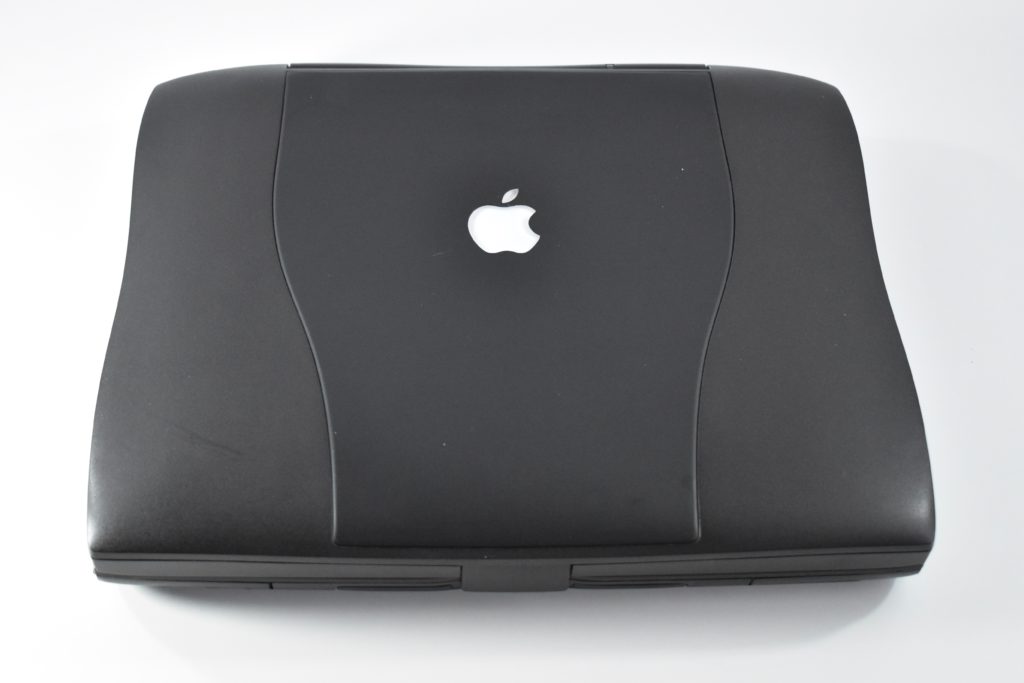
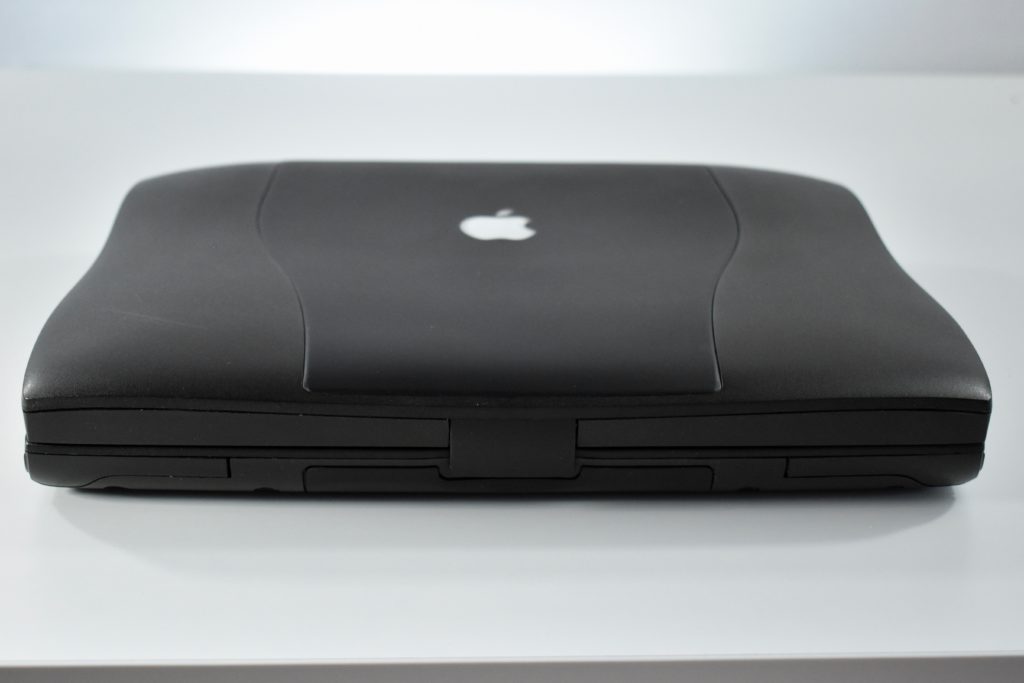
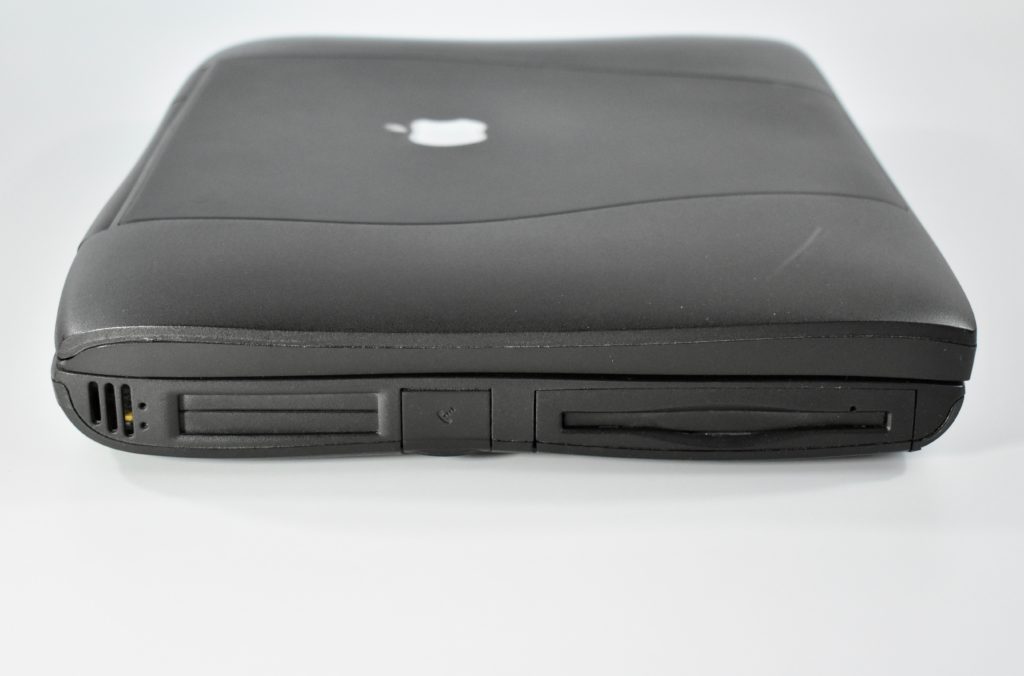
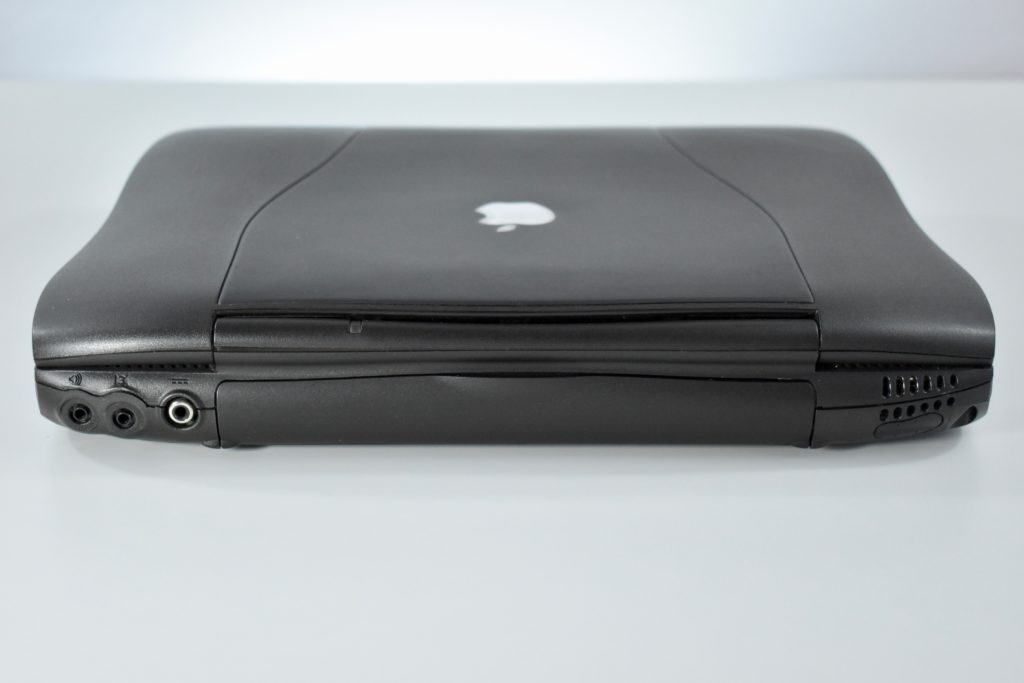
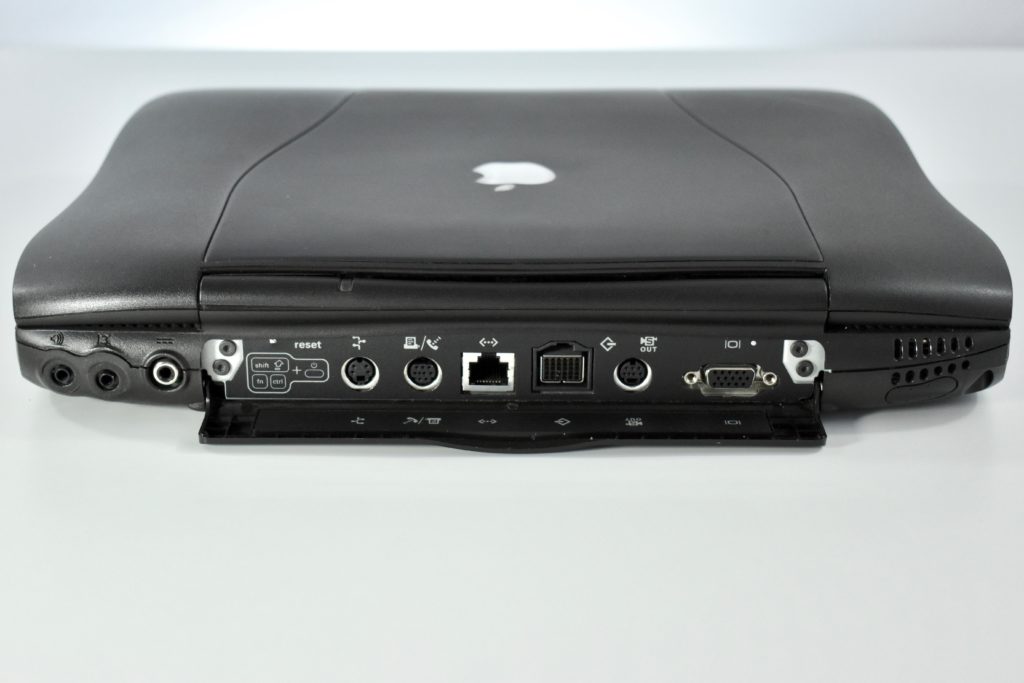
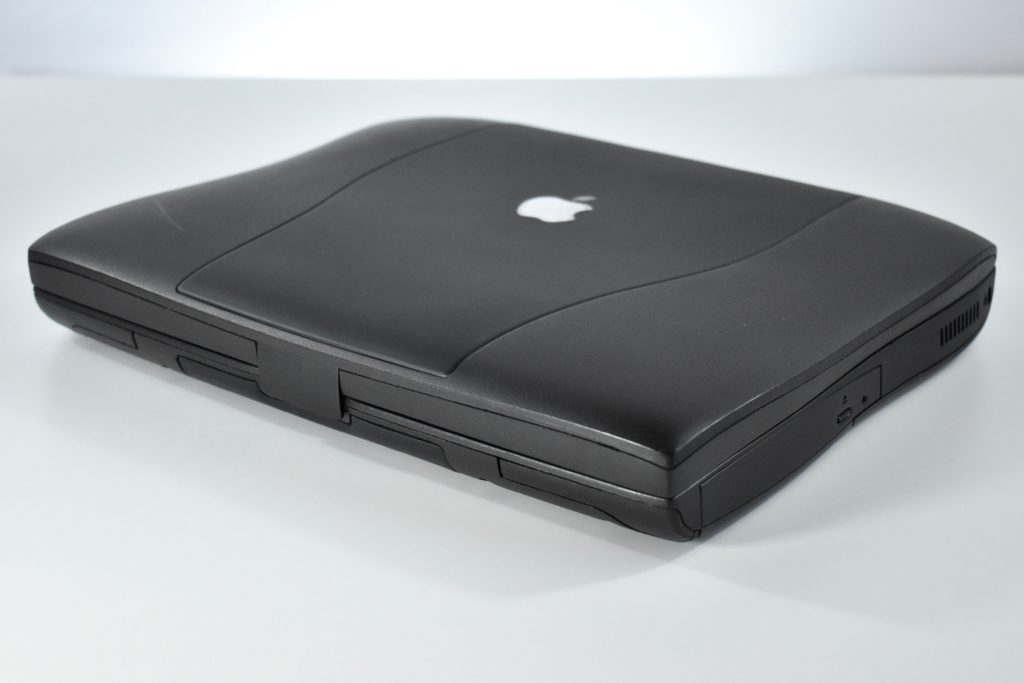
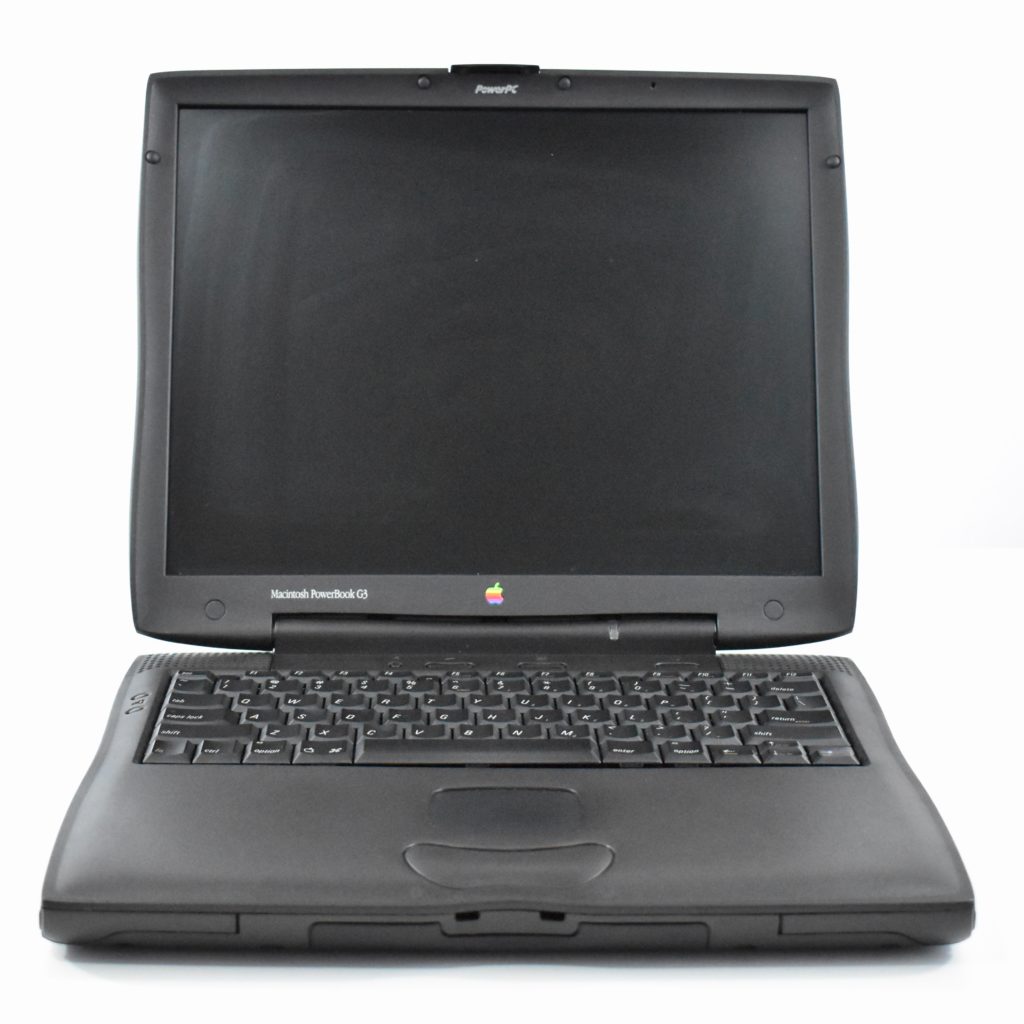
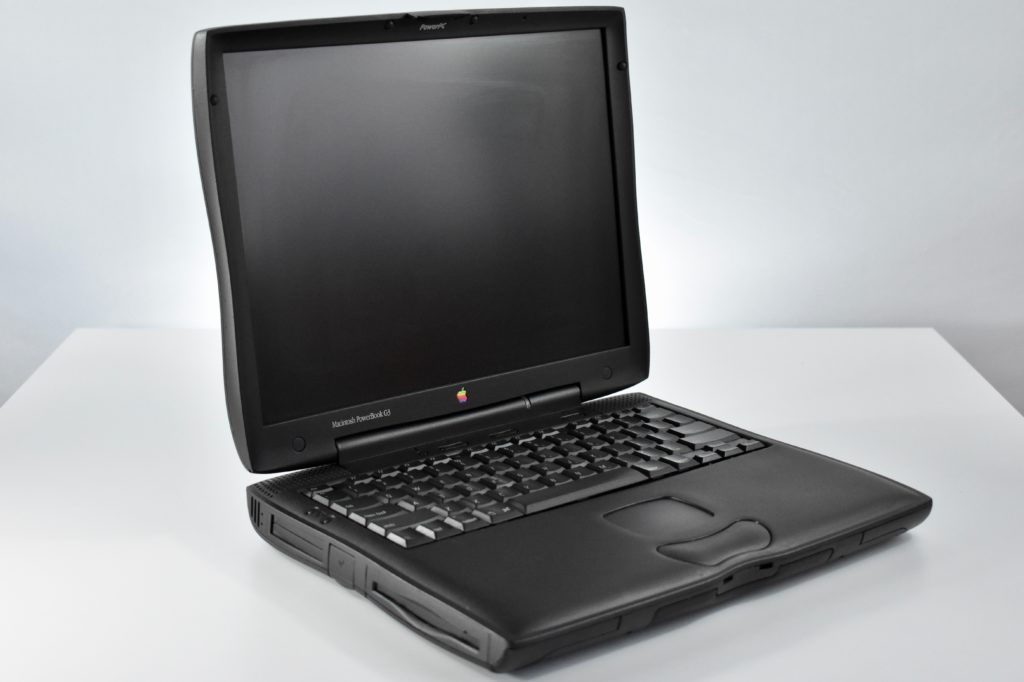
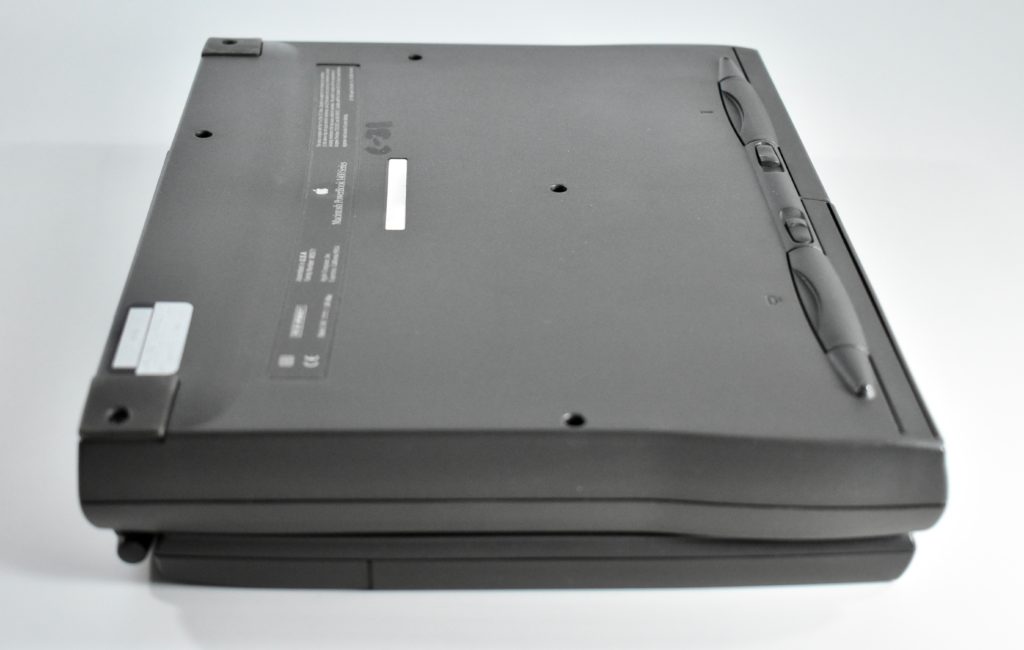
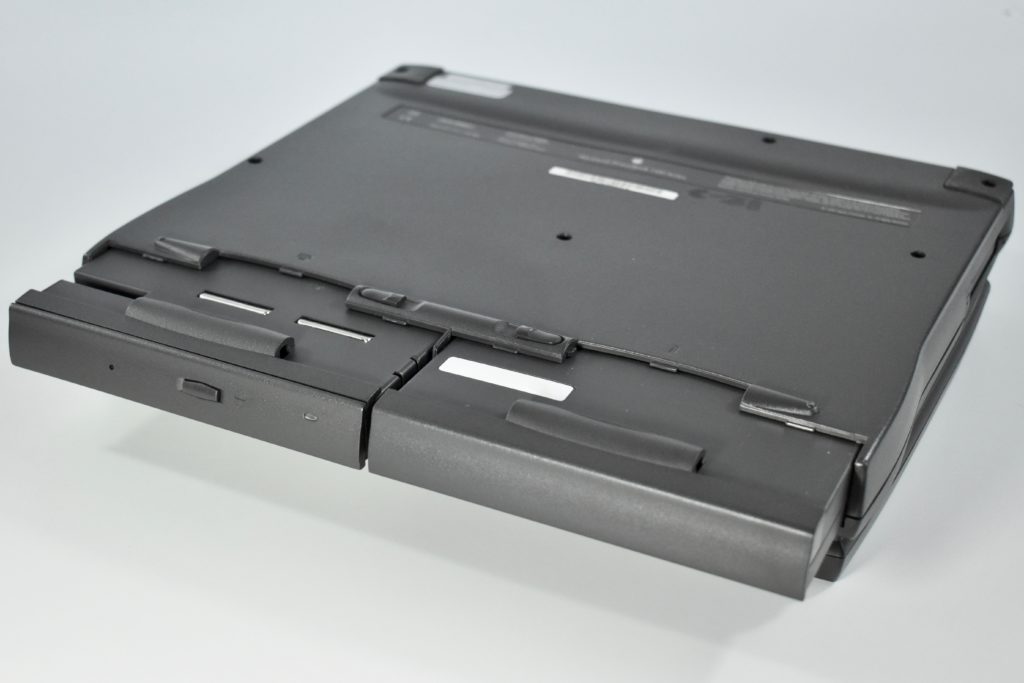
