On September 13, 2000, Steve Jobs released the Mac OS X Public Beta at Apple Expo in Paris. During the unveiling, Jobs said:
“Mac OS X is the future of the Macintosh, and the most technically advanced personal computer operating system ever. We’re excited to have our users test drive this public beta version and provide us with their valuable feedback.”
Somewhat controversially, Apple charged $29.95 for the software—a Beta version that was known to be buggy and not quite finished. The issue was not that the operating system was buggy and unfinished—that is the definition of a software “Beta”—but that Apple was charging faithful users to get an early look at the future of their products while testing it for the purpose of improving the final release. In an article at the time, a writer at Ars Technica provided a balanced opinion:
“Taken all together, ‘Mac OS X Public Beta’…means that for $29.95 you get an unfinished, buggy version of Apple’s next generation operating system. Charging for public beta software is increasingly common among the big software companies… If you don’t want to pay for buggy software, don’t buy the beta.”
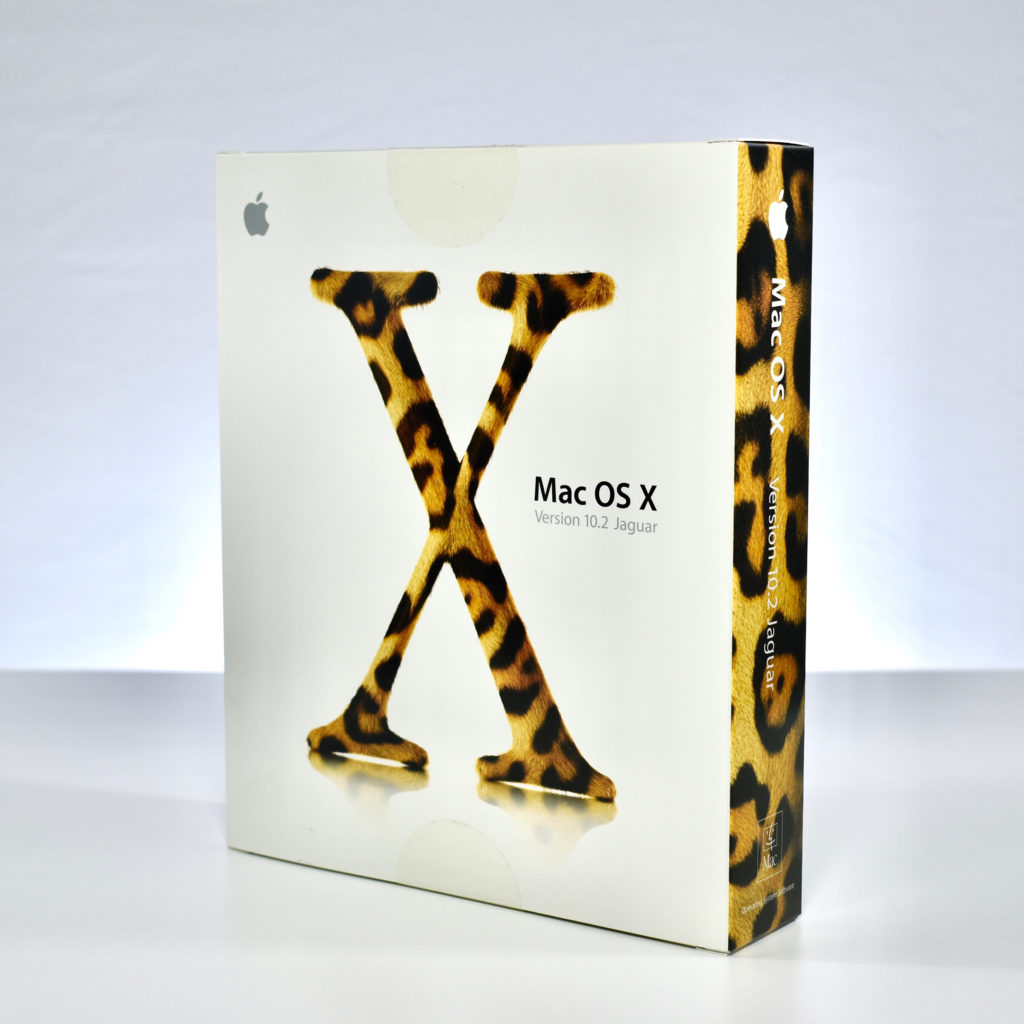
The Mac OS X public beta was a completely new operating system for the Mac and provided the foundation of the macOS we still use today—over 20 years later. Apple’s press release described some highlights of Mac OS X:
“Mac OS X features true memory protection, pre-emptive multi-tasking, and symmetric multiprocessing when running on the new dual-processor Power Mac G4 line. Mac OS X includes Apple’s new Quartz 2D graphics engine (based on the Internet-standard Portable Document Format) for stunning graphics and broad font support; OpenGL for spectacular 3D graphics and gaming, and QuickTime for streaming audio and video. In addition, Mac OS X features Apple’s new user interface named ‘Aqua,’ which combines superior ease-of-use with amazing new functionality such as the ‘Dock,’ a breakthrough for organizing applications, documents and miniaturized windows.”
This white cardboard folder measures 8 x 9.5 x 0.25 inches and opens to reveal a compartment for a single CD. Unfortunately, the original installer CD is not included in this folder. The welcome message in the folder reads:
“Dear Mac OS X Beta Tester,
You are holding the future of the Macintosh in your hands.
Mac OS X is a new, super-modern operating system that will usher in a new era for the Macintosh. New from the ground up, Mac OS X is specifically designed for the Internet and includes advanced technologies for incredible improvements in stability and performance. It also features a stunning new interface called Aqua.
This Public Beta will give you a chance to start using Mac OS X and give us a chance to hear what you think. Let us know by visiting our website at www.apple.com/macosx.
Thanks for your help and for being a part of Apple history. We couldn’t do it without you.”
Sources: Ars Technica, Apple