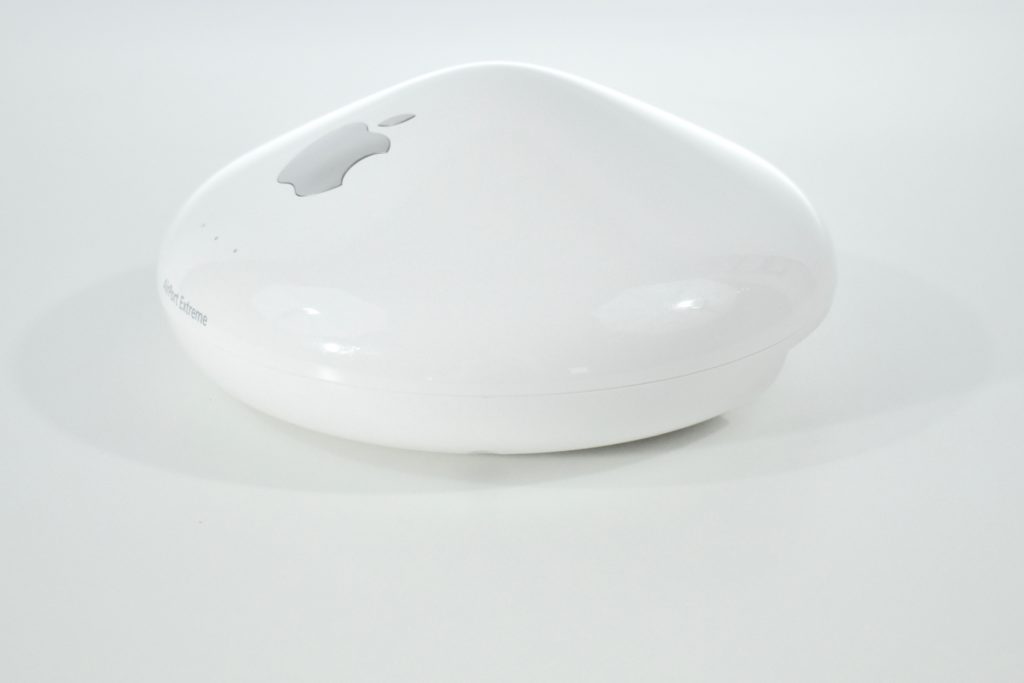
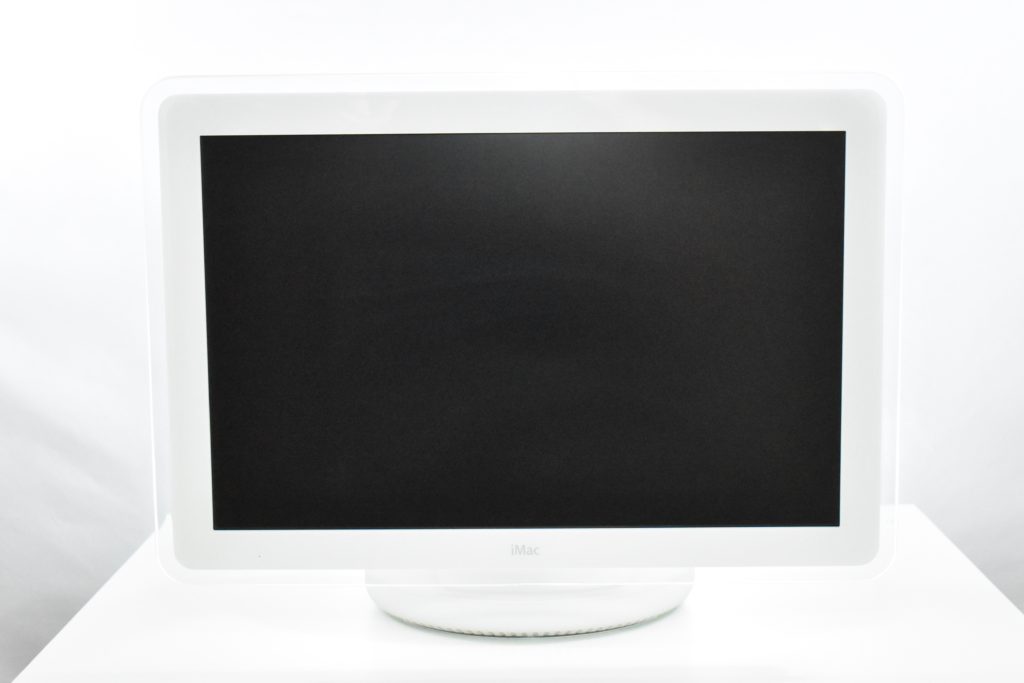
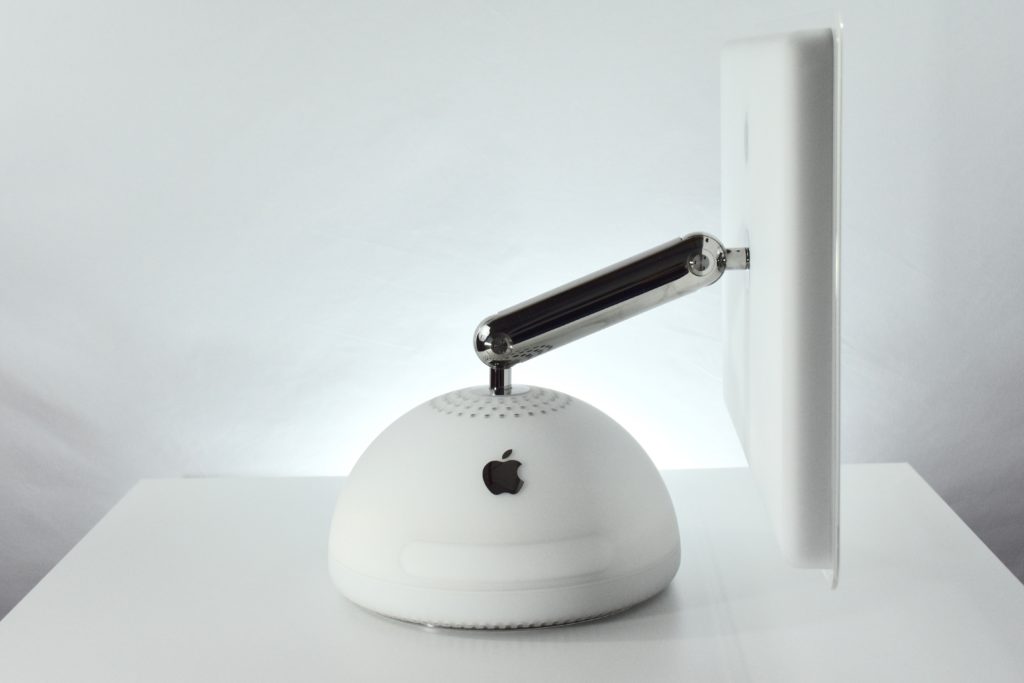
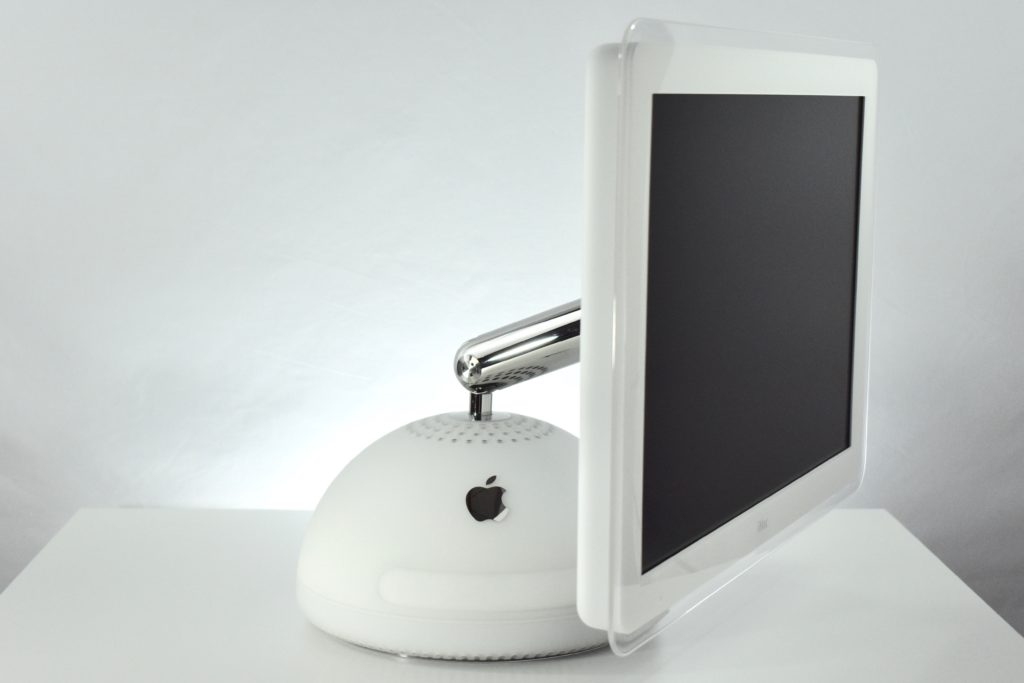
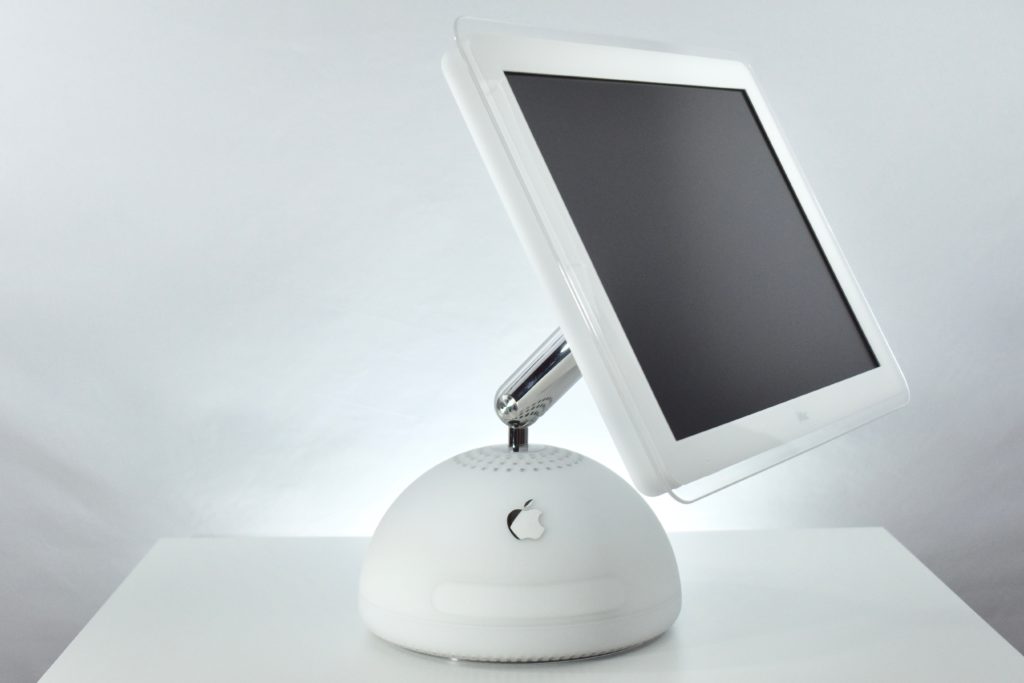
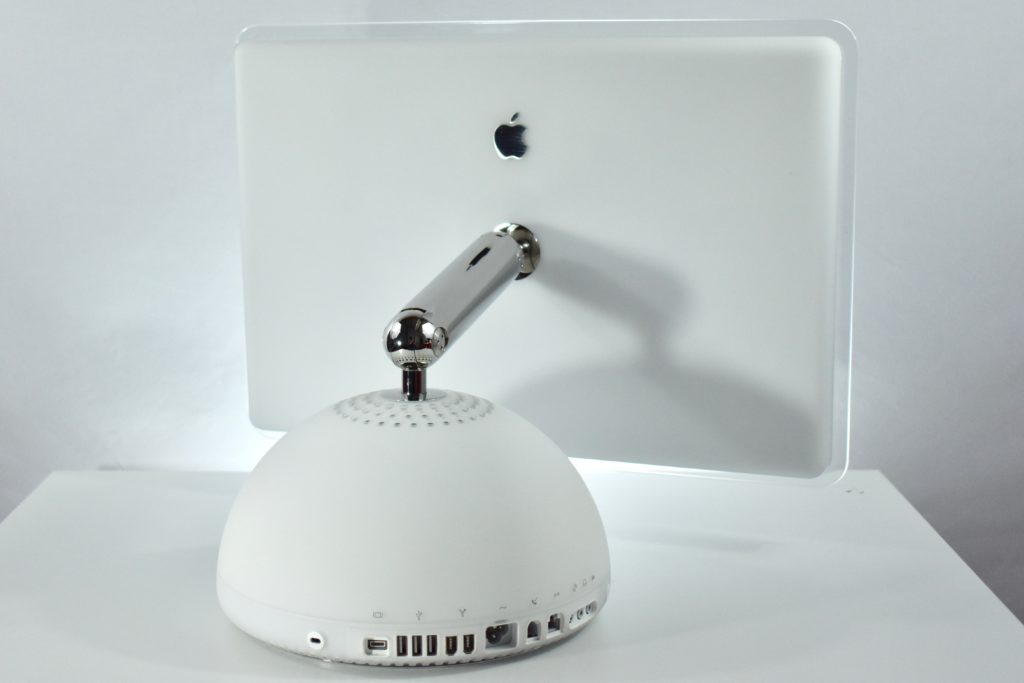