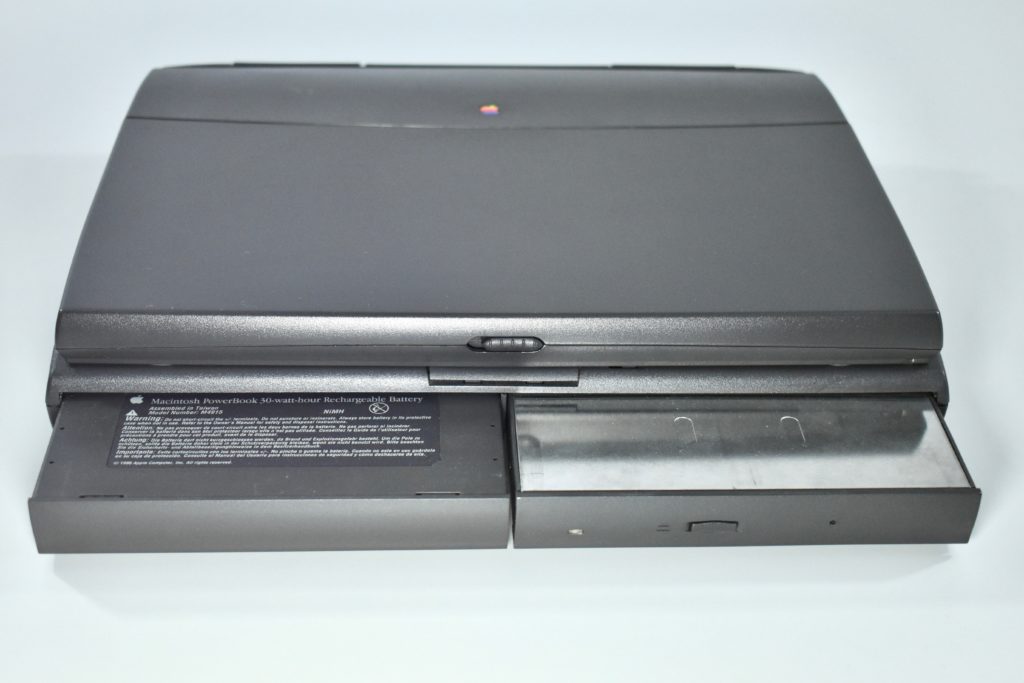
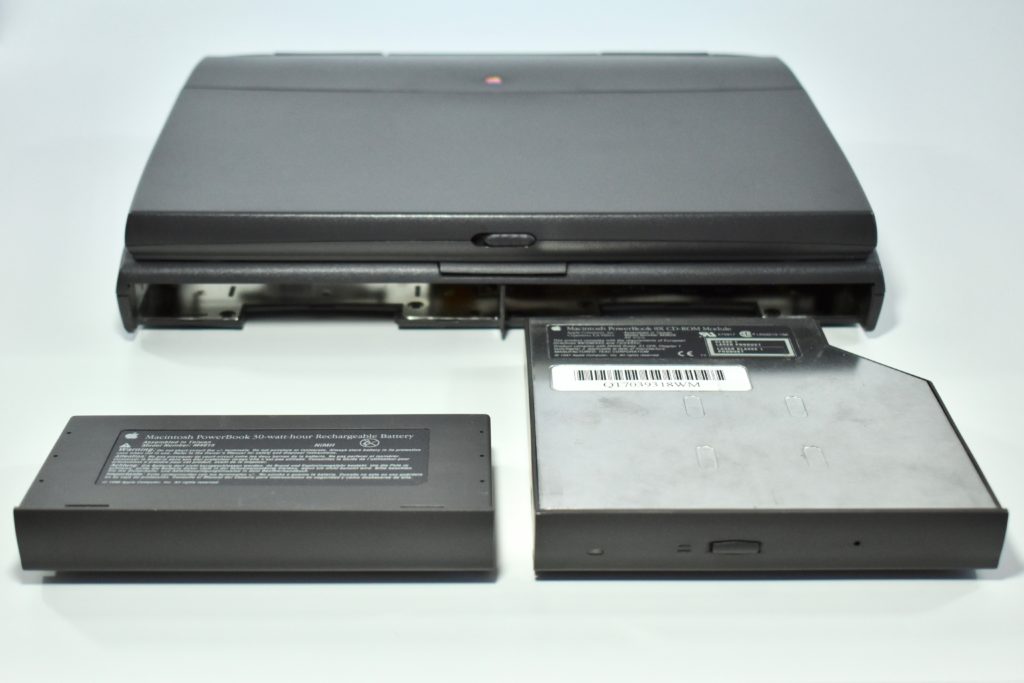
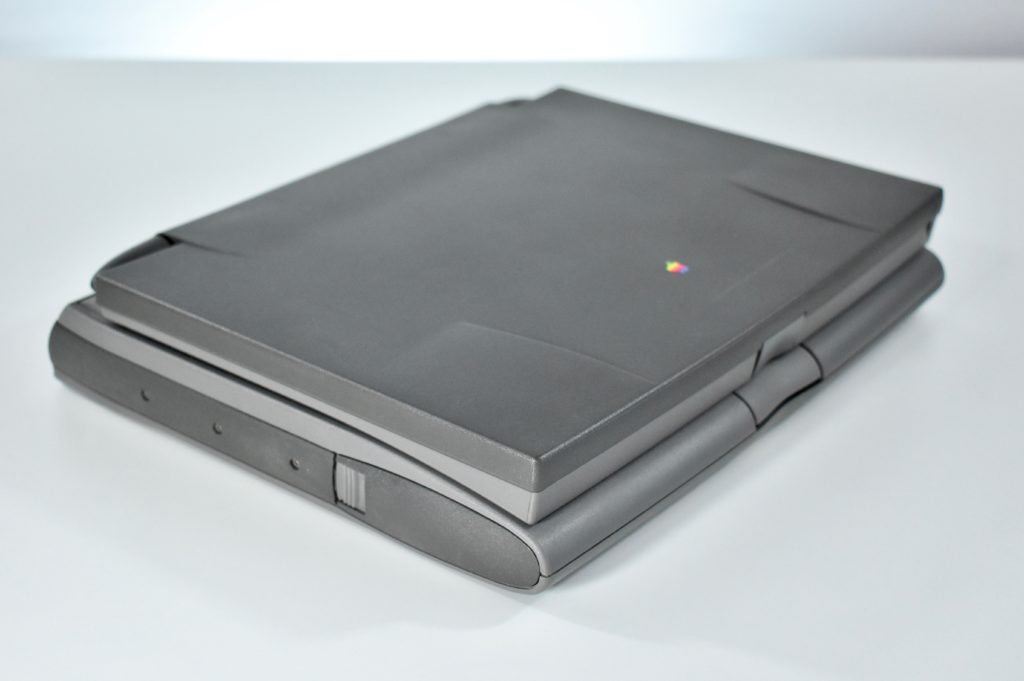
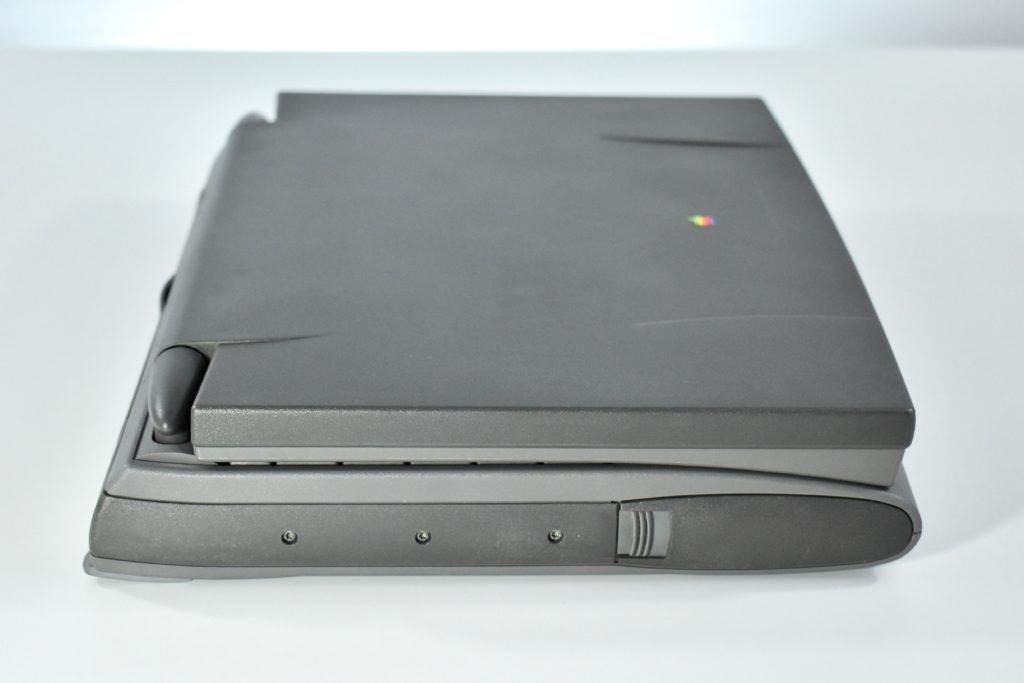
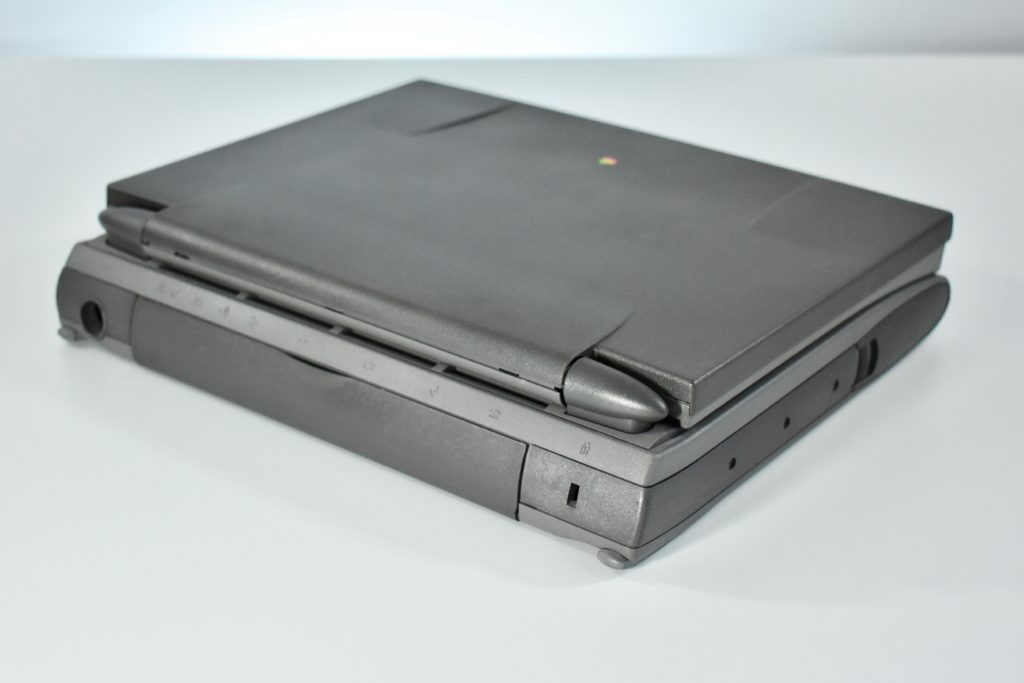
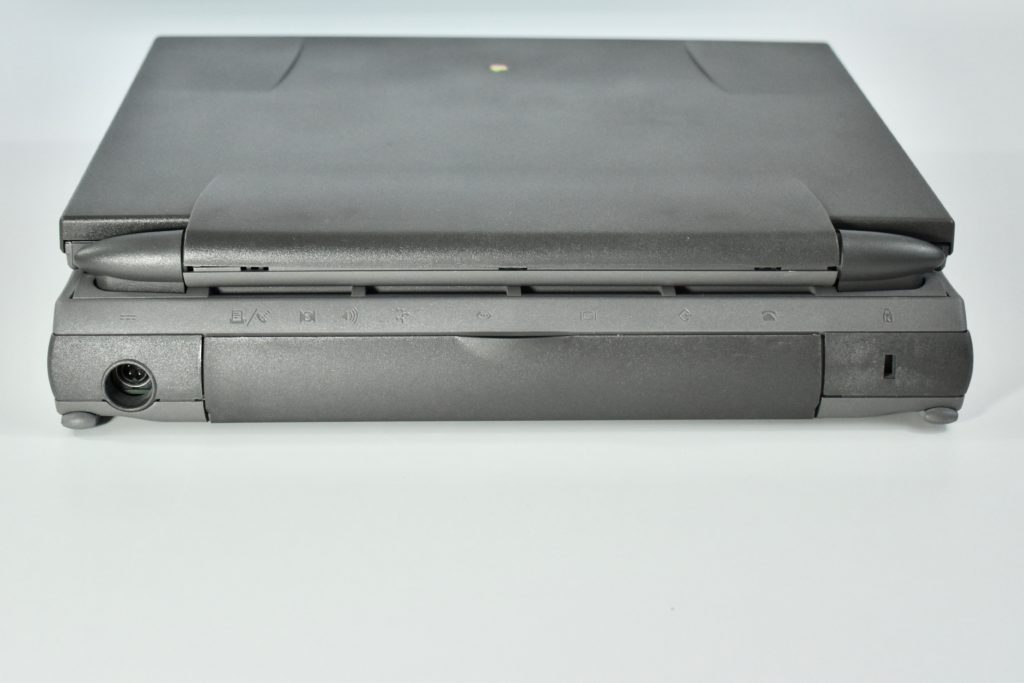
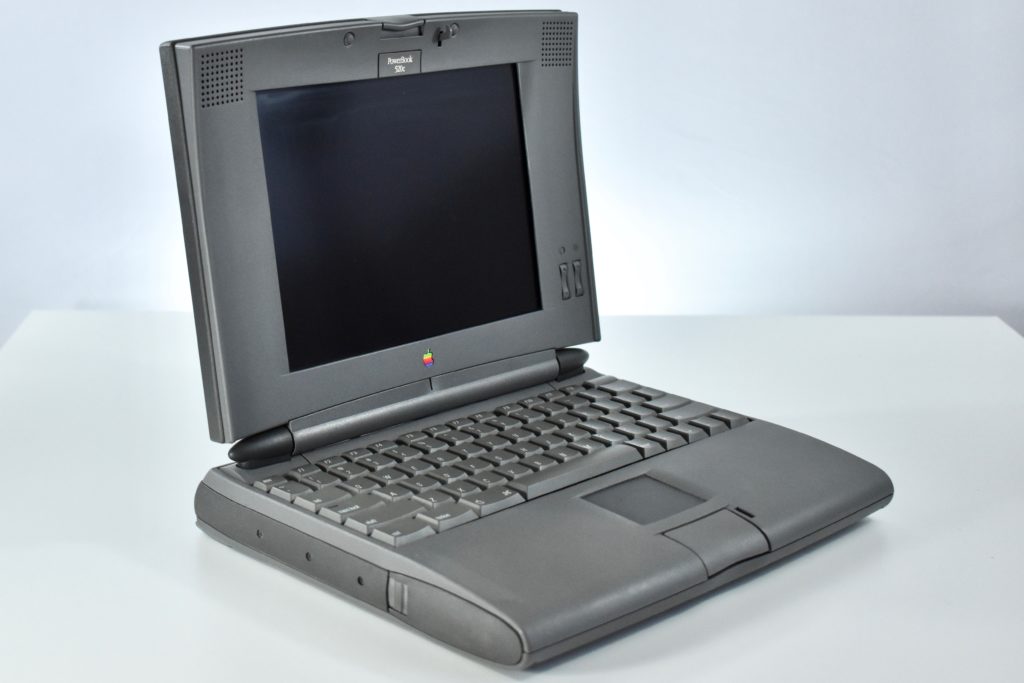
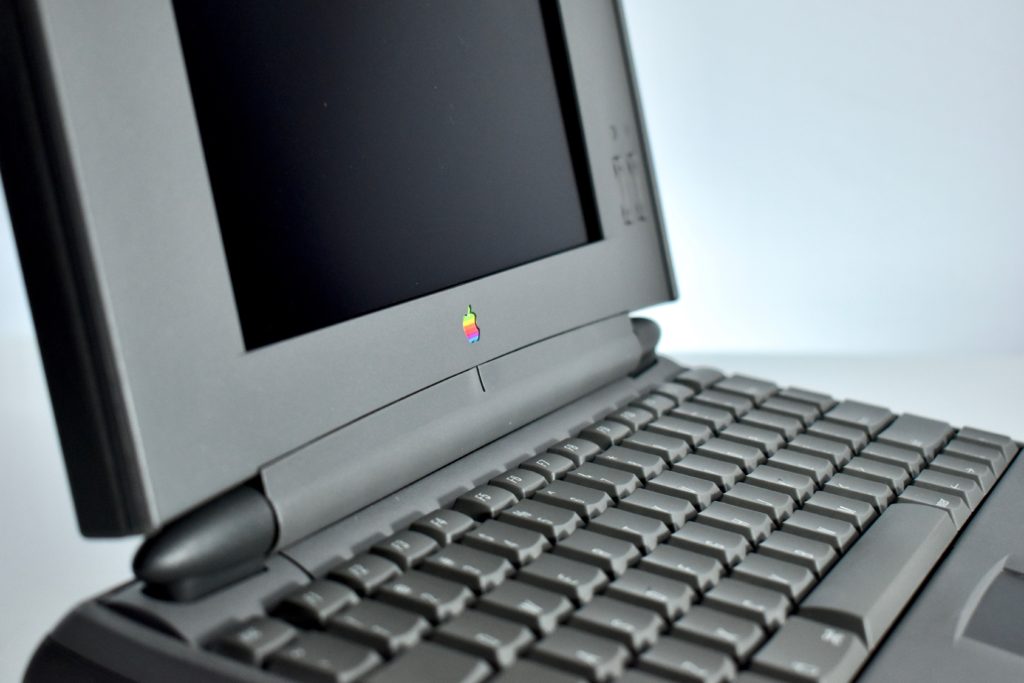
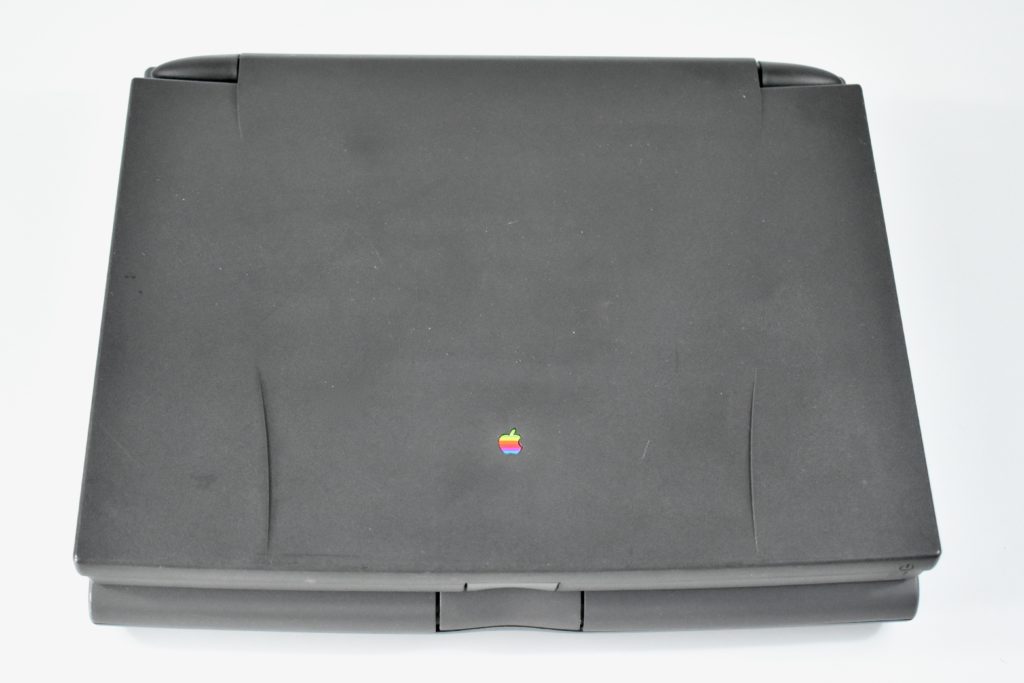
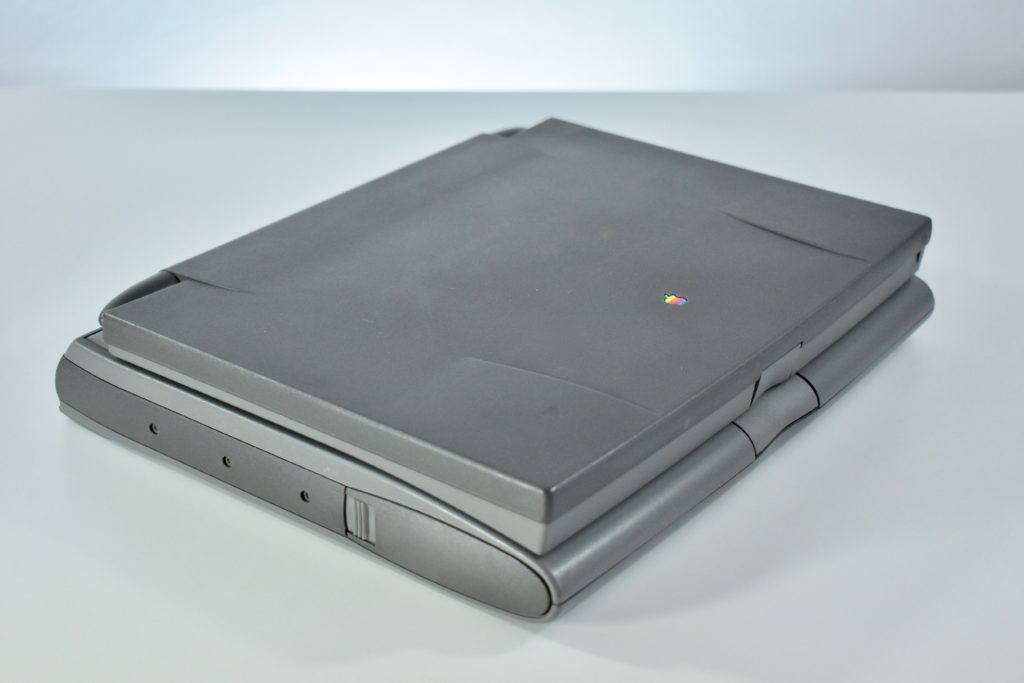
