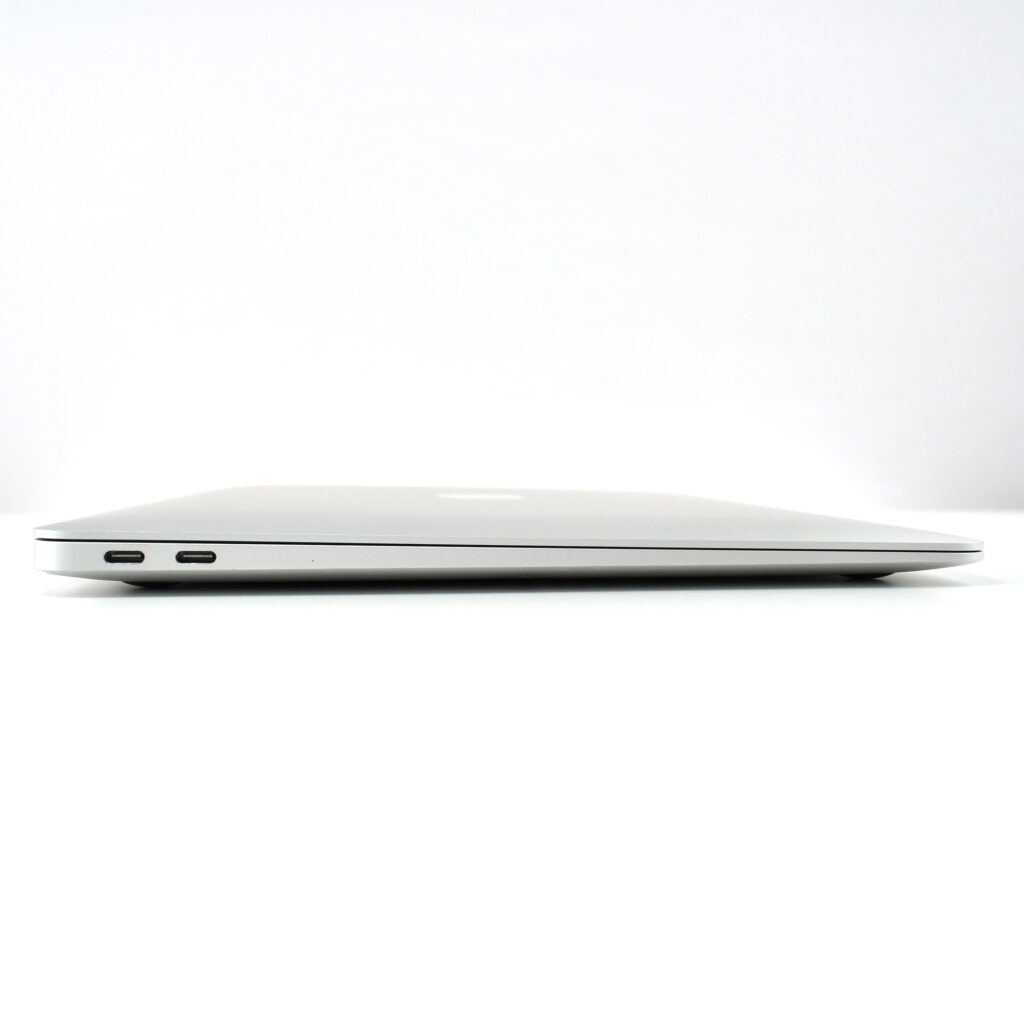
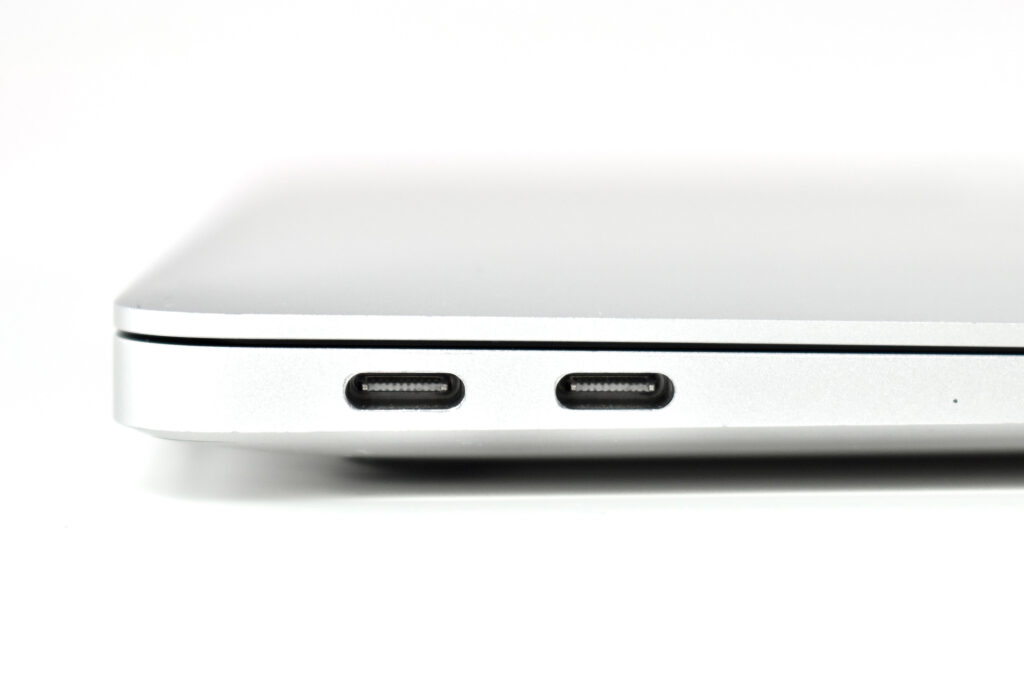
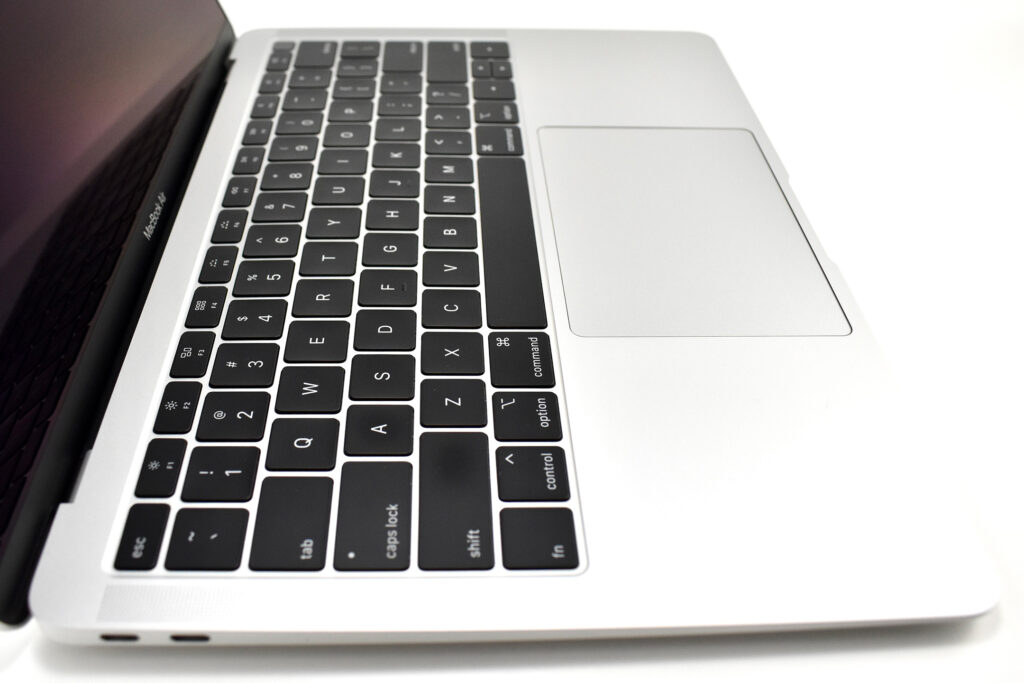
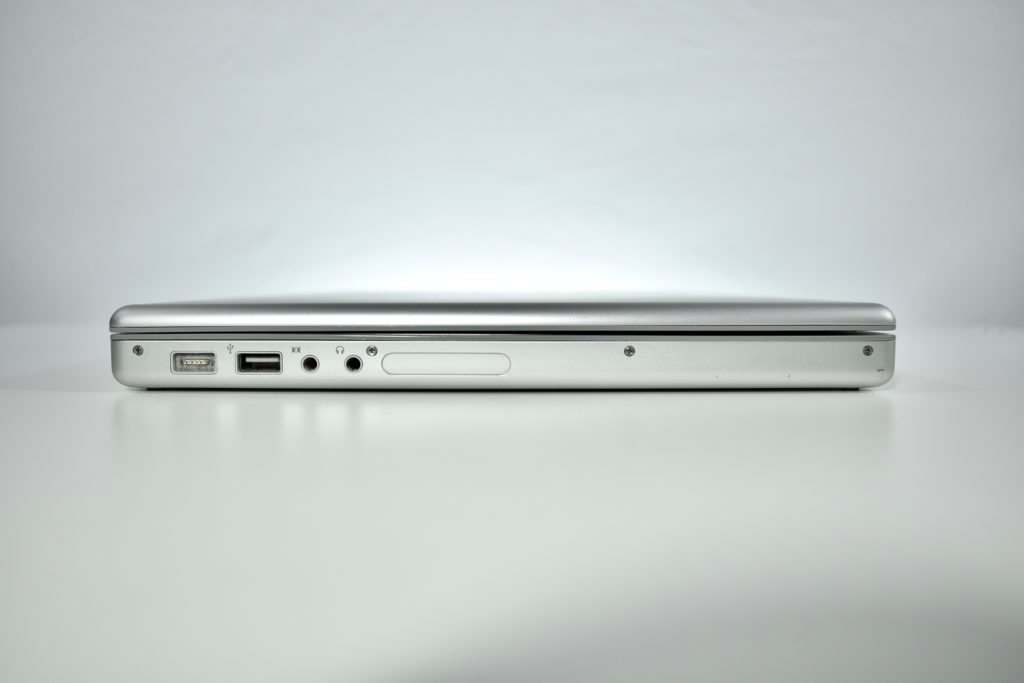
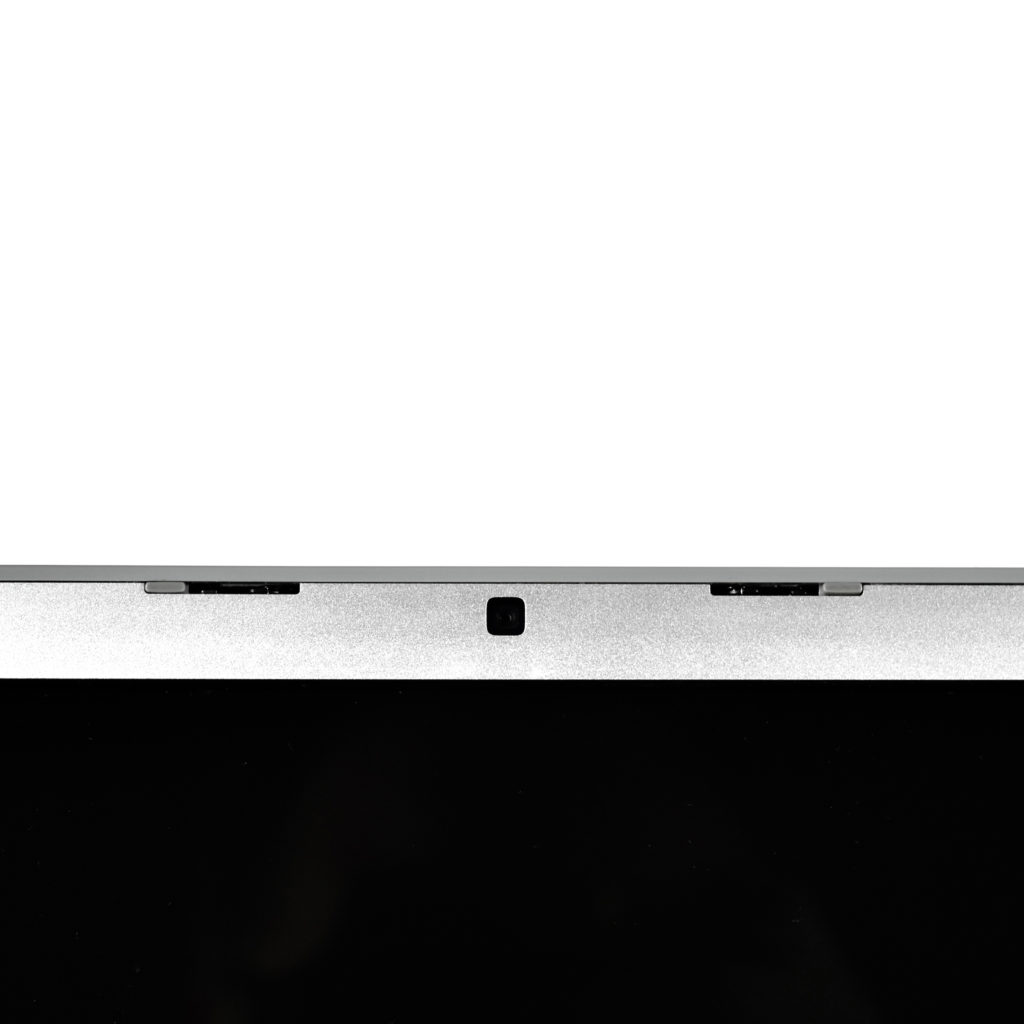
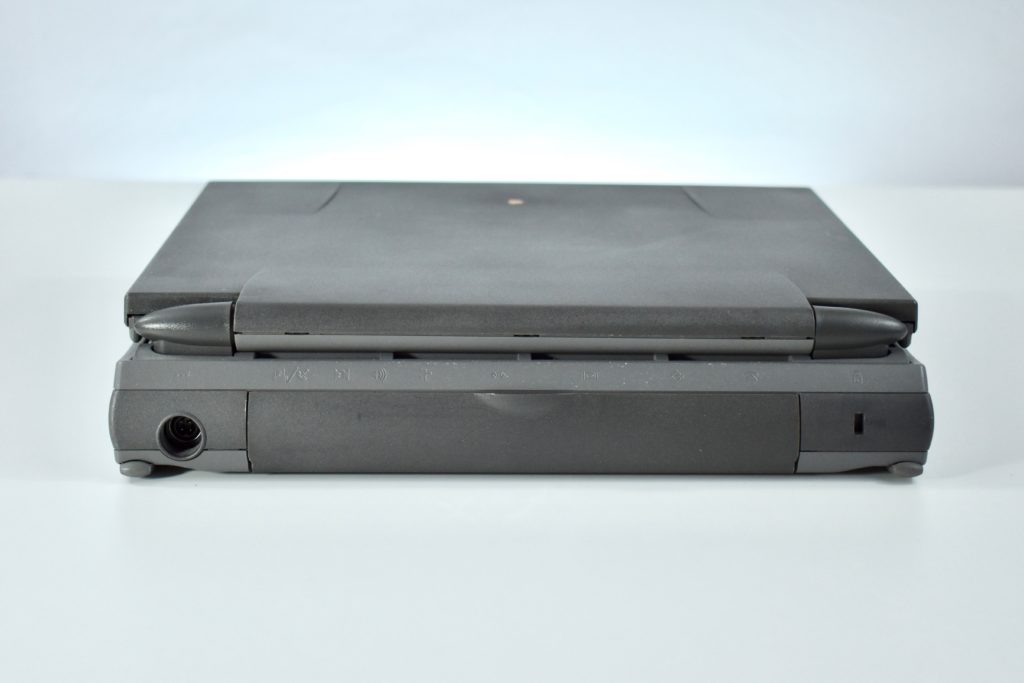