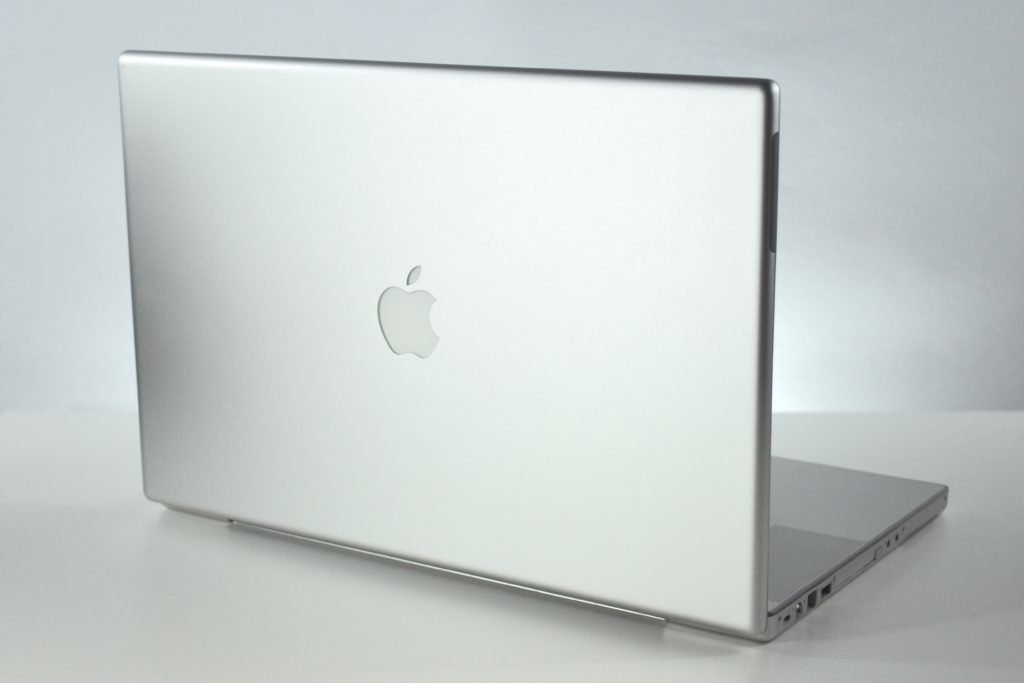
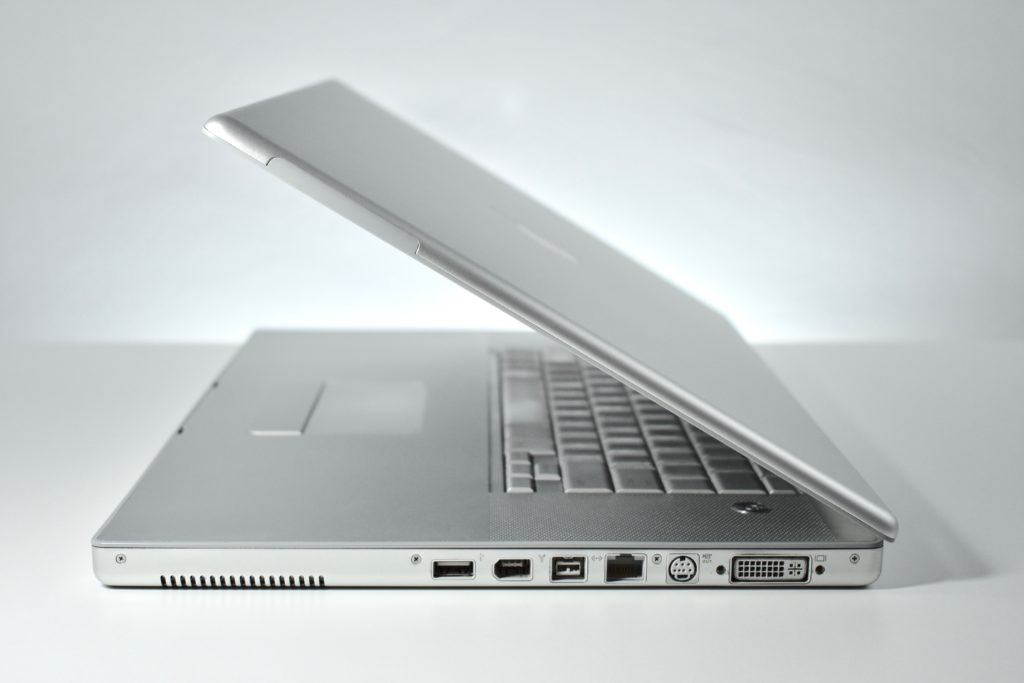
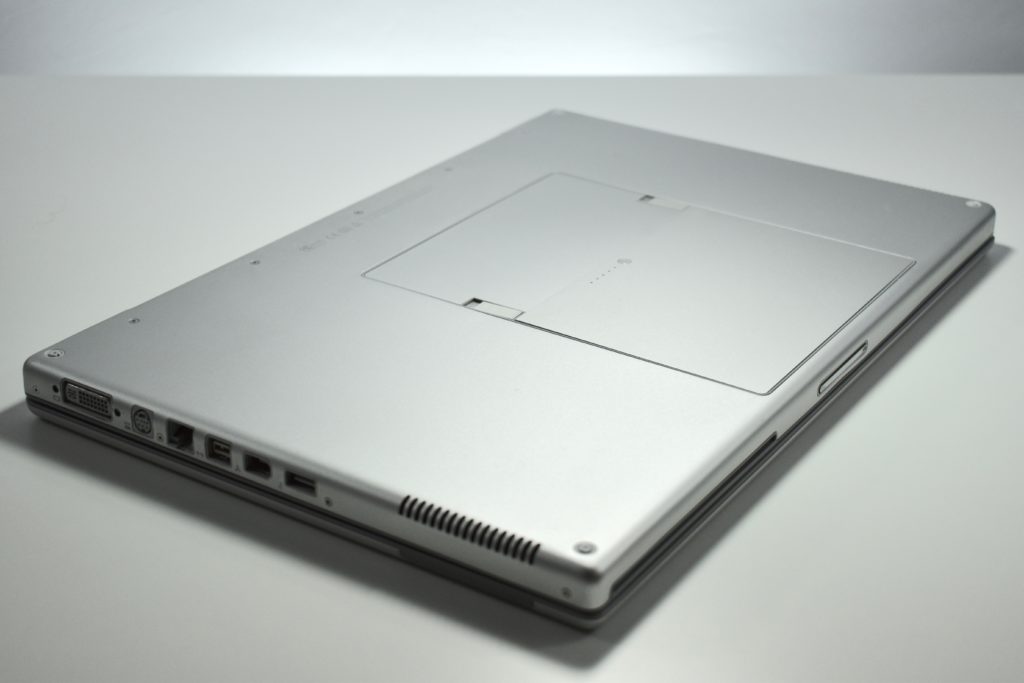
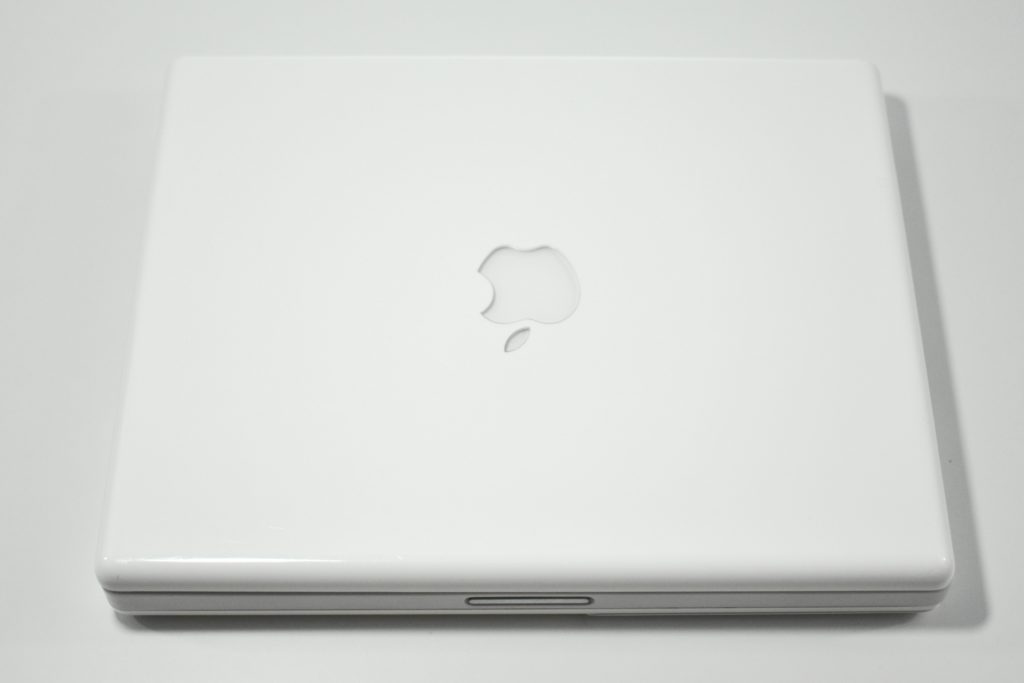
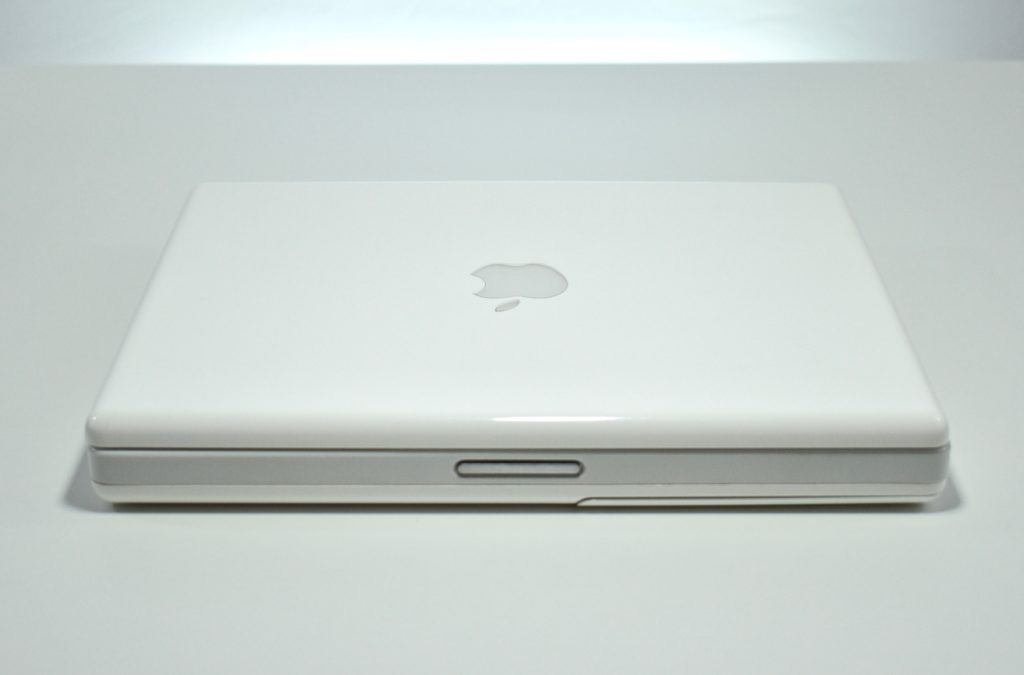
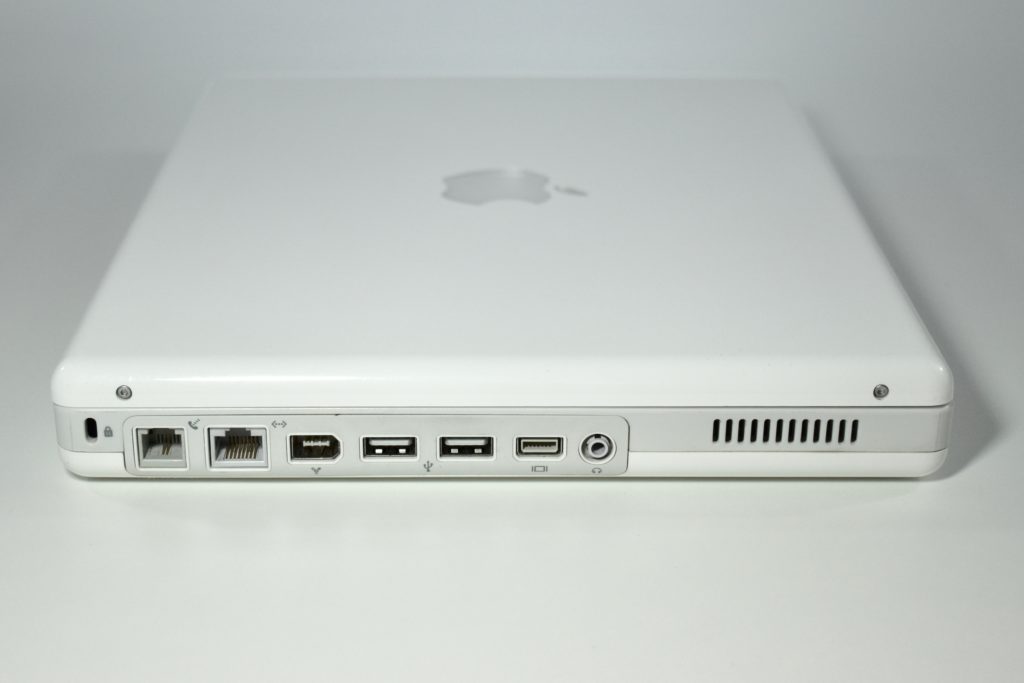