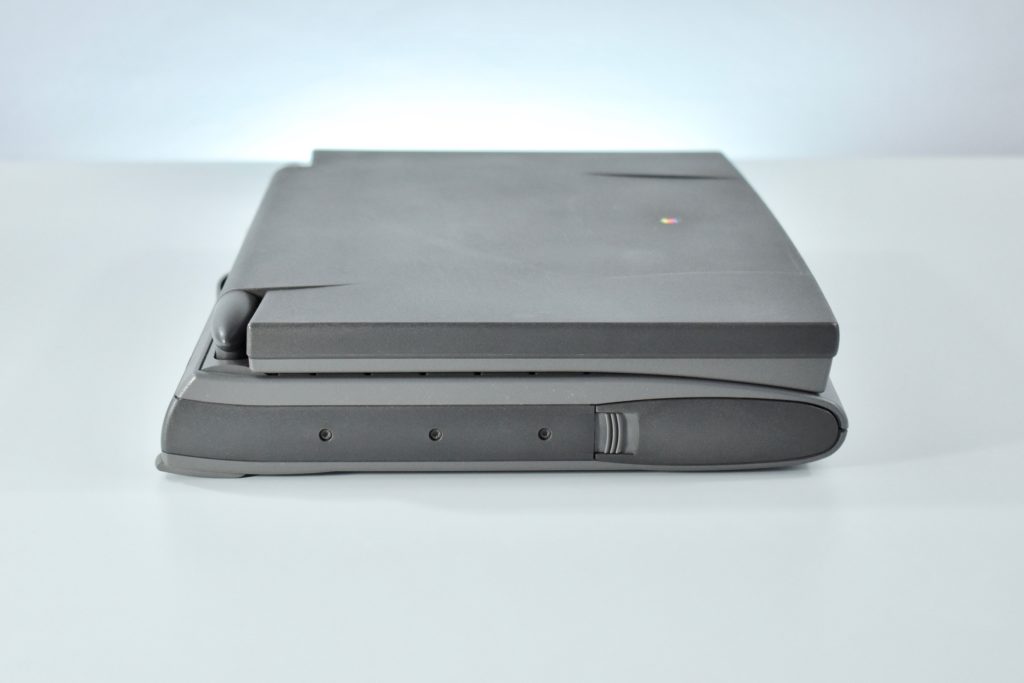
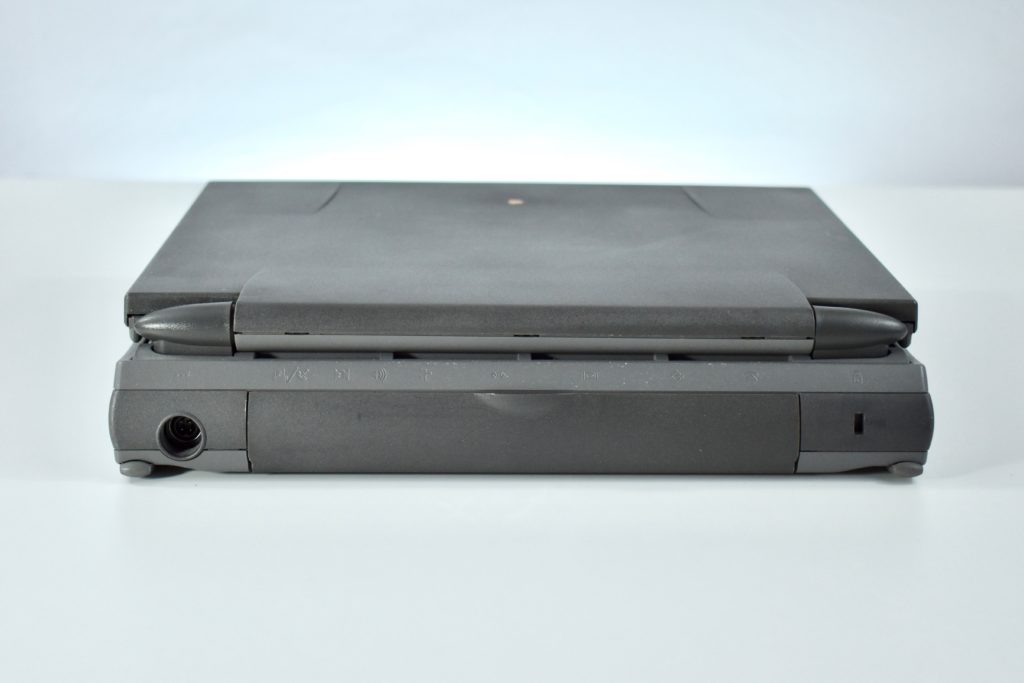
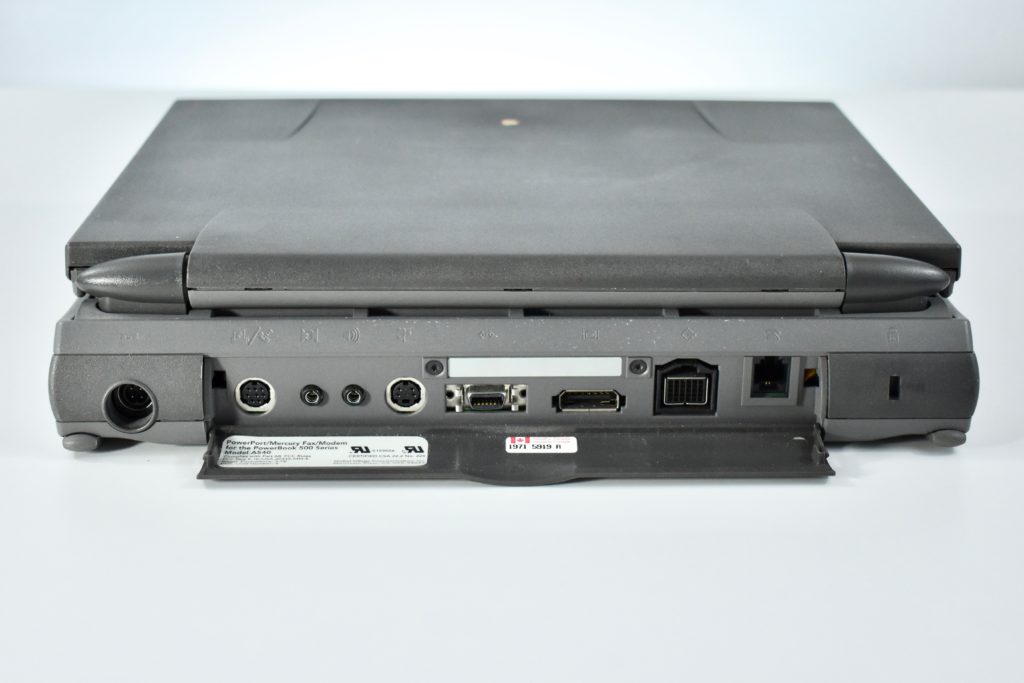
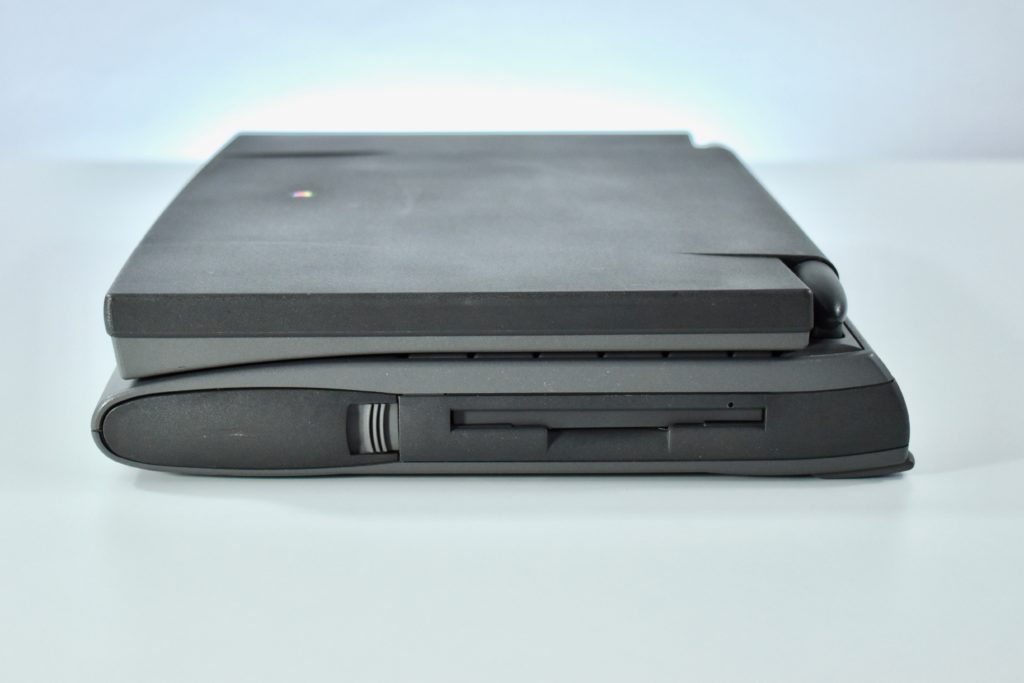
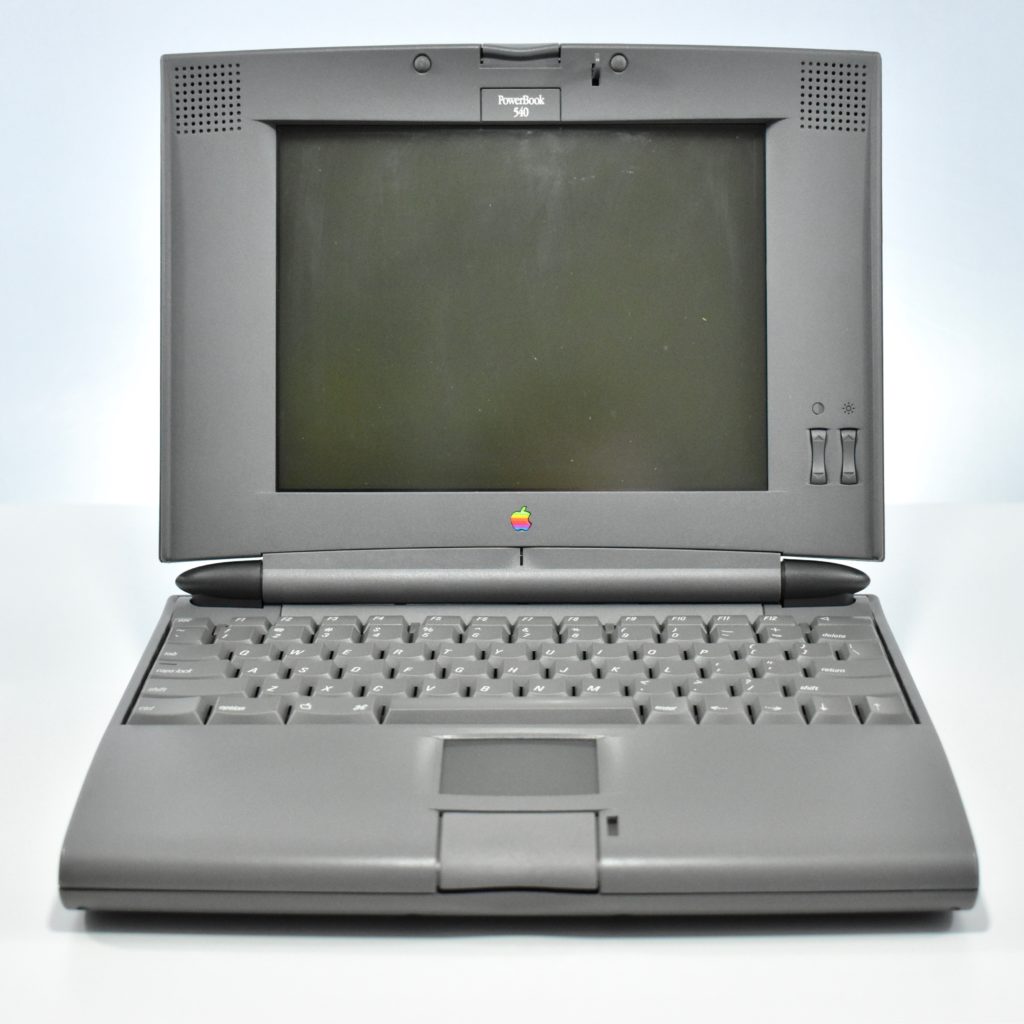
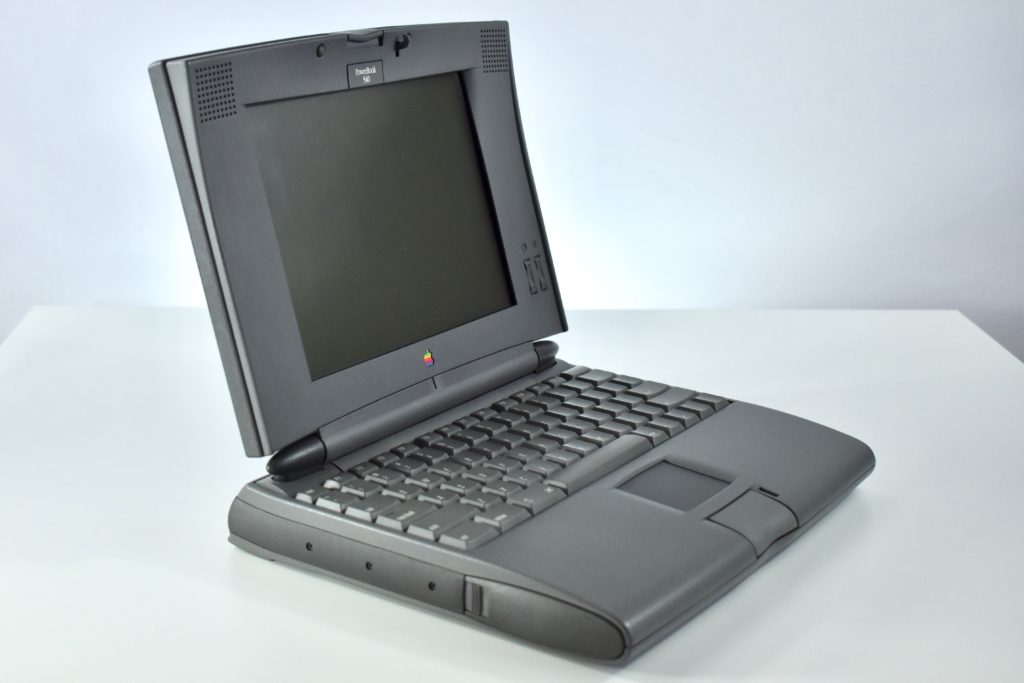
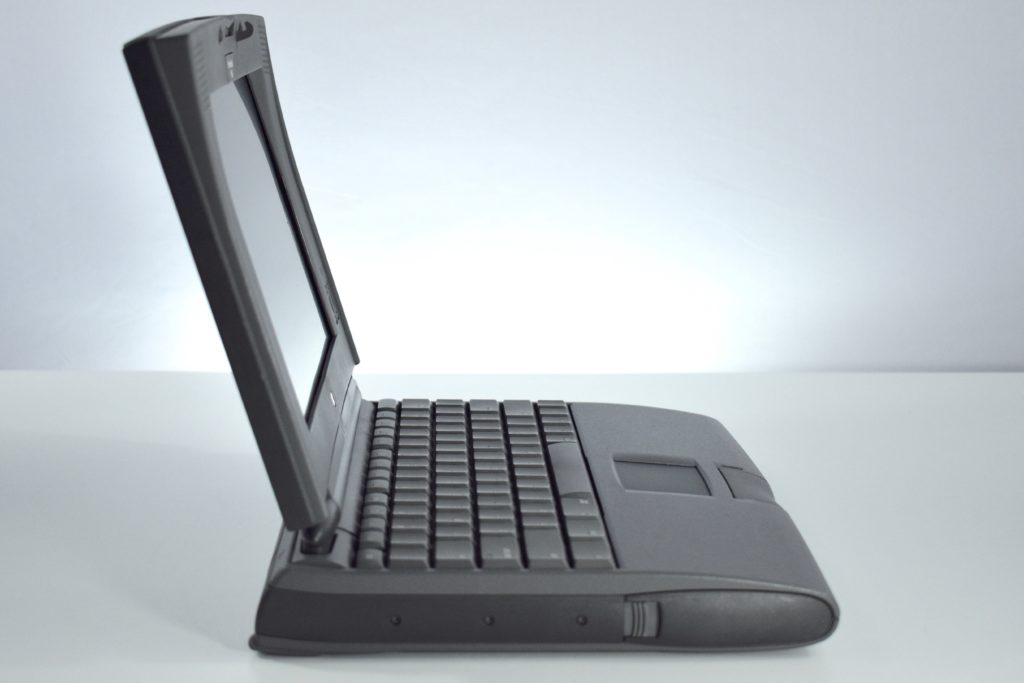
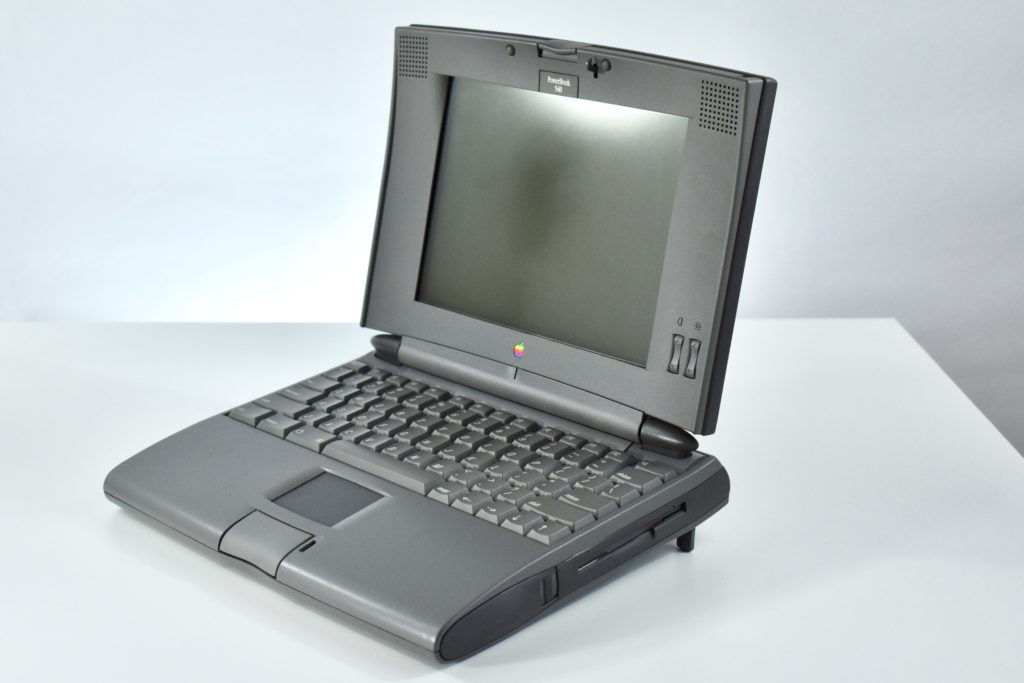
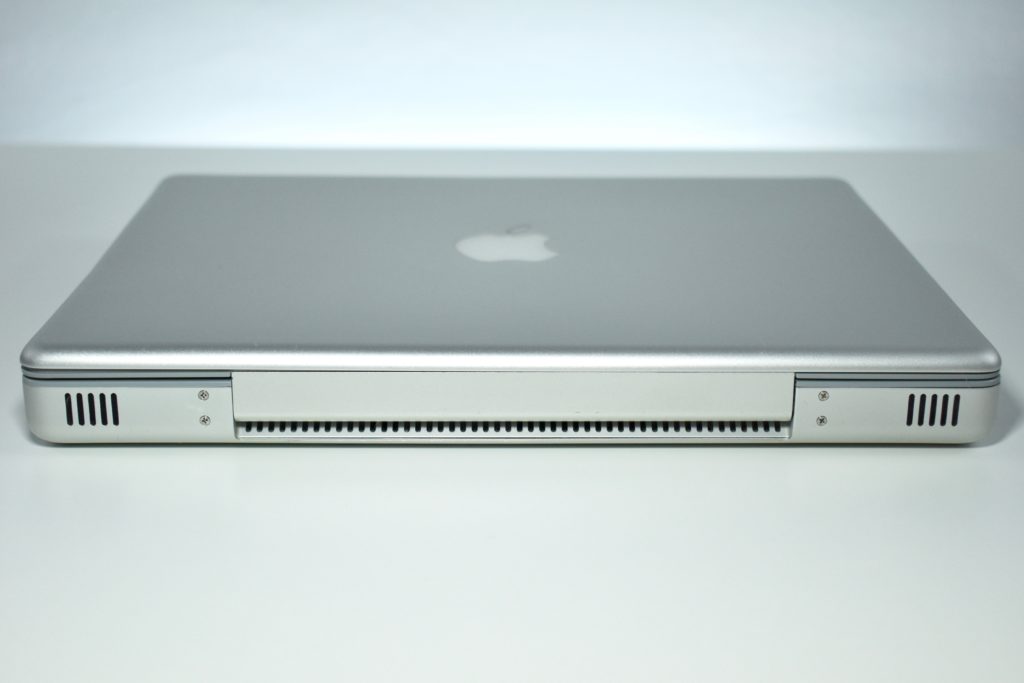
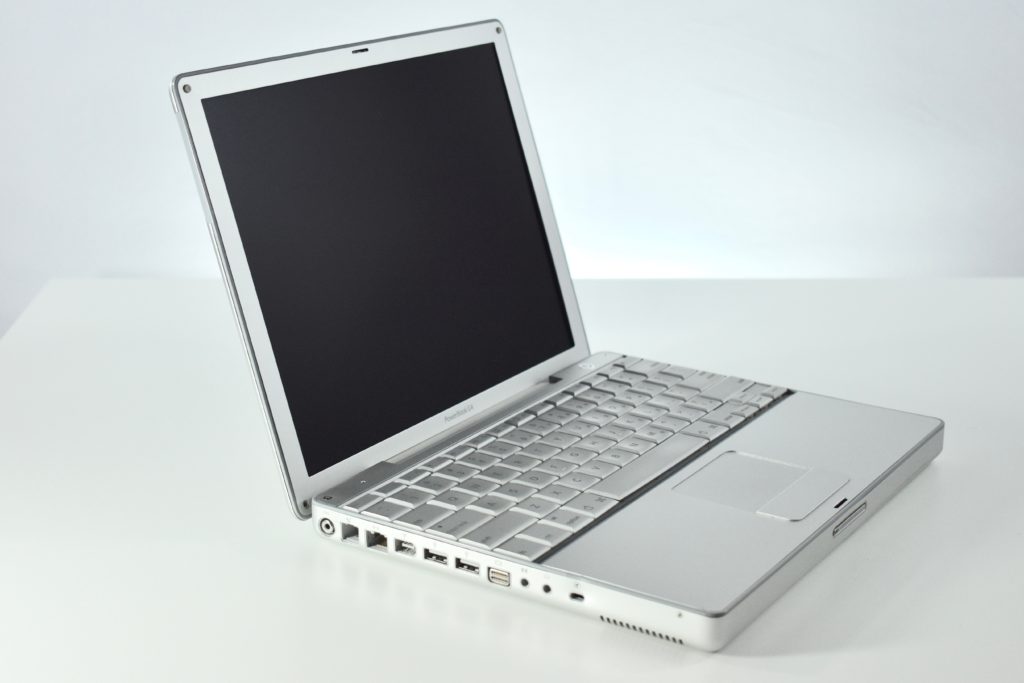
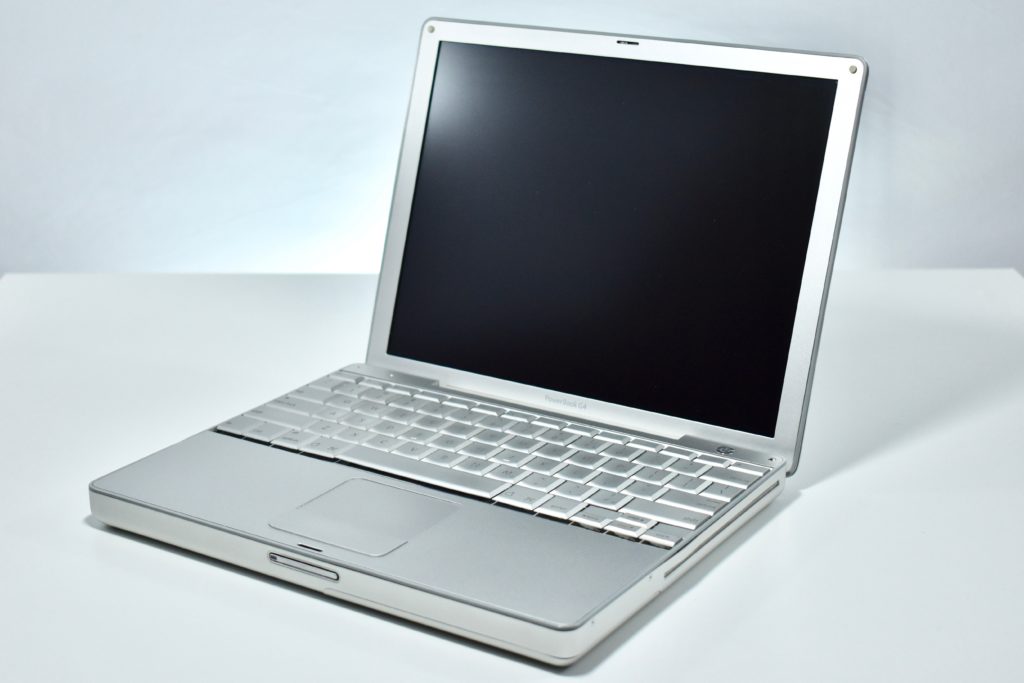
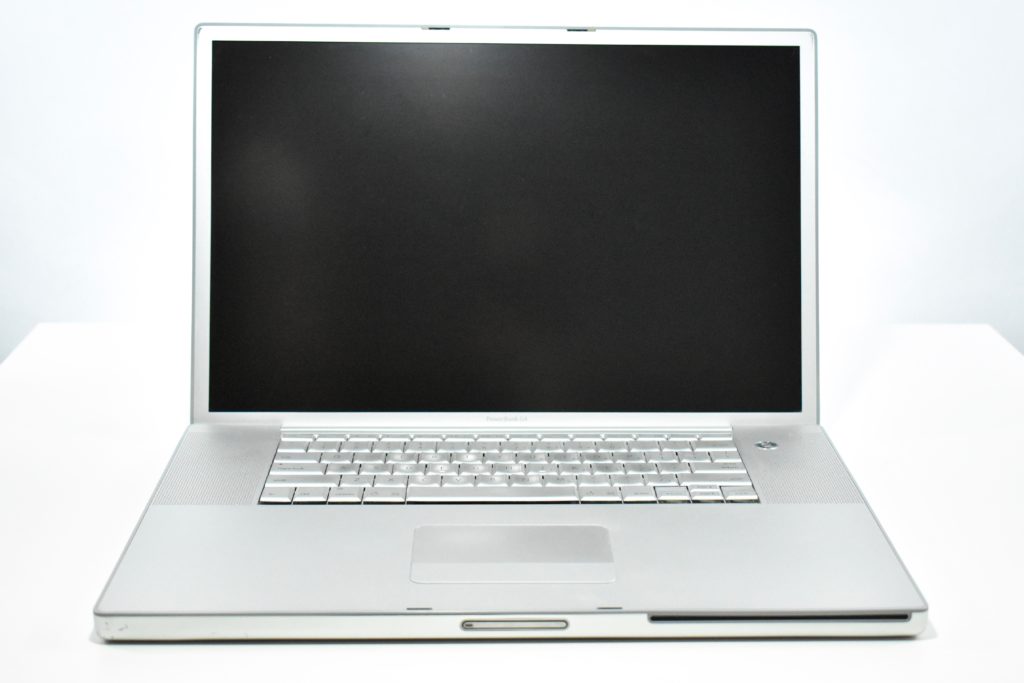
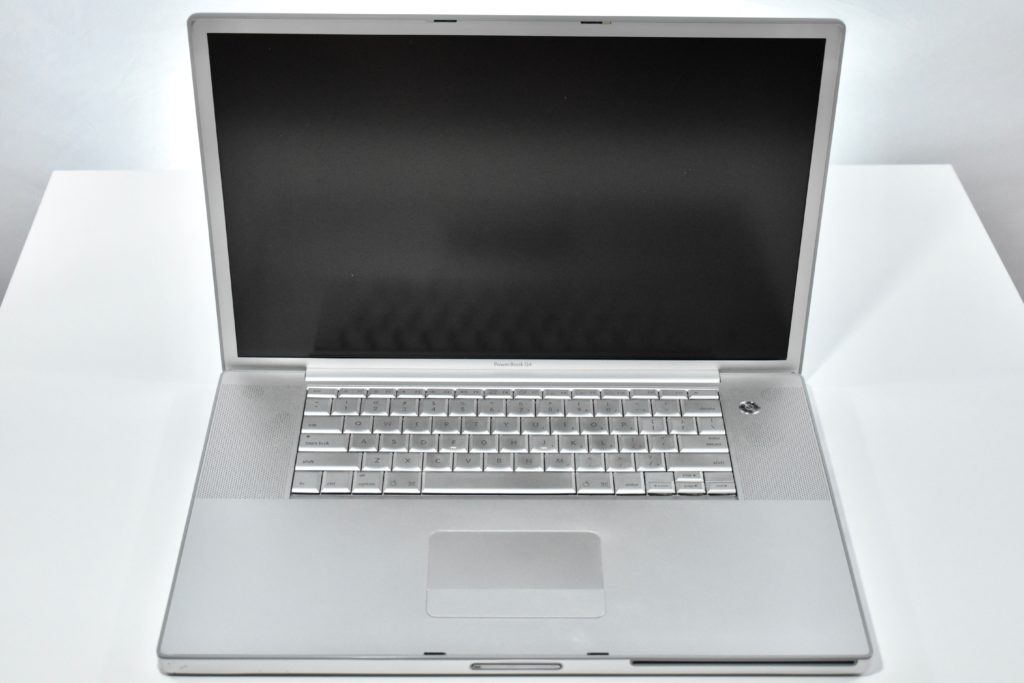
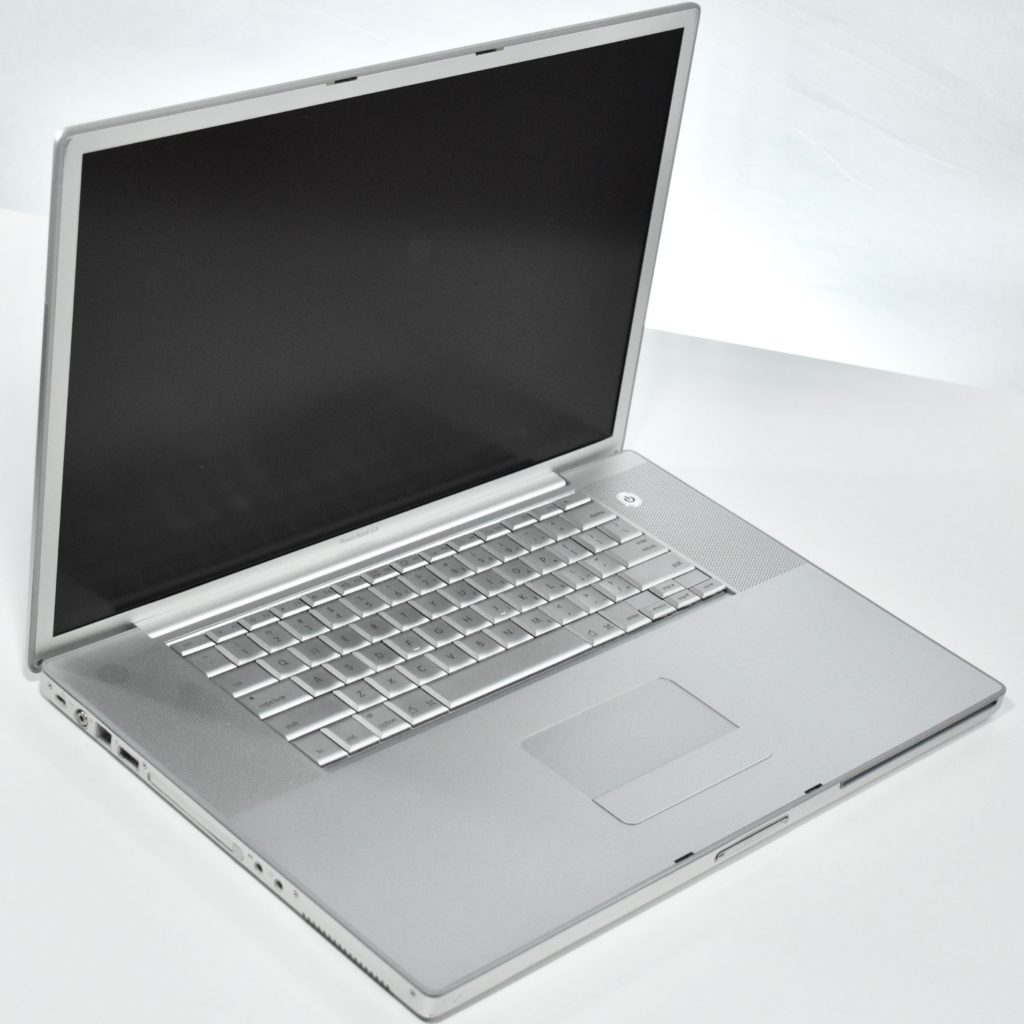
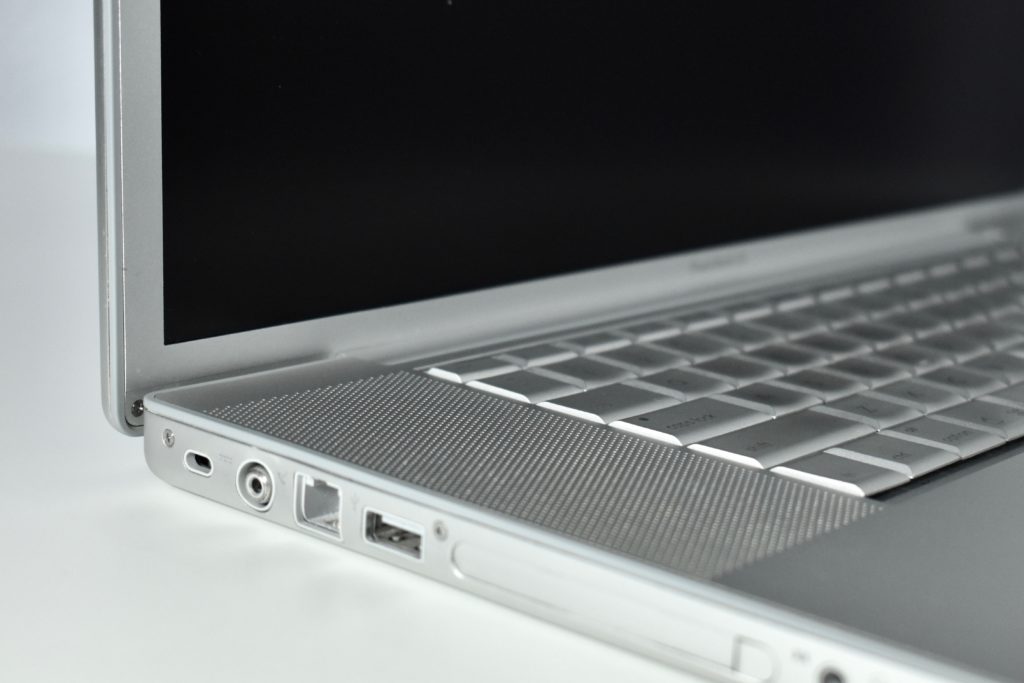
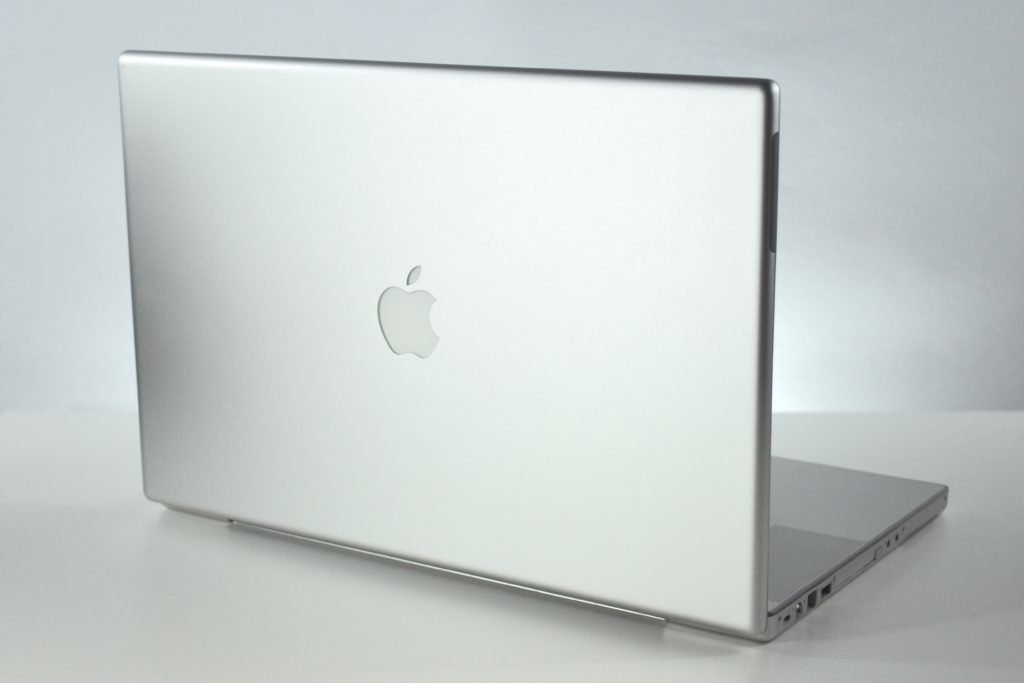
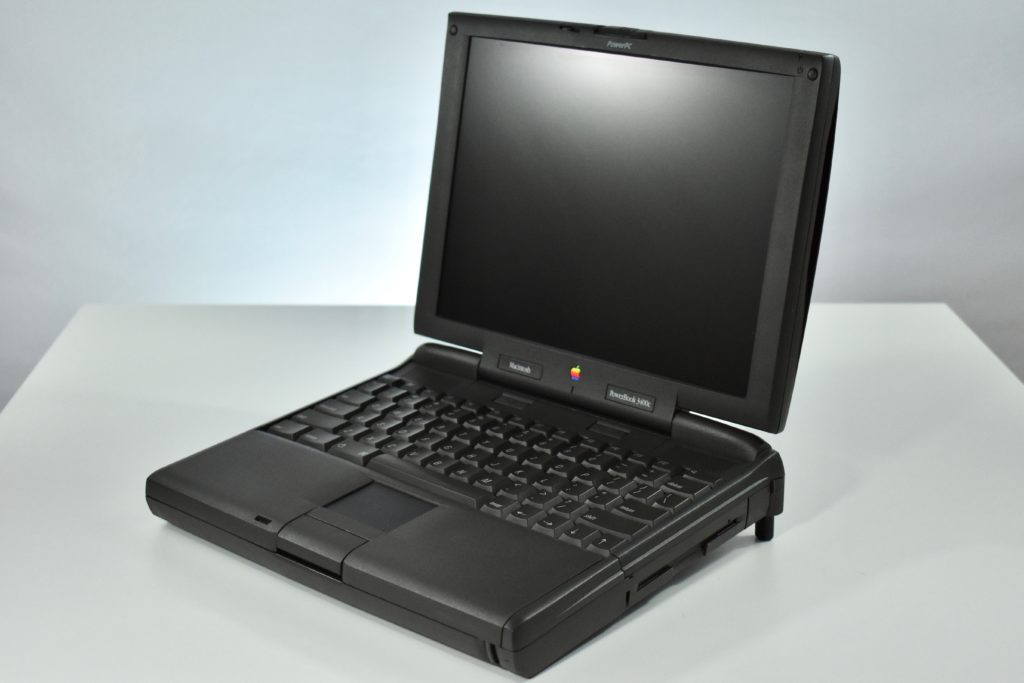
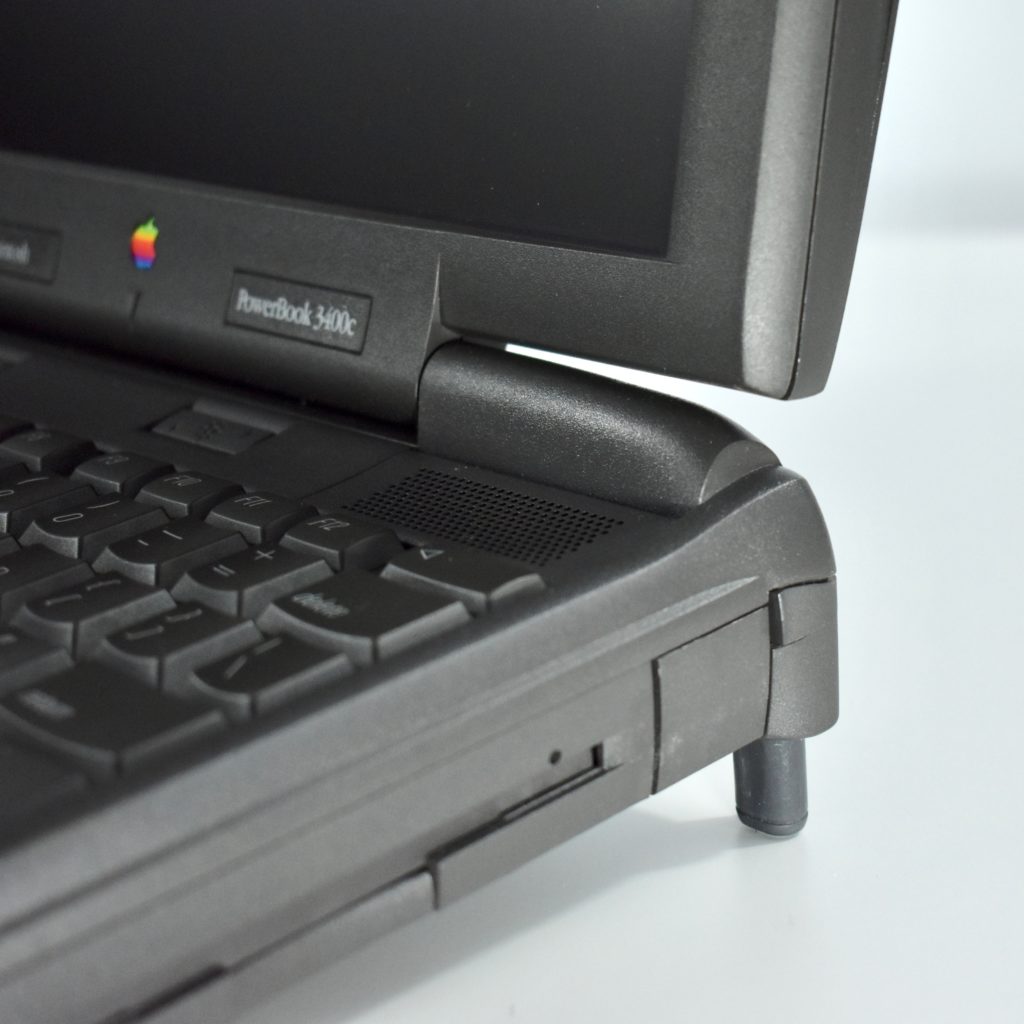
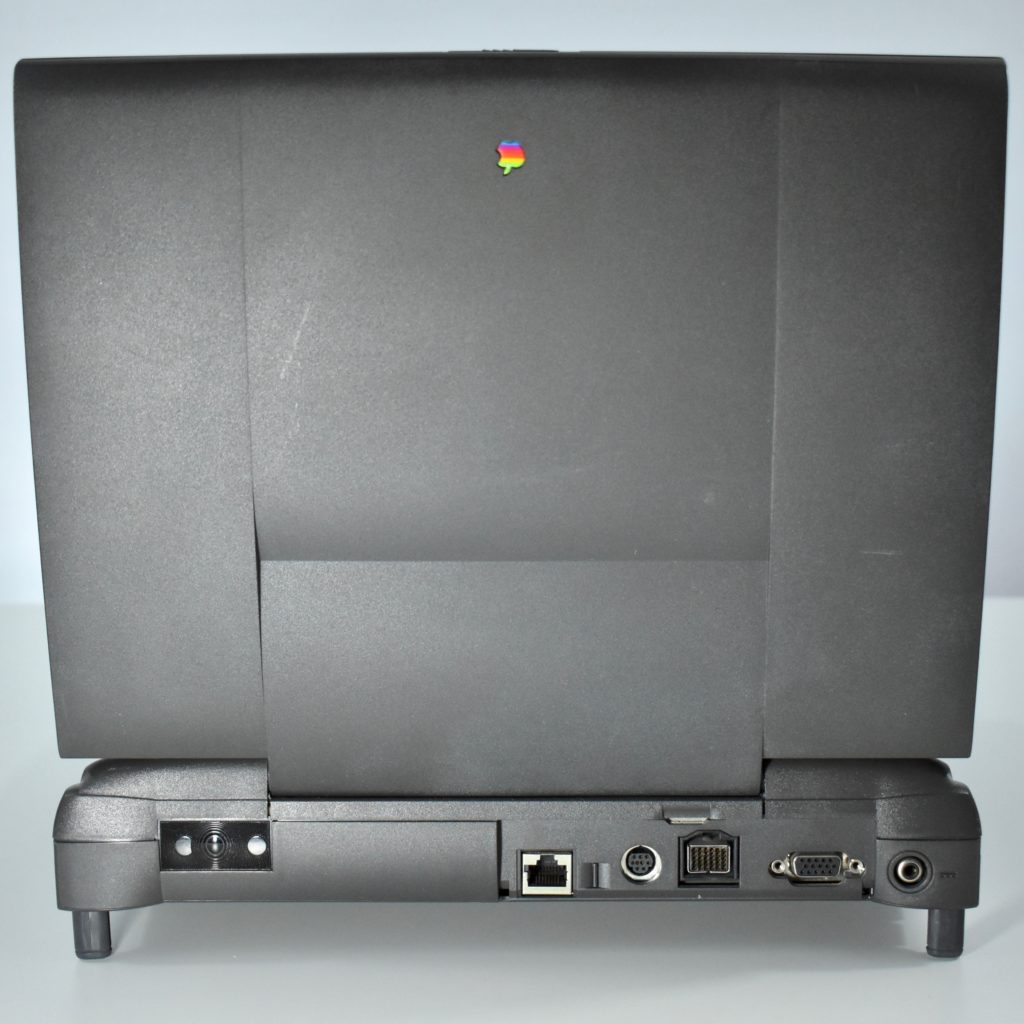
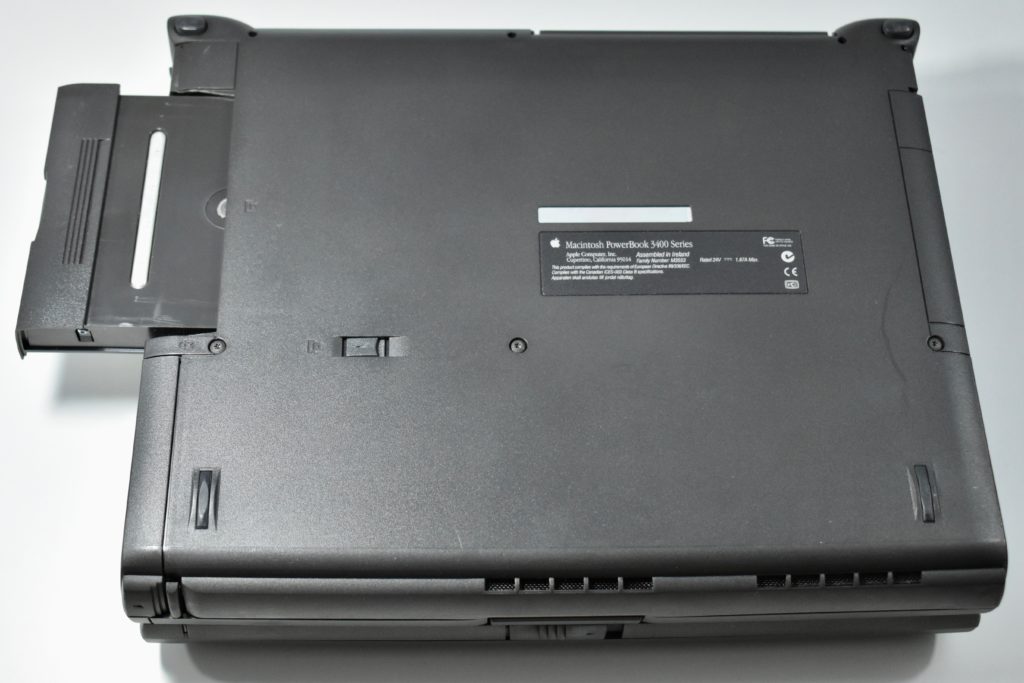
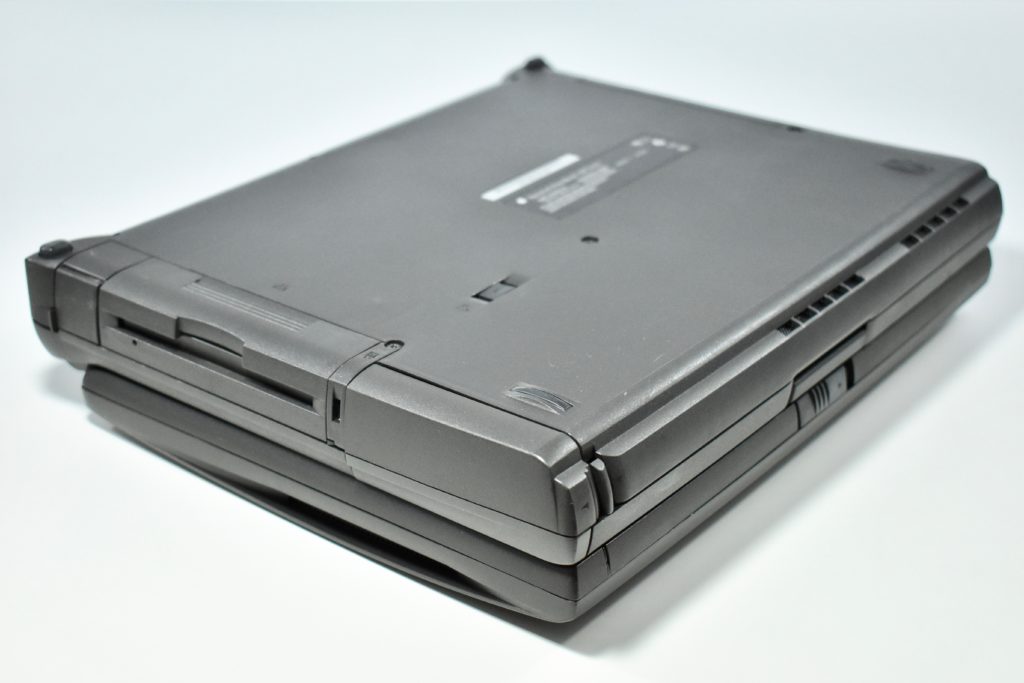
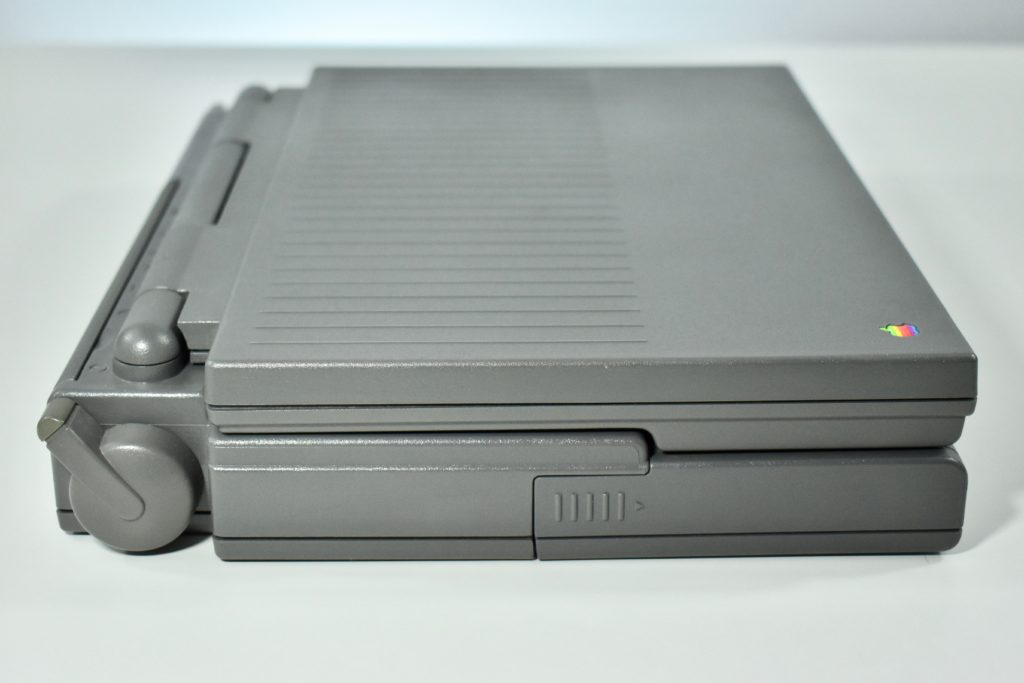
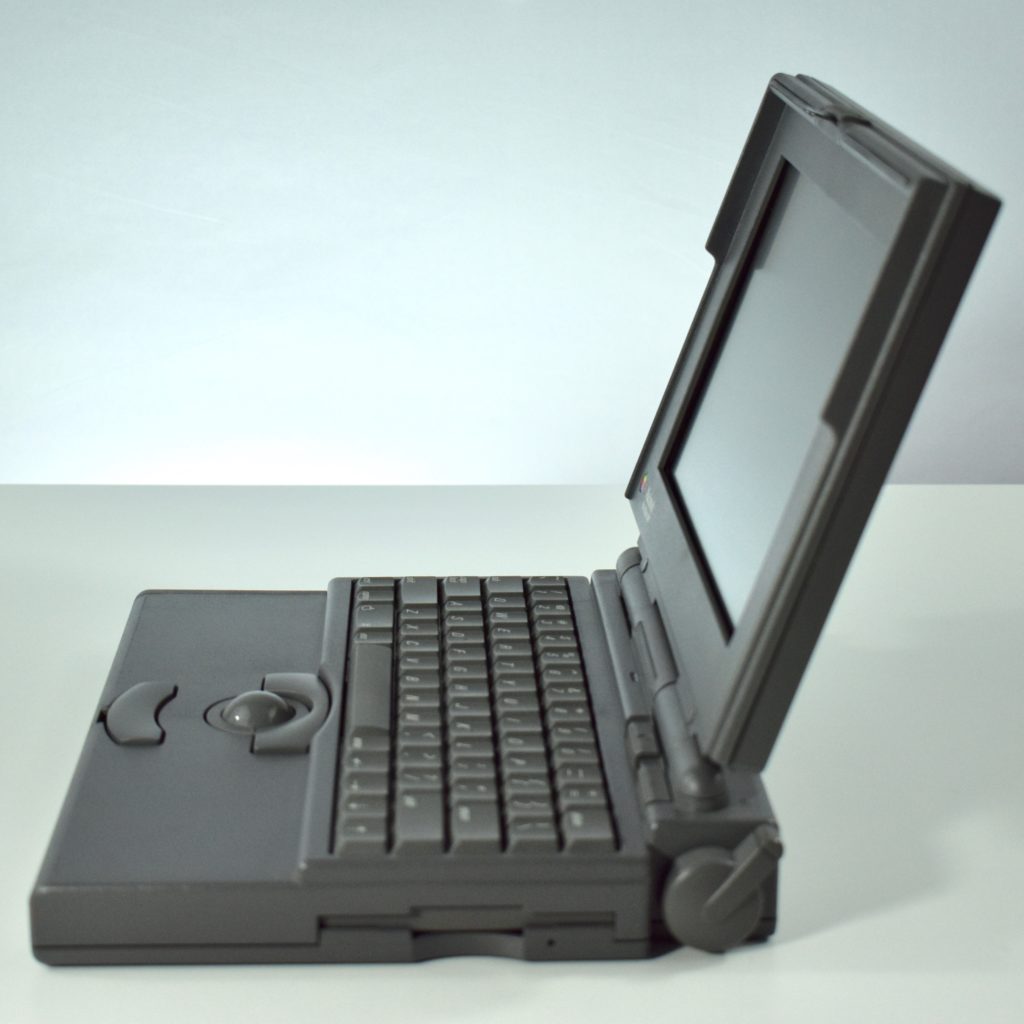
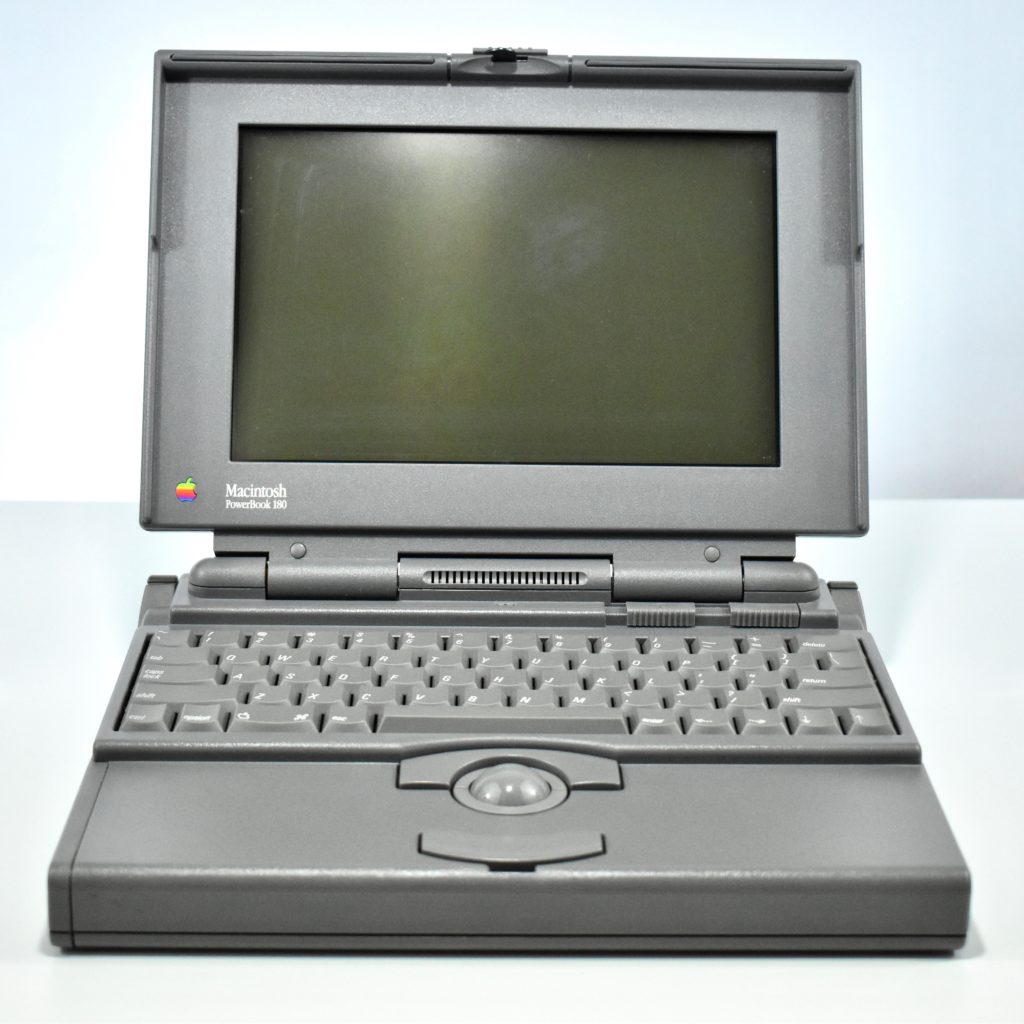
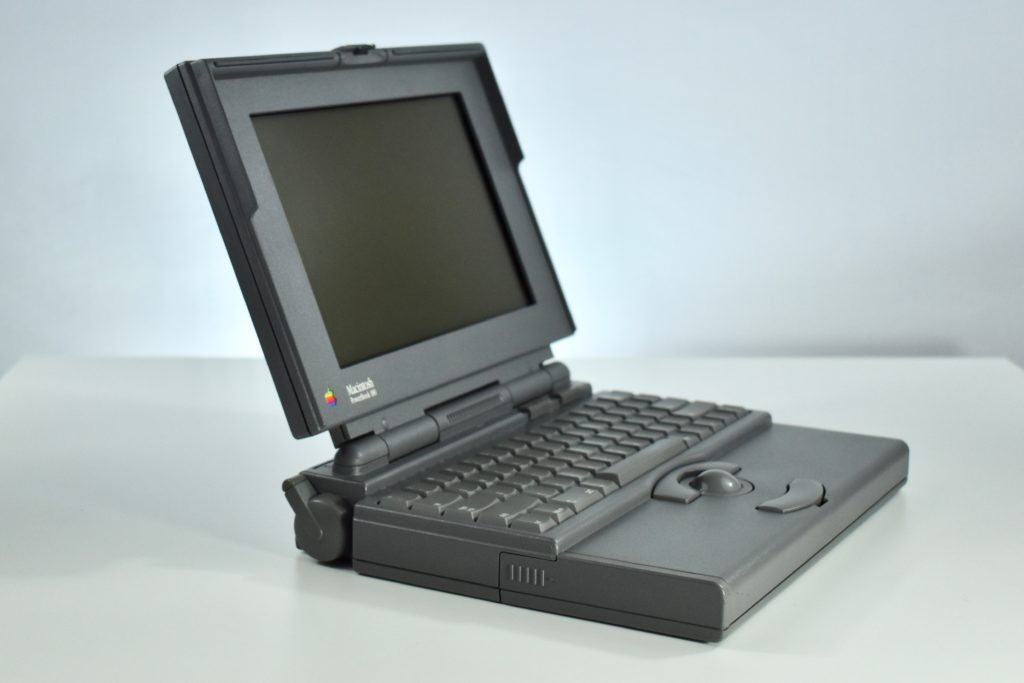
The PowerBook G3 Series was Apple’s second PowerBook G3 line. The different PowerBook G3 Series models used internal codenames and this laptop was referred to as “PDQ” (Pretty Darn Quick).
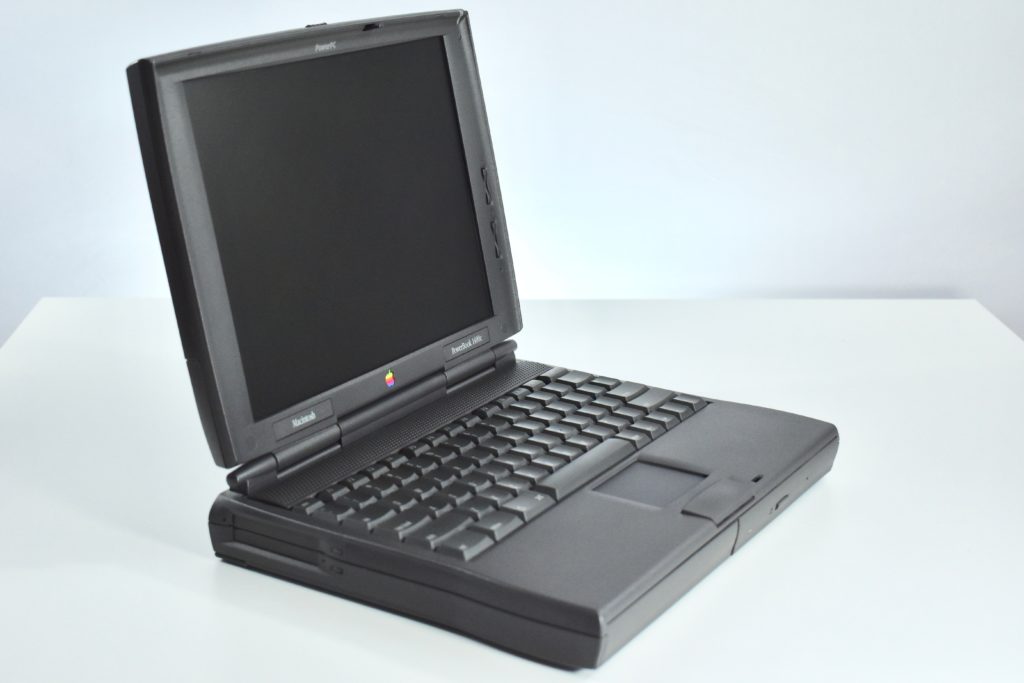
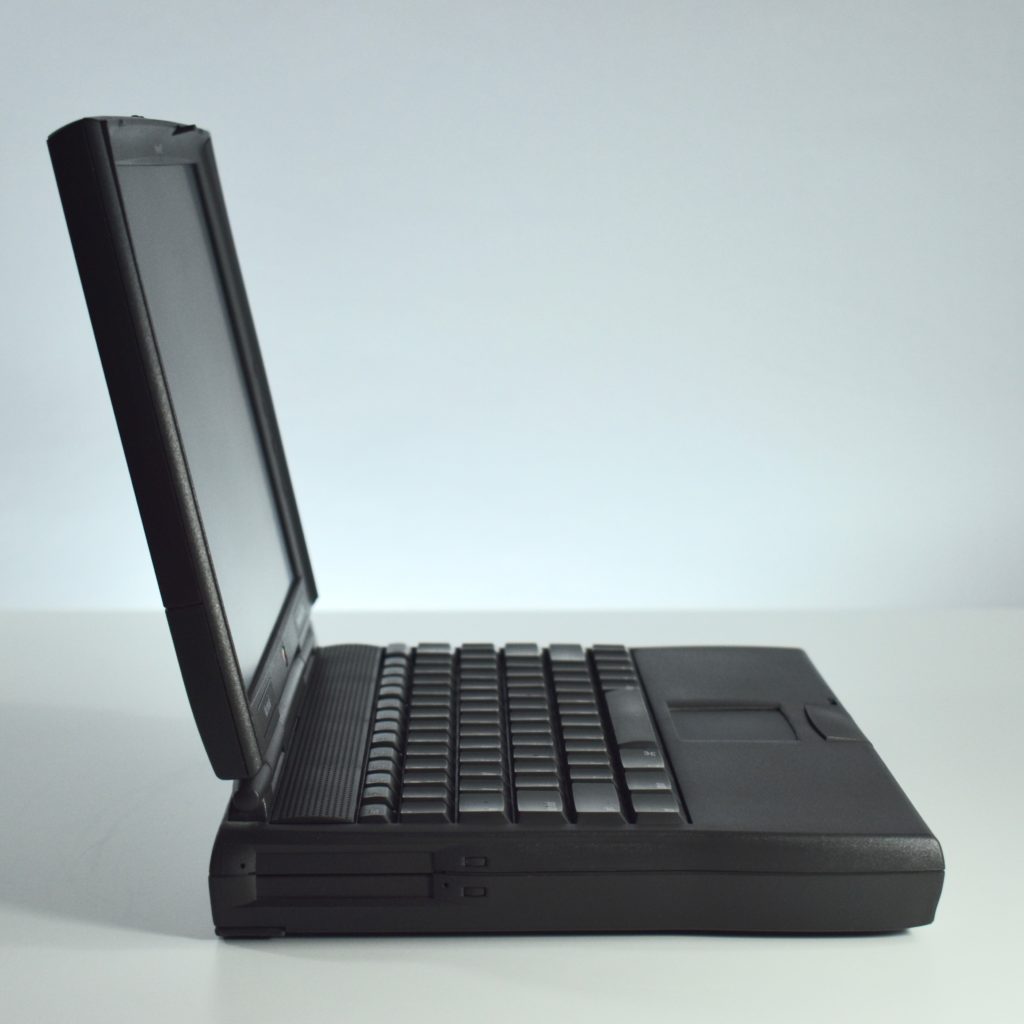
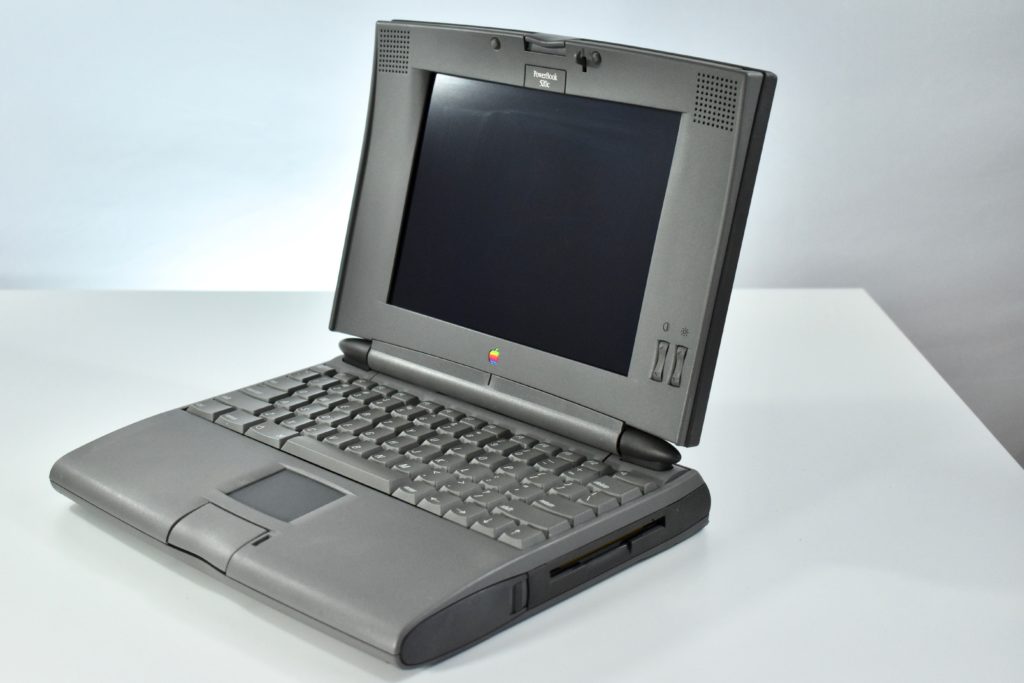
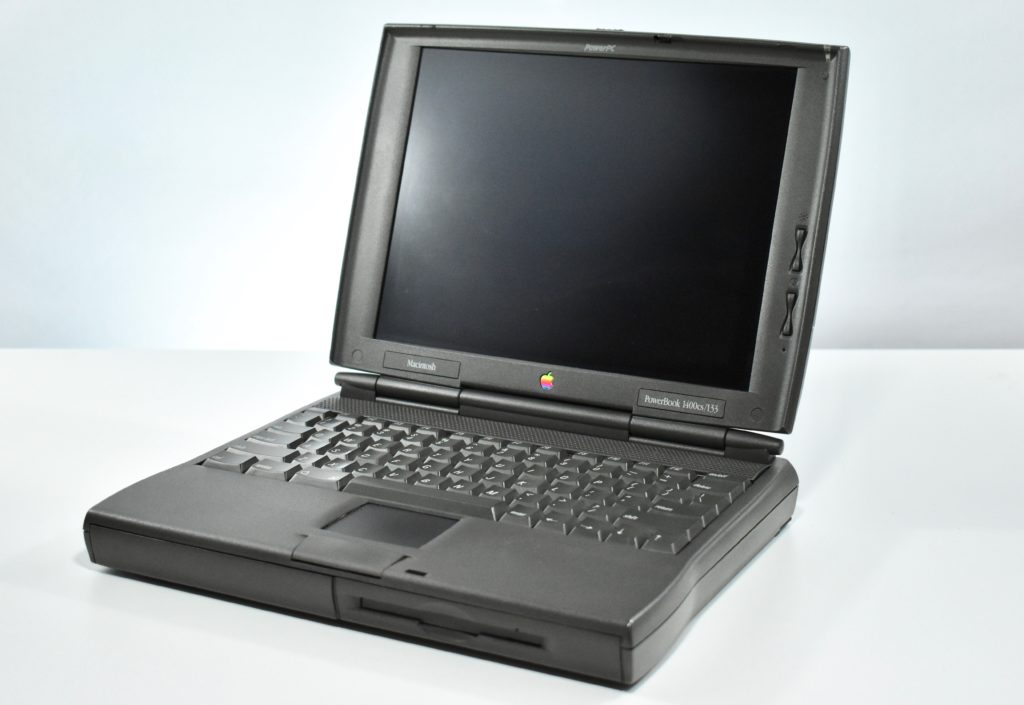
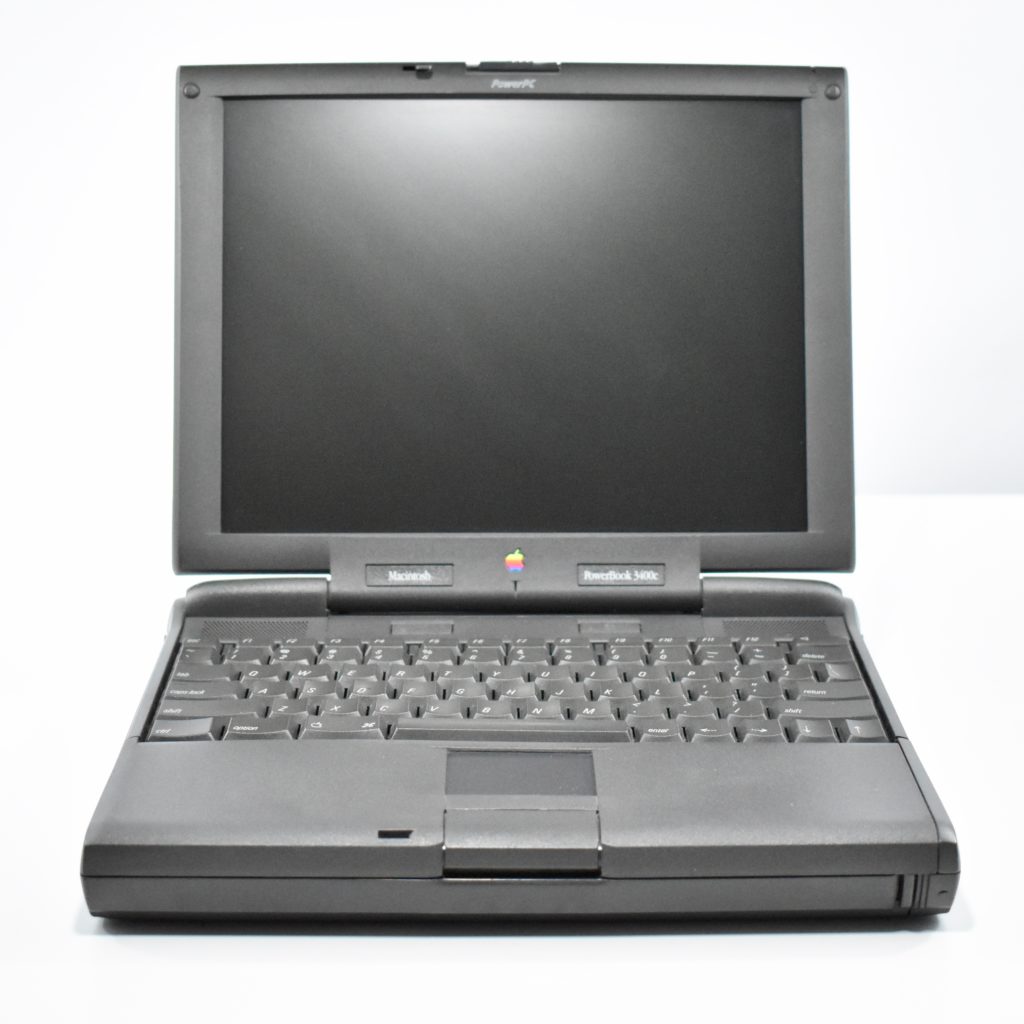
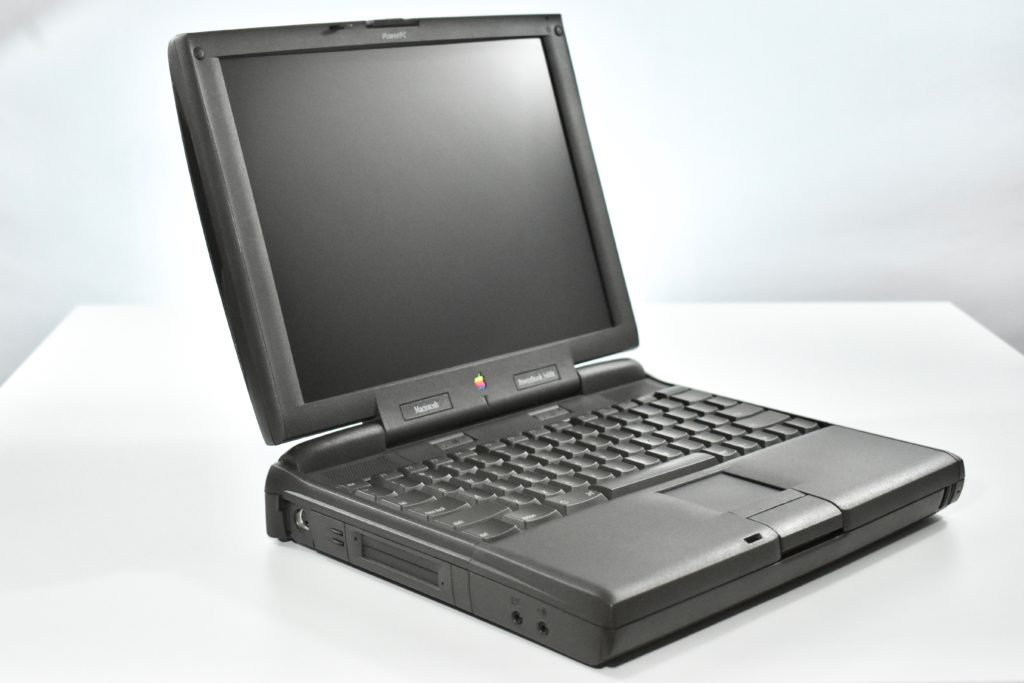
The PowerBook G3/233 (“PDQ,” Late 1998) featured a 233 MHz PowerPC 750 (G3) processor, 32 MB of RAM, 4 MB of SGRAM for video, a 2.0 GB hard drive, and a 20X tray-loading CD-ROM drive. The screen was a 14.1-inch TFT active-matrix color display.
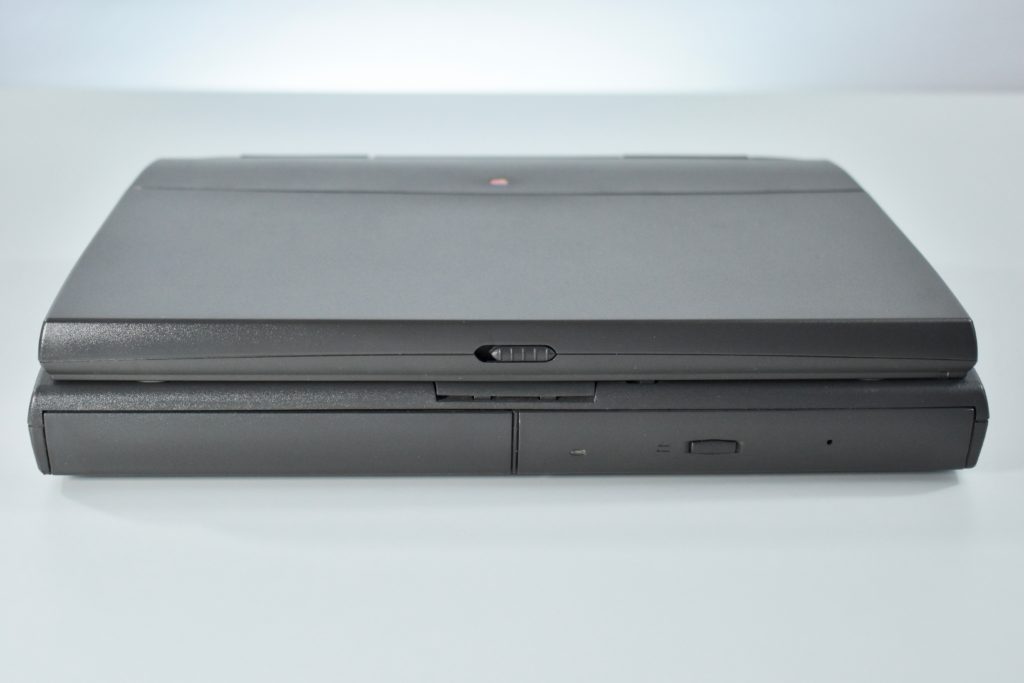
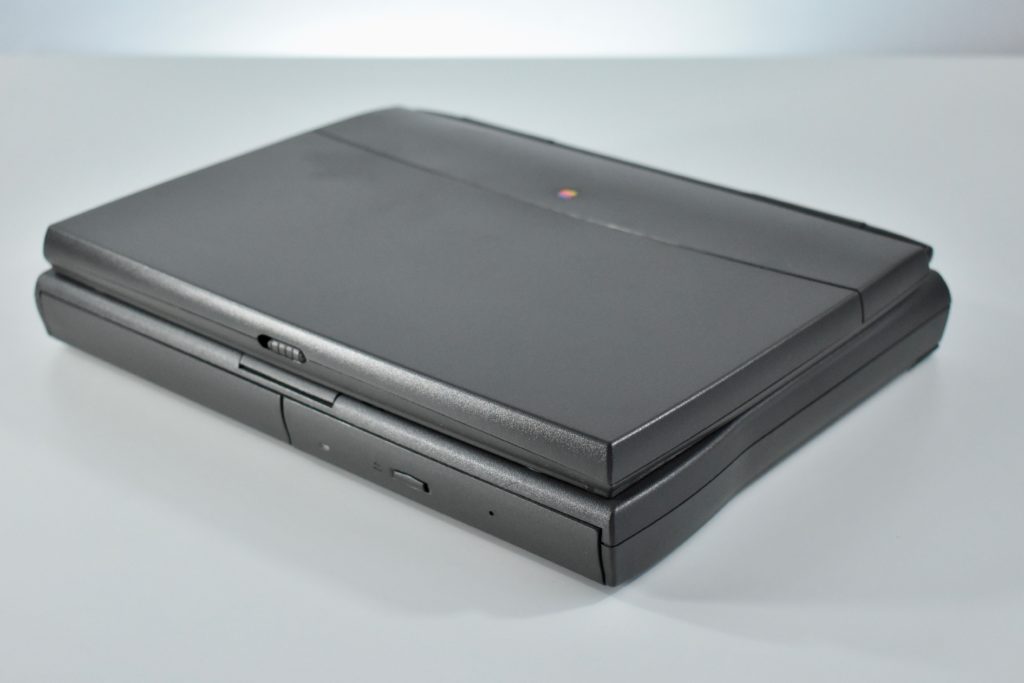
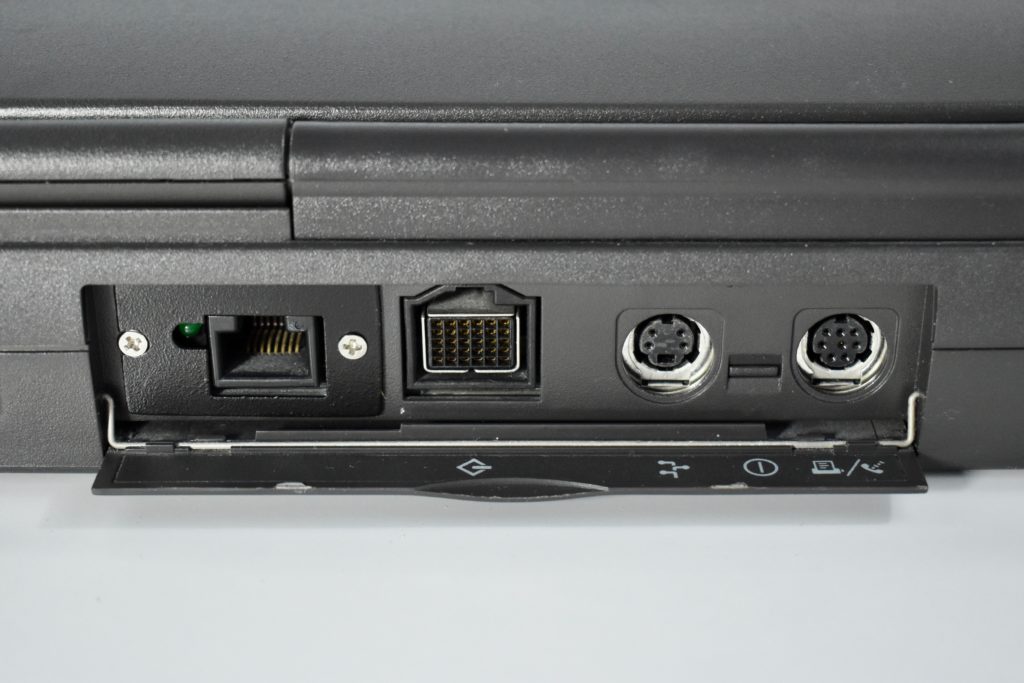
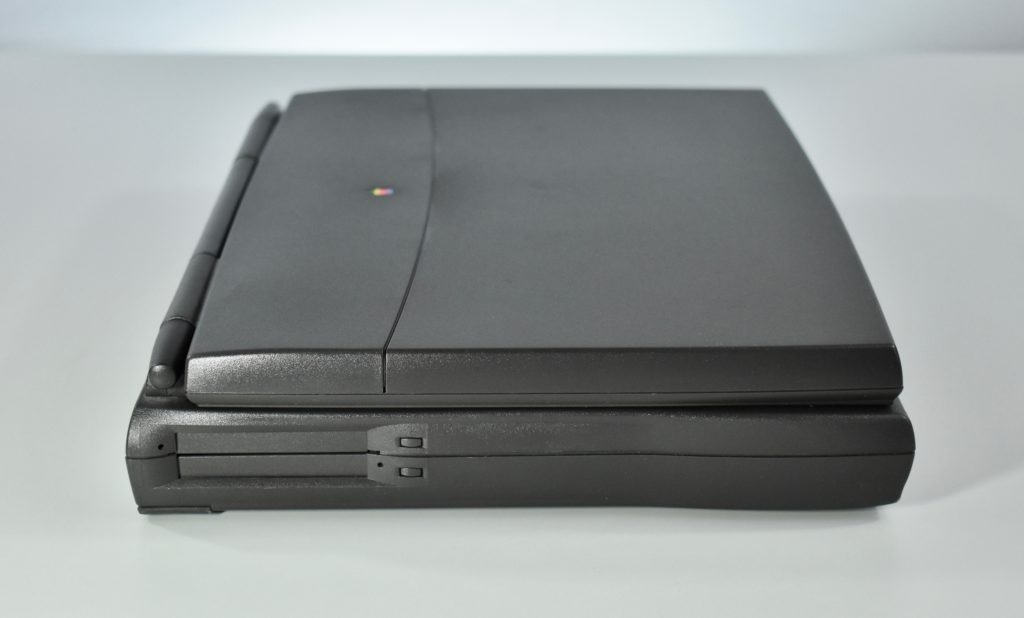
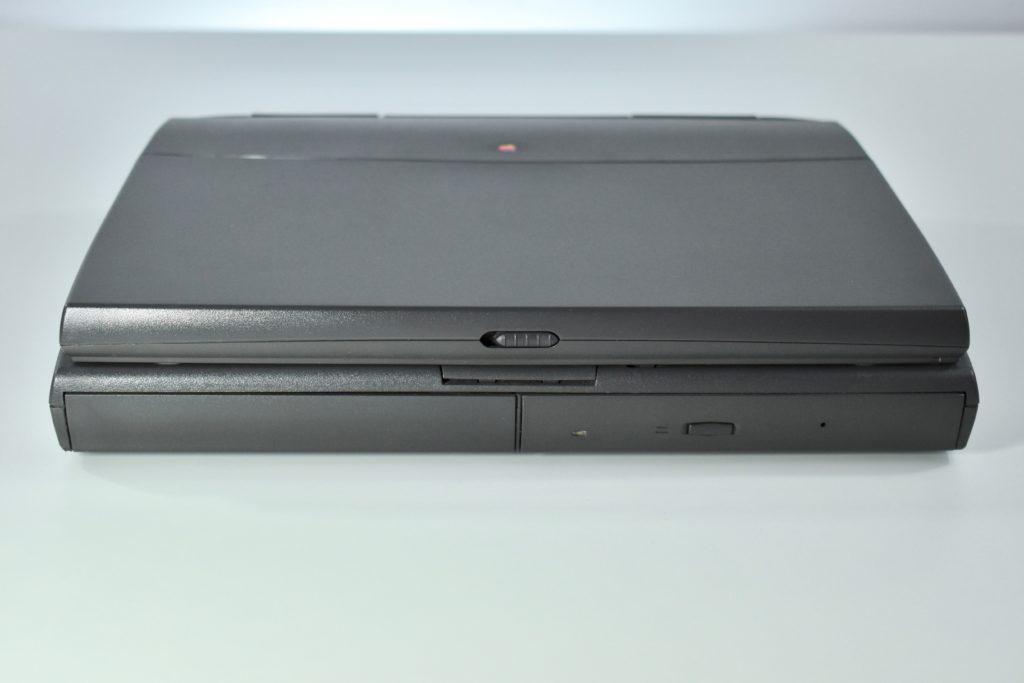
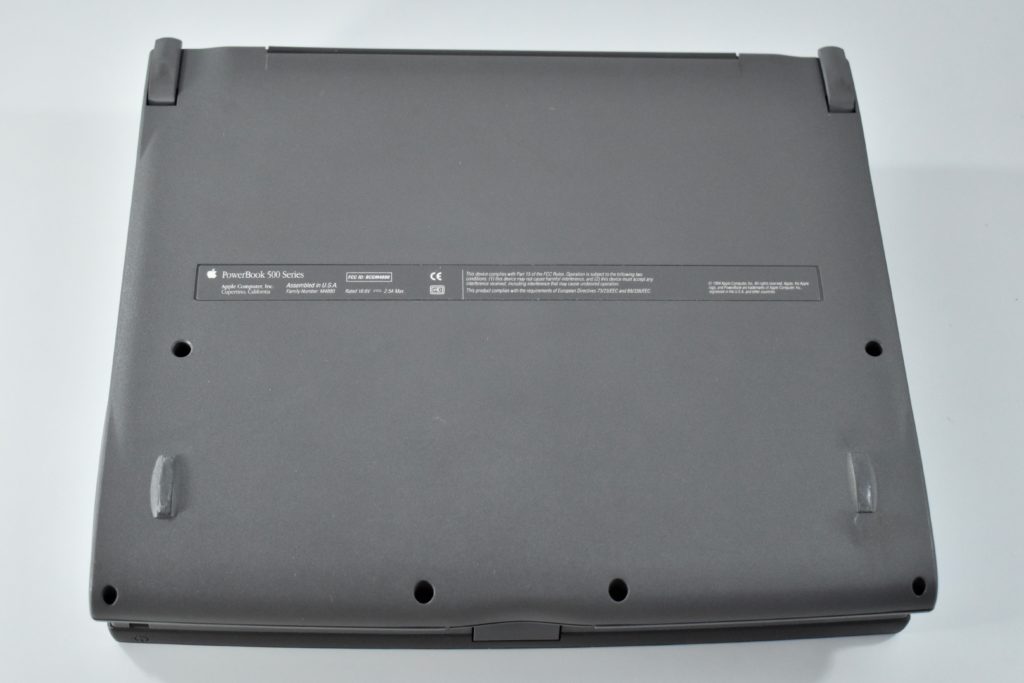
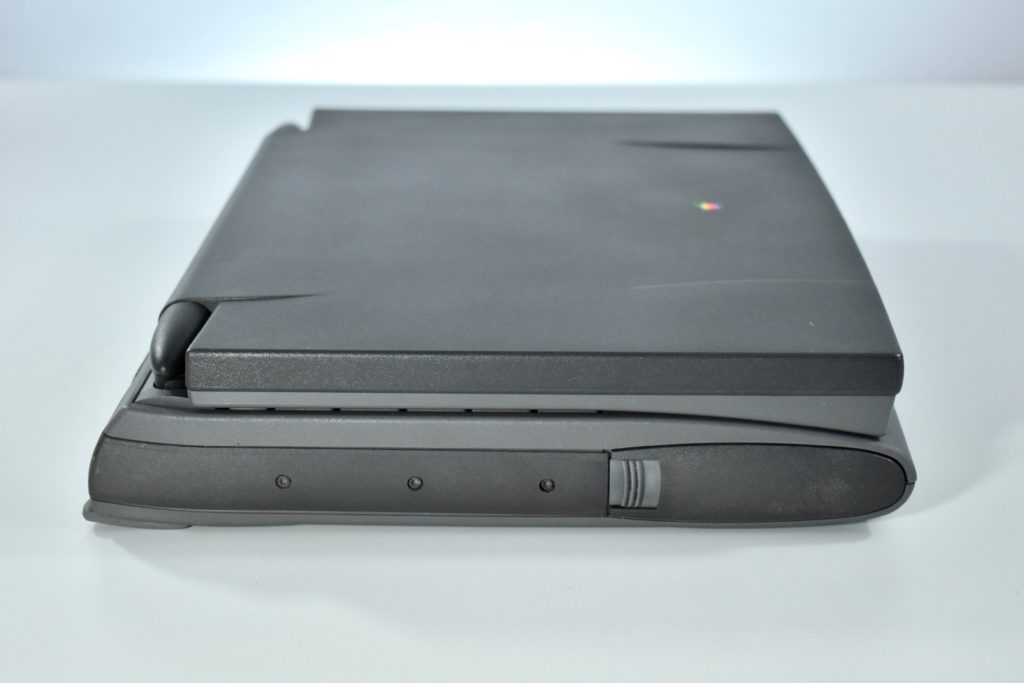
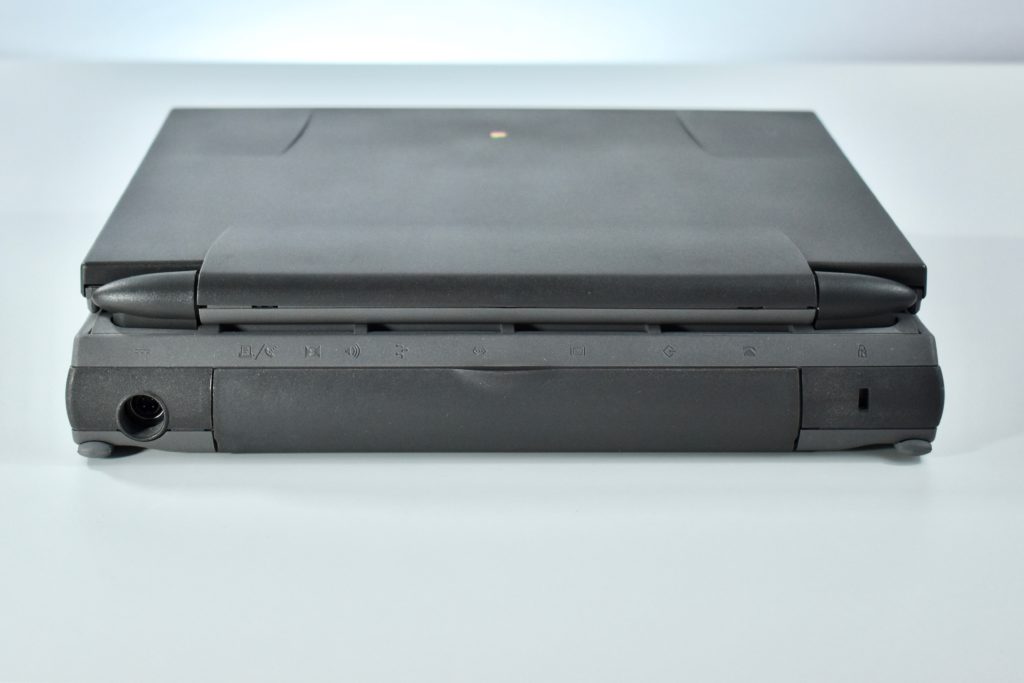
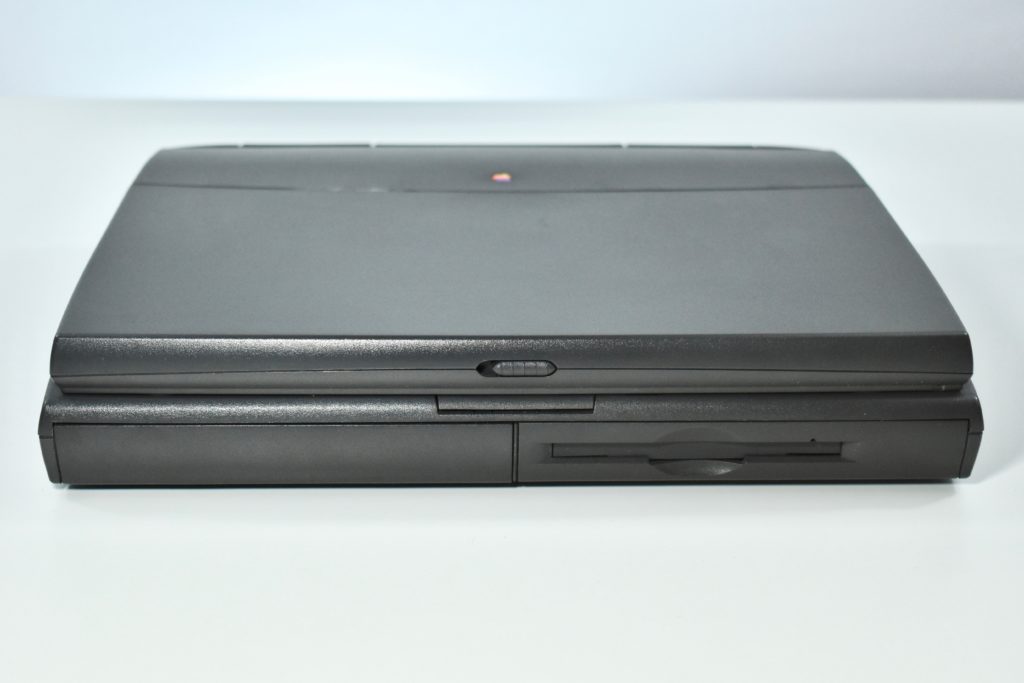
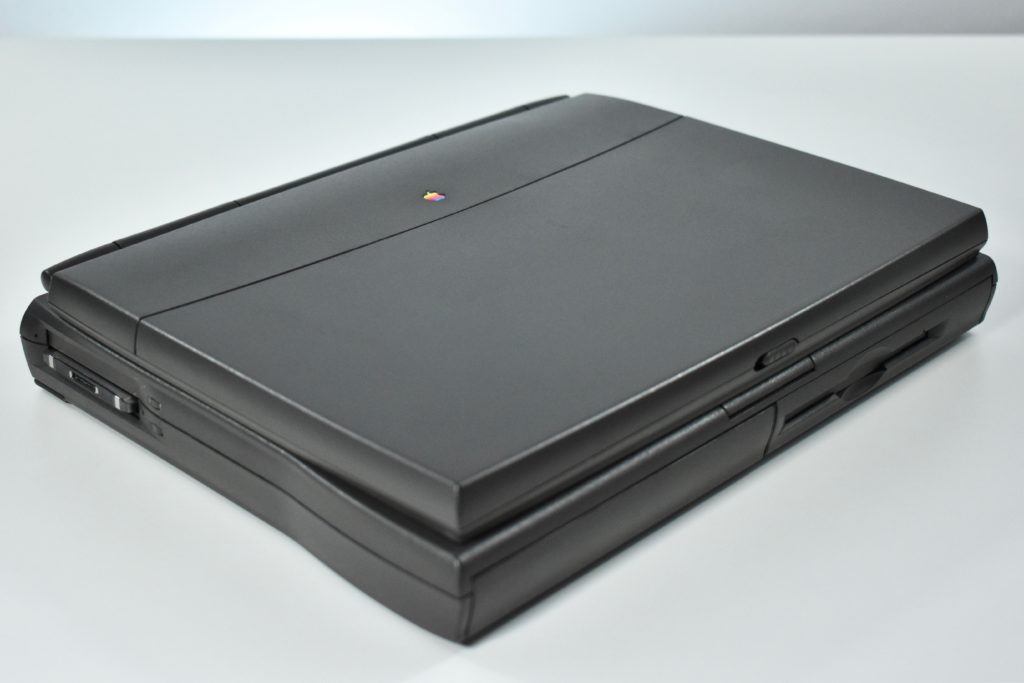
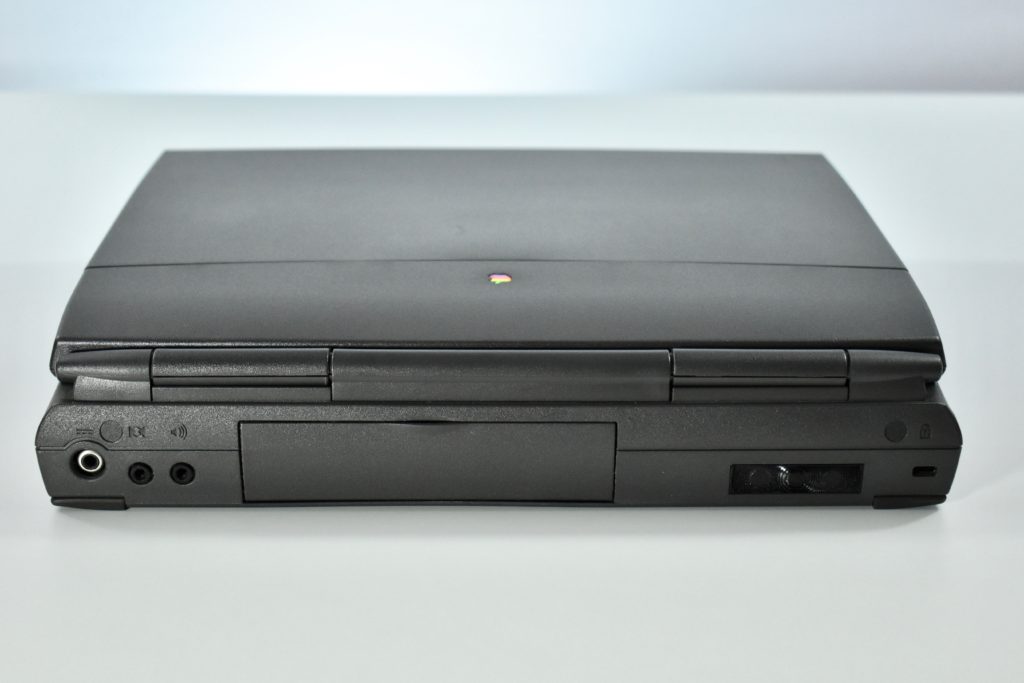
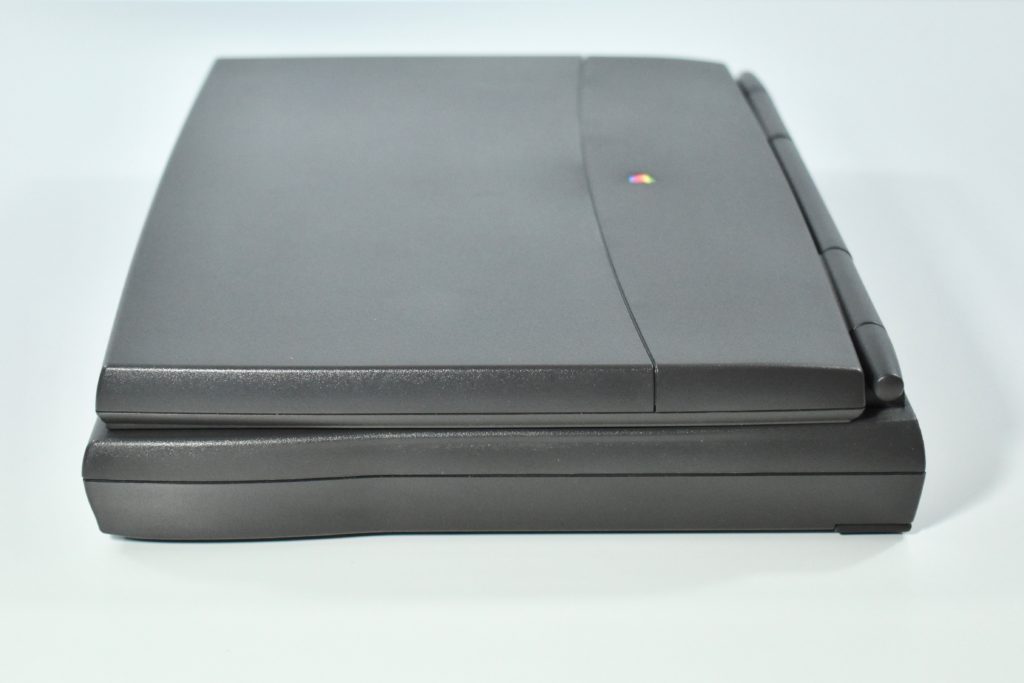
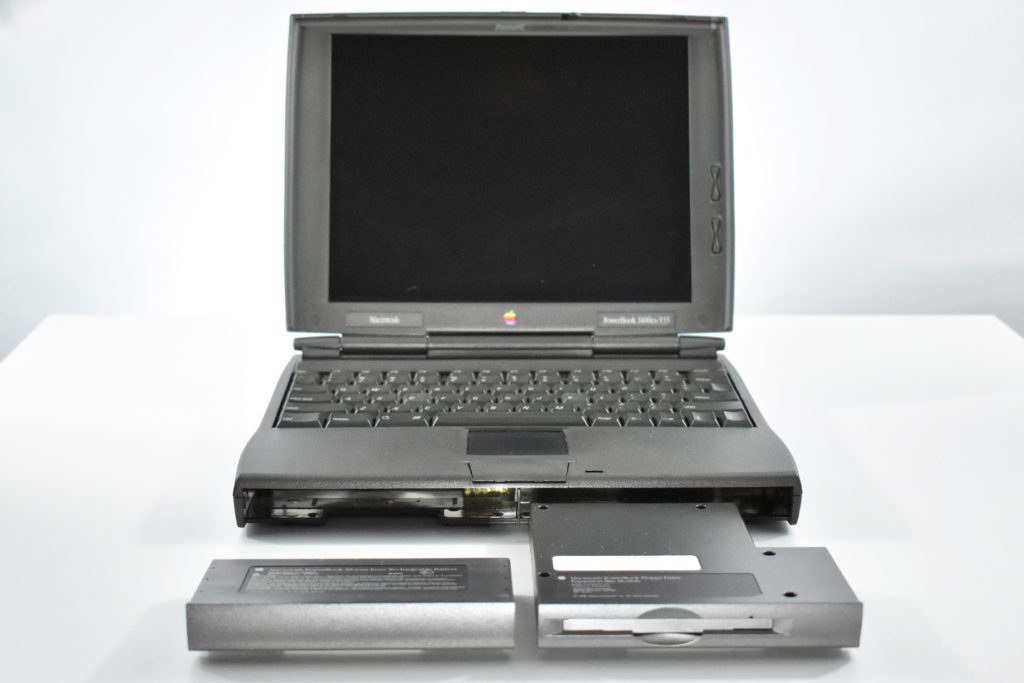
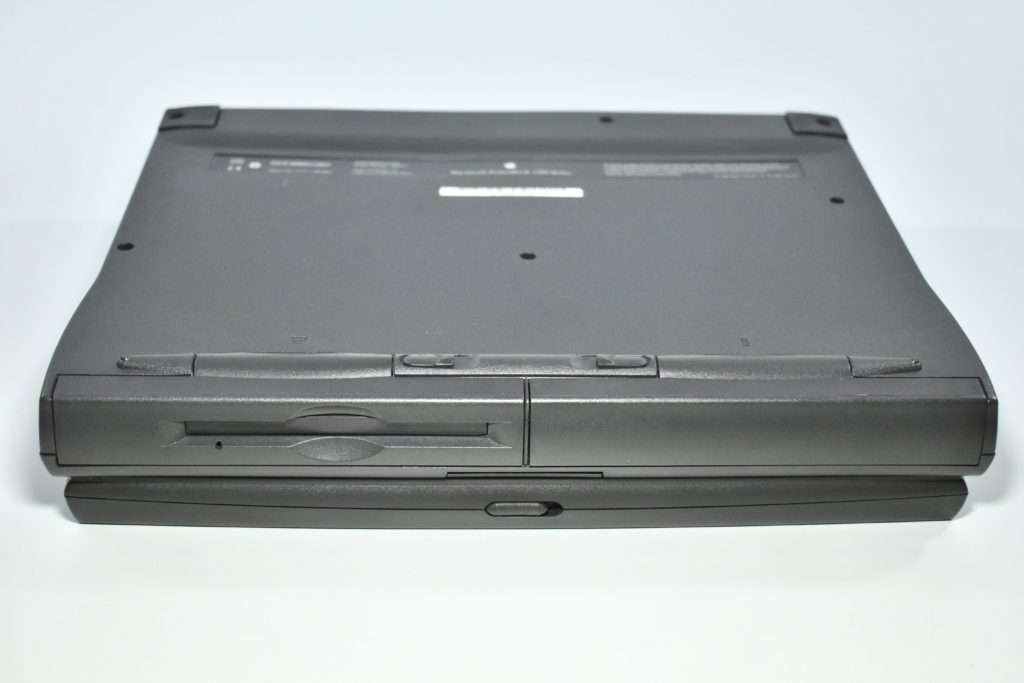
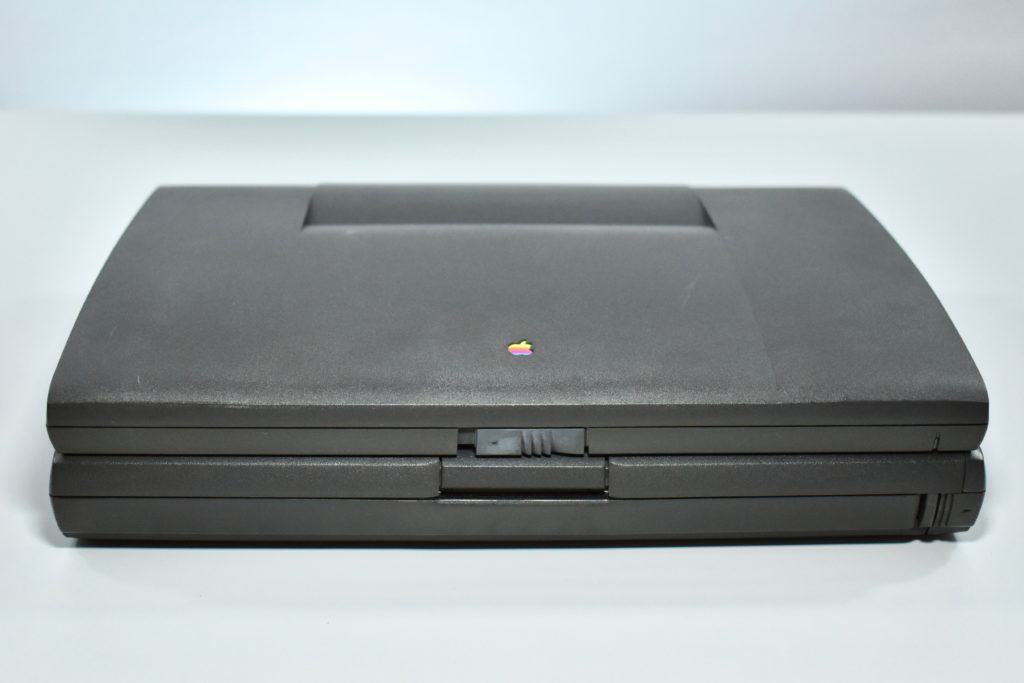
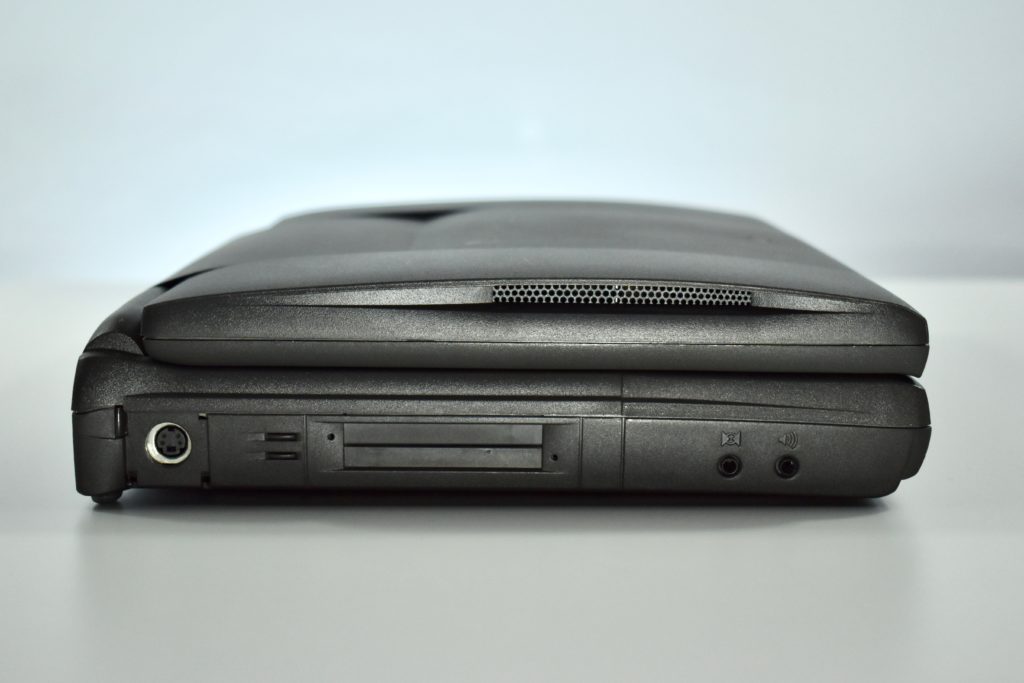
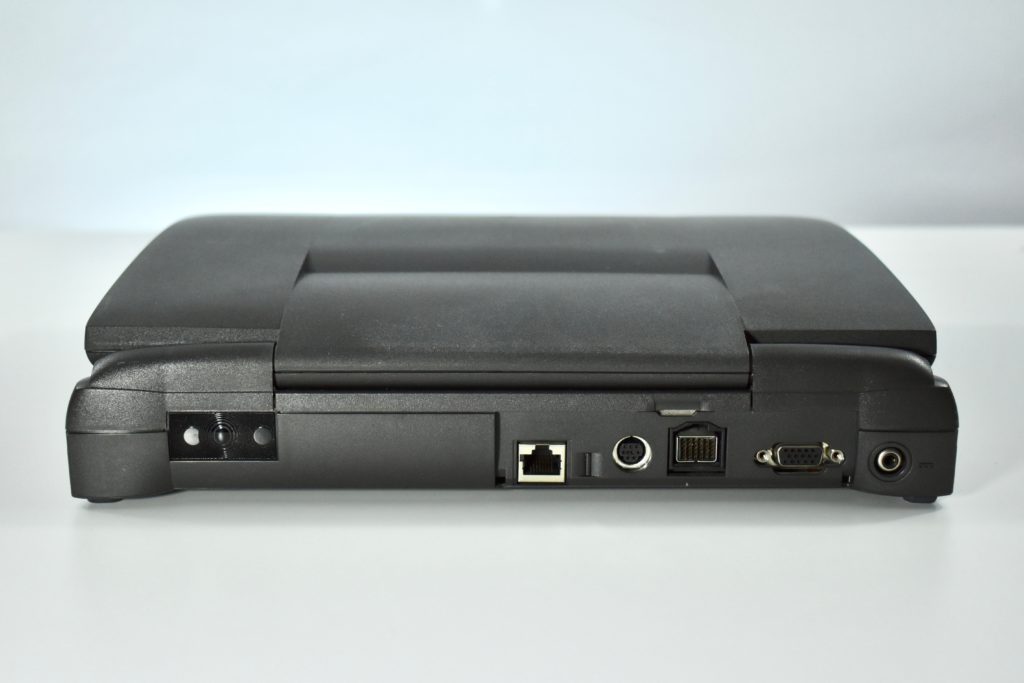
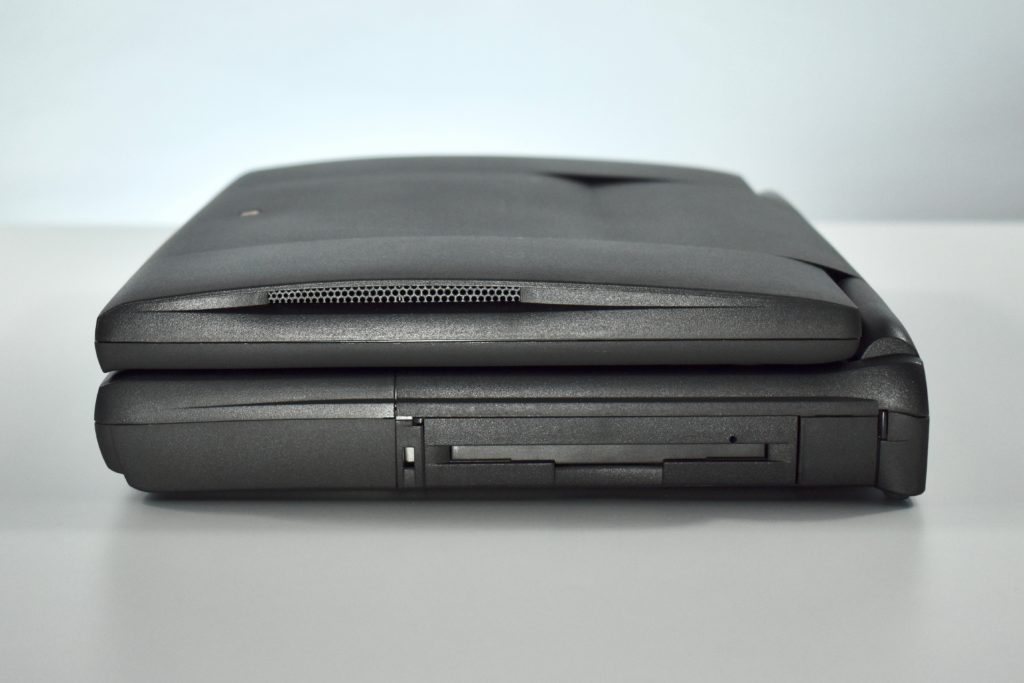