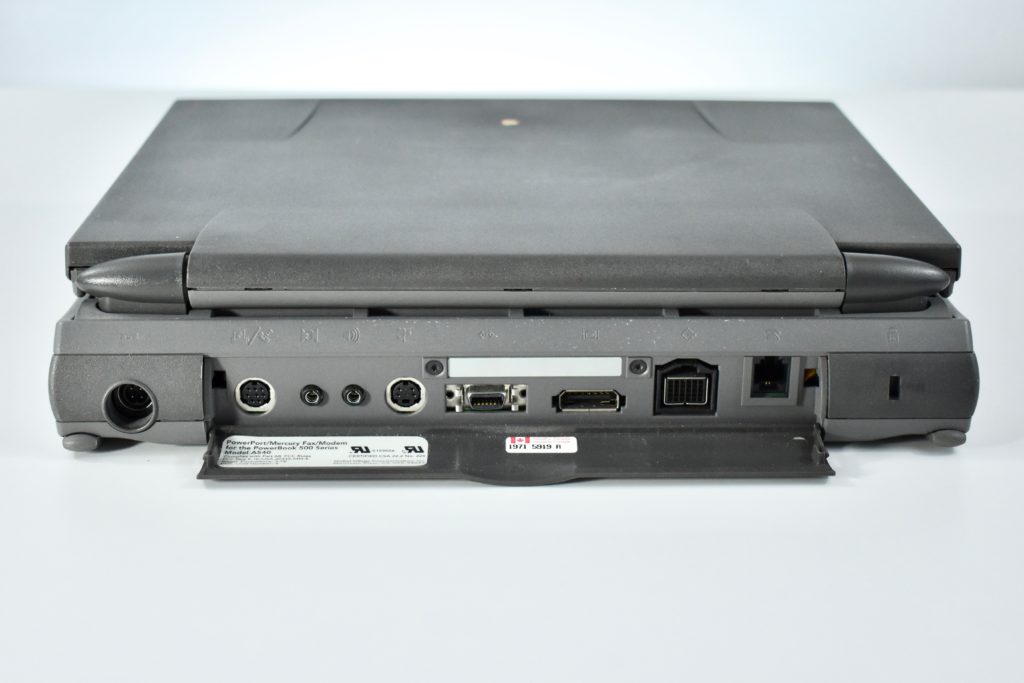
The front camera was a 720p FaceTime HD camera. This was the first MacBook Air to ship with 2 USB-C connections, and it also had a 3.5mm headphone jack. Further, this was the first MacBook Air to include an Integrated Touch ID sensor.
The 2018 MacBook Air was released at a time when its features were potentially confusing to customers when compared to other Apple laptop offerings at the time. A reviewer at The Verge noted:
“Is this new Air like a 12-inch MacBook, just blown up to a slightly bigger size? Is it more like a 13-inch MacBook Pro (sans Touch Bar), just with cheaper parts?”
When released, this this MacBook Air only was offered in a 13-inch option, dropping the 11-inch version available in the previous design. This was also the final MacBook Air with an Intel chip—future versions included Apple Silicon, such as the M1.
Source: Apple (Newsroom, Tech Specs), The Verge