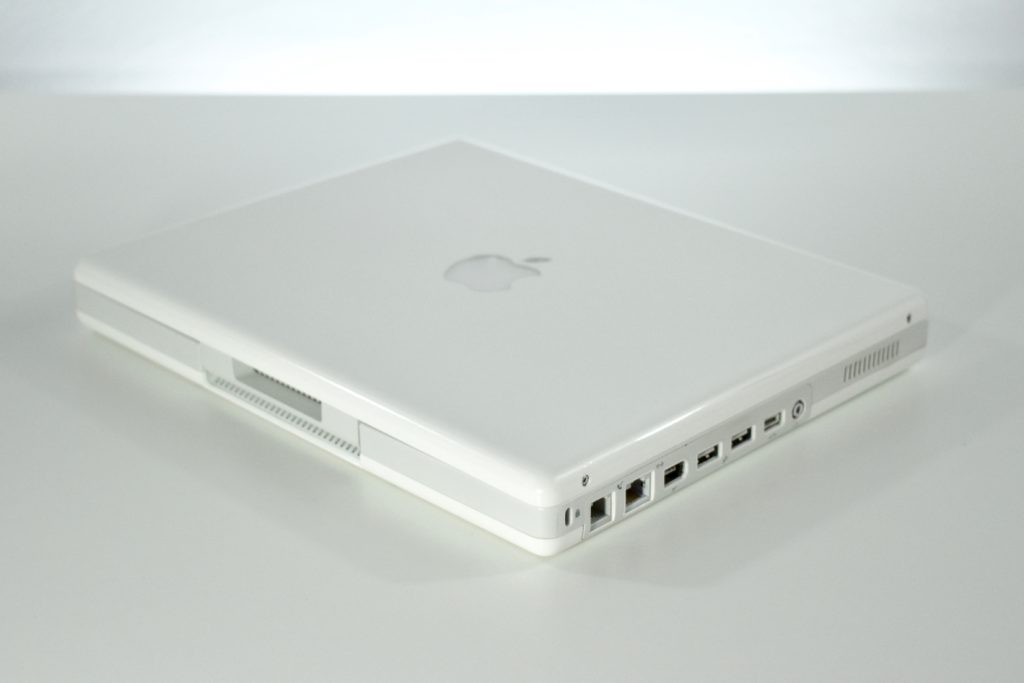
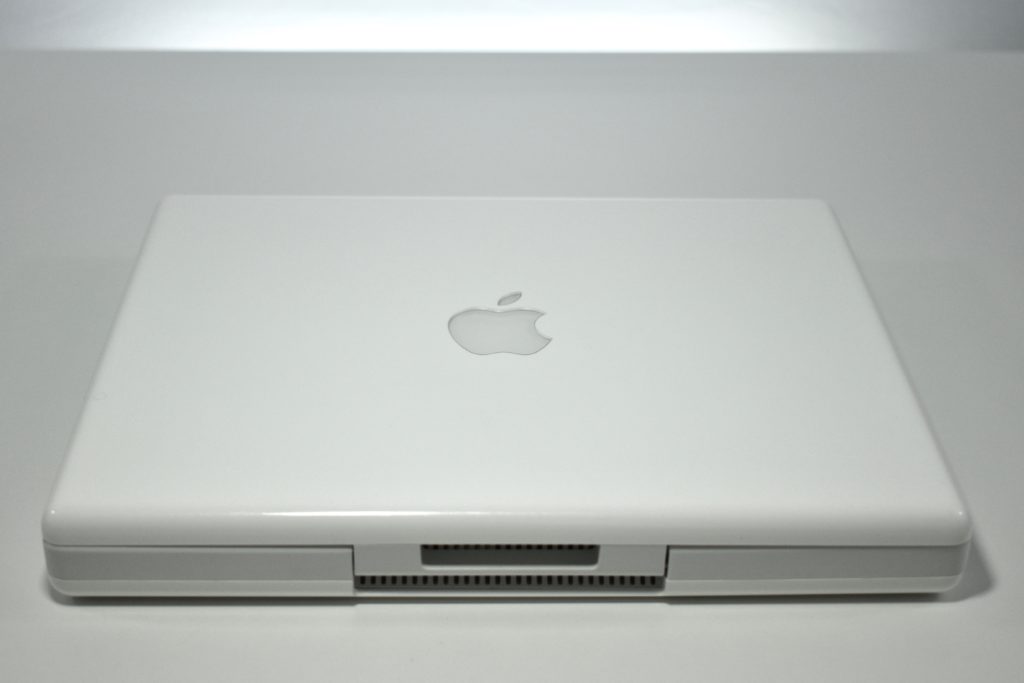
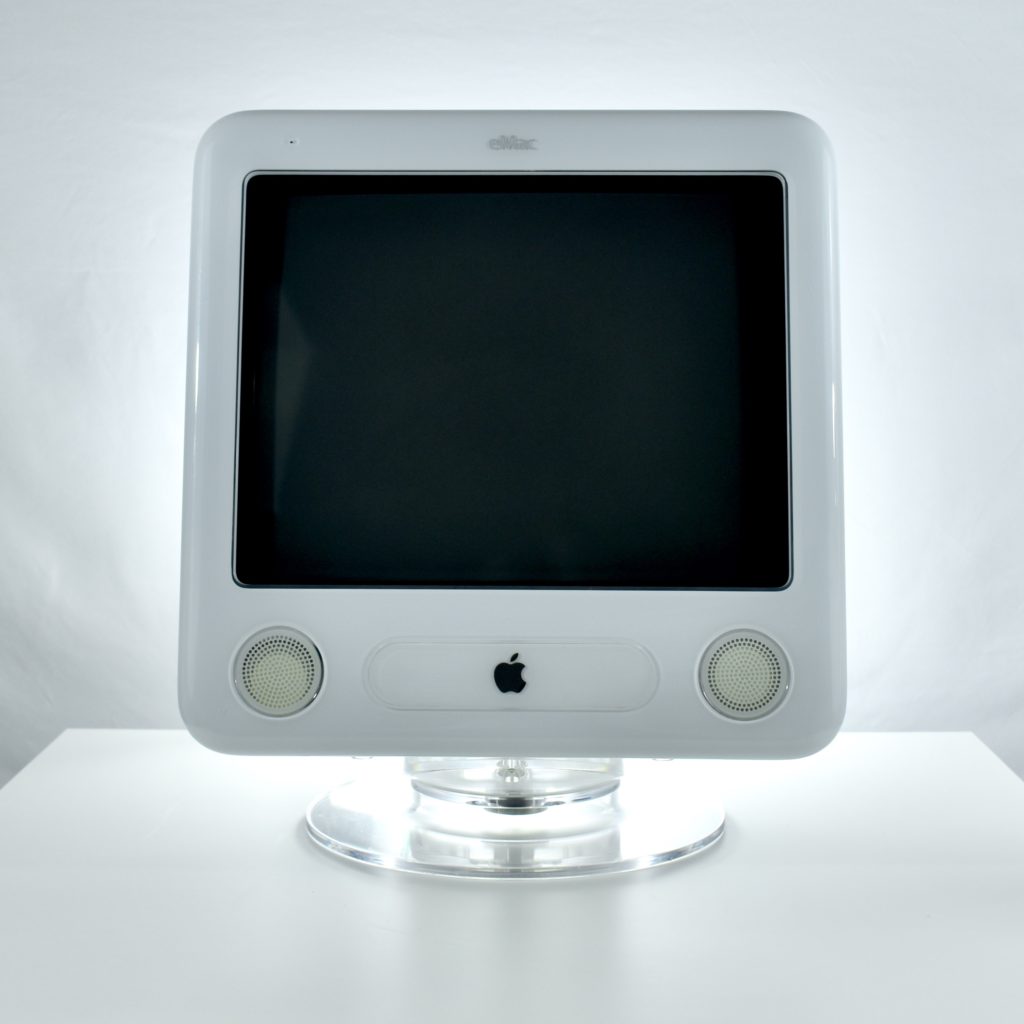
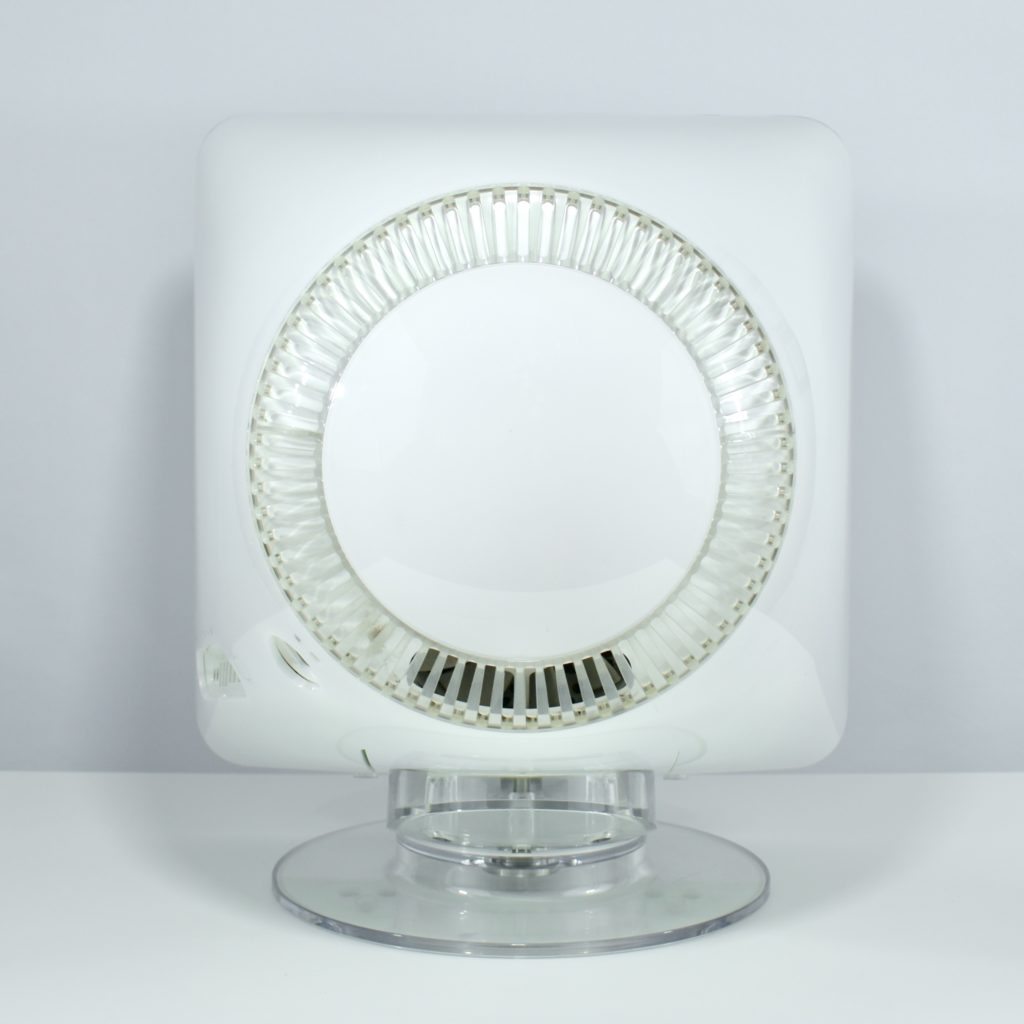
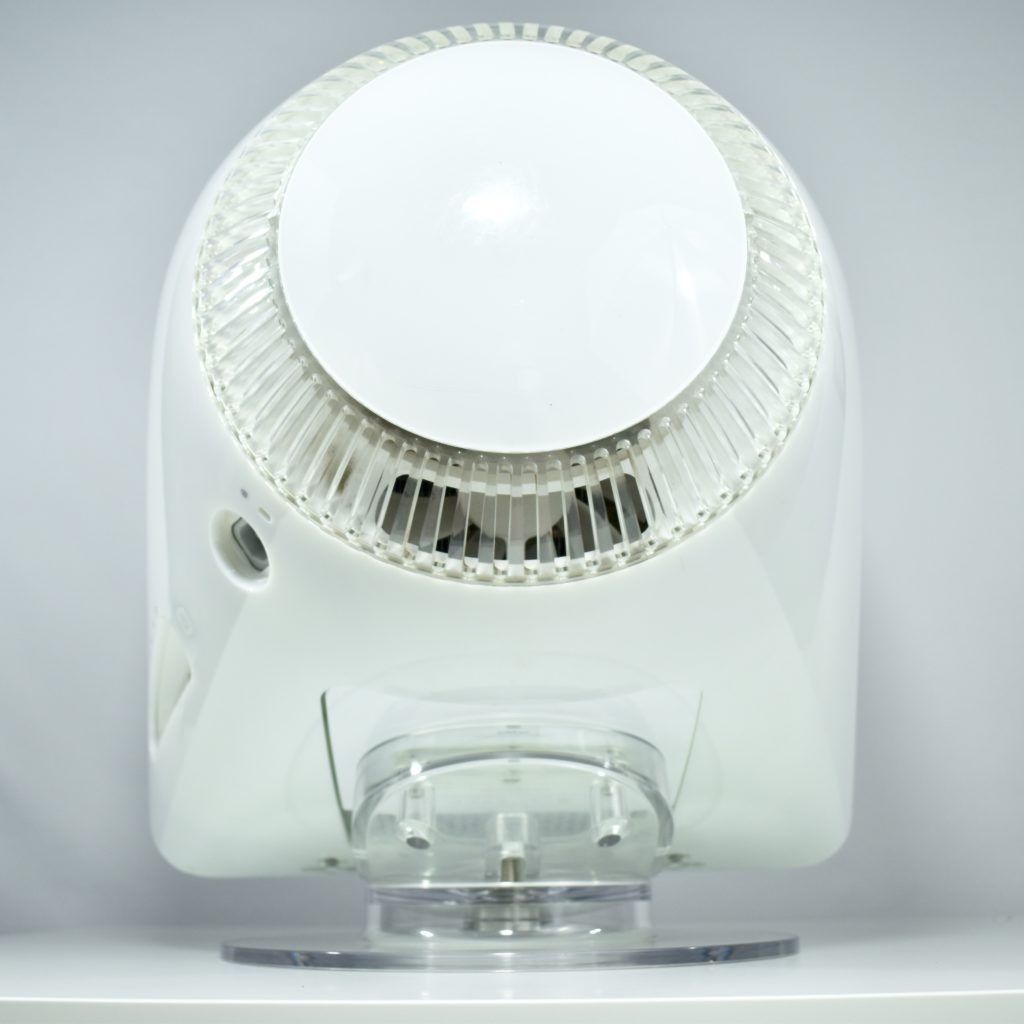
The AirPort Extreme was a wireless networking base station that combined the functions of a network router and wireless access point. When the Extreme model of this device was released, the “extreme” modifier denoted its increased Wi-Fi speed from 802.11a/b to the faster 802.11g Wi-Fi standard, a major speed difference at the time.
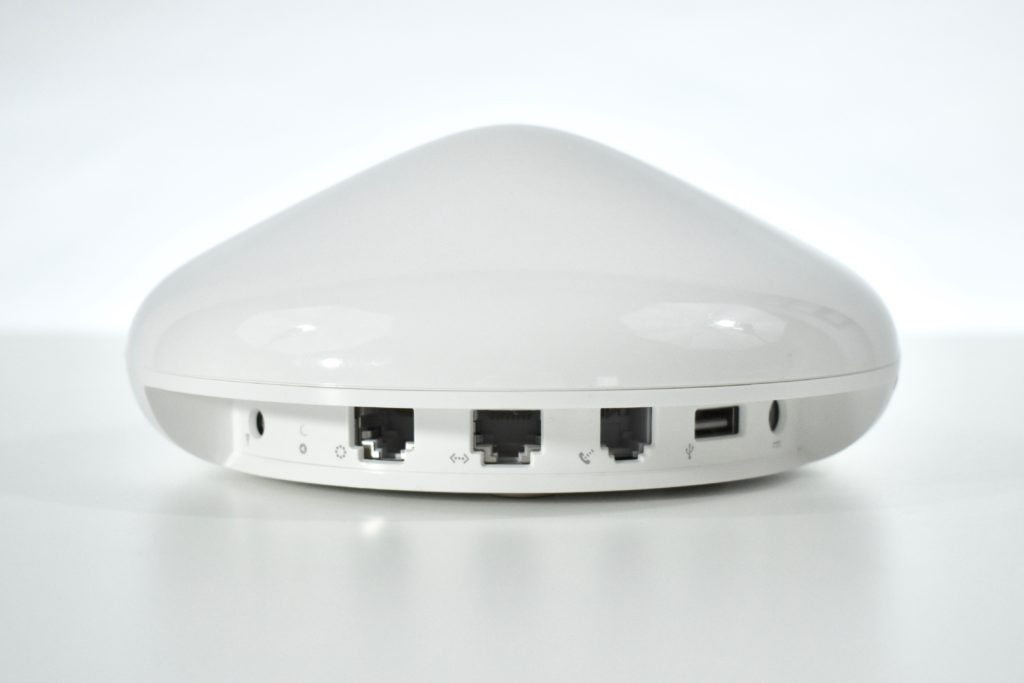
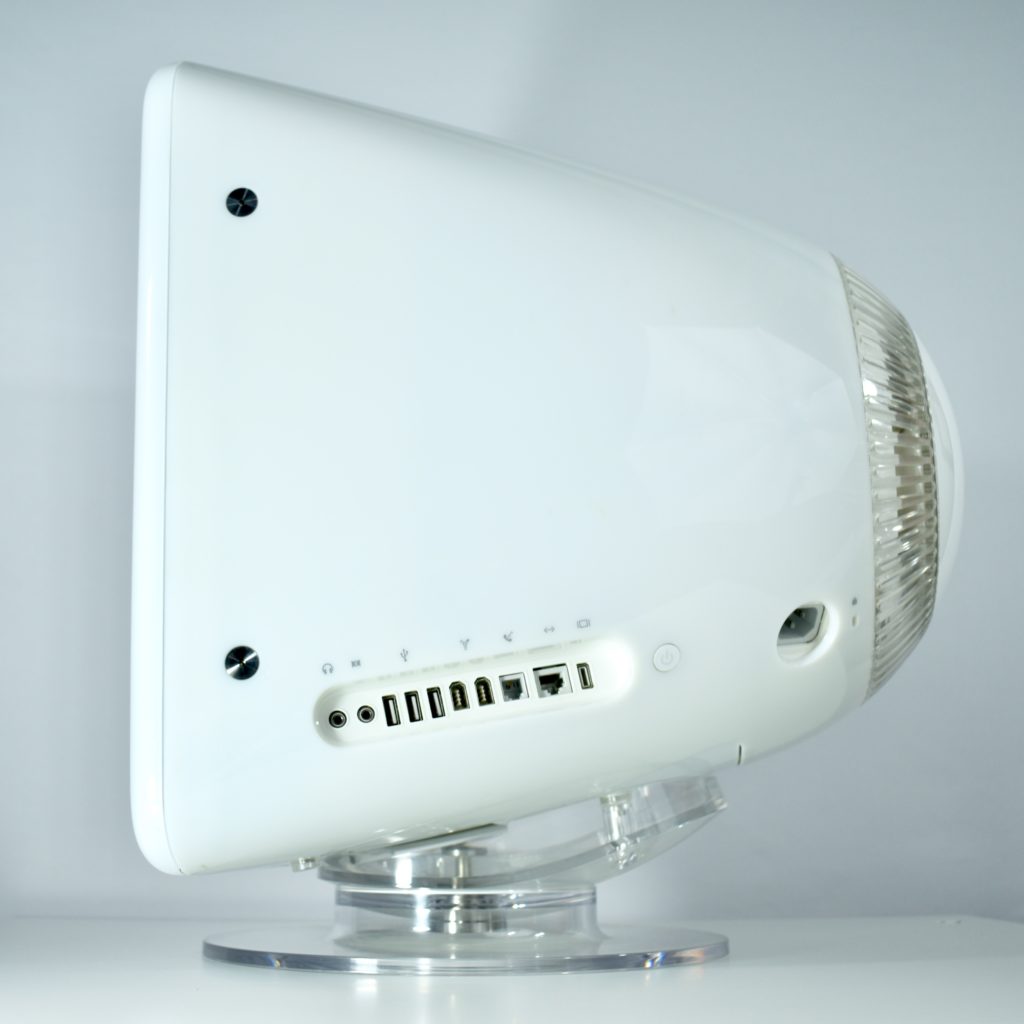
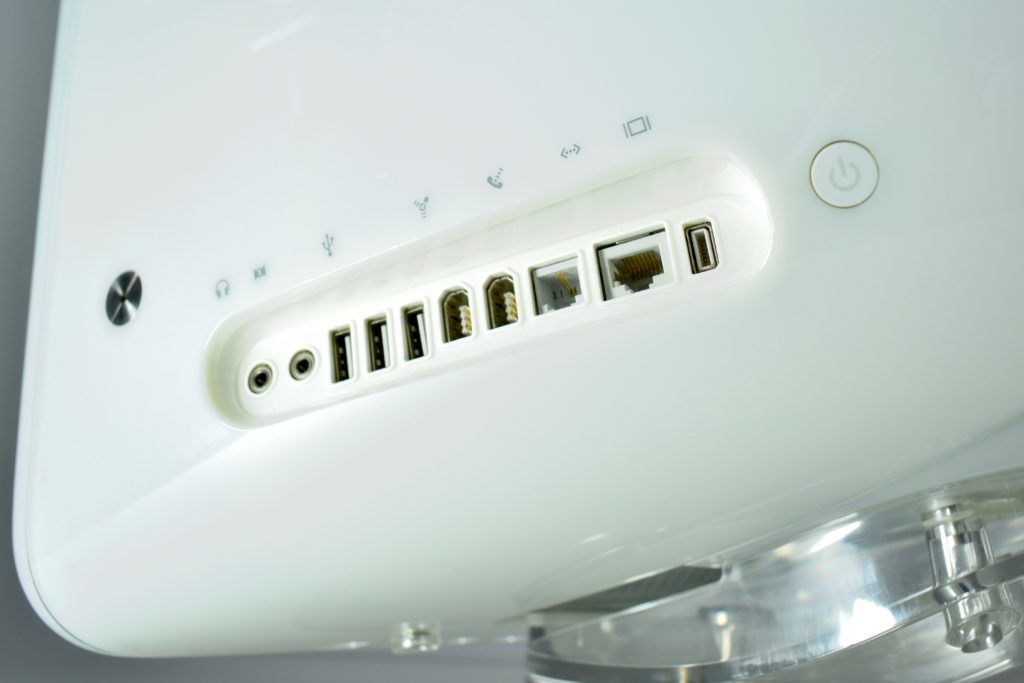
The AirPort Extreme base station model retained the form factor as the original AirPort base station in shape, but the AirPort Extreme was cast in opaque white plastic, used a mirrored Apple logo, and moved the ports to the bottom of the device. The shape was sometimes referred to as the “flying saucer.” Not only was it shaped like a flying saucer, a 1999 TV commercial that introduced the original AirPort showed it behaving like a UFO.
The original AirPort Extreme Base Station could provide wireless access to up to 50 Macs or PCs simultaneously, although performance was noticeably affected as connections exceeded about 12 connected devices. This version was also notable to include a 56K dial-up modem that allowed homes without broadband Internet to have wireless Internet.
Reference: Wikipedia.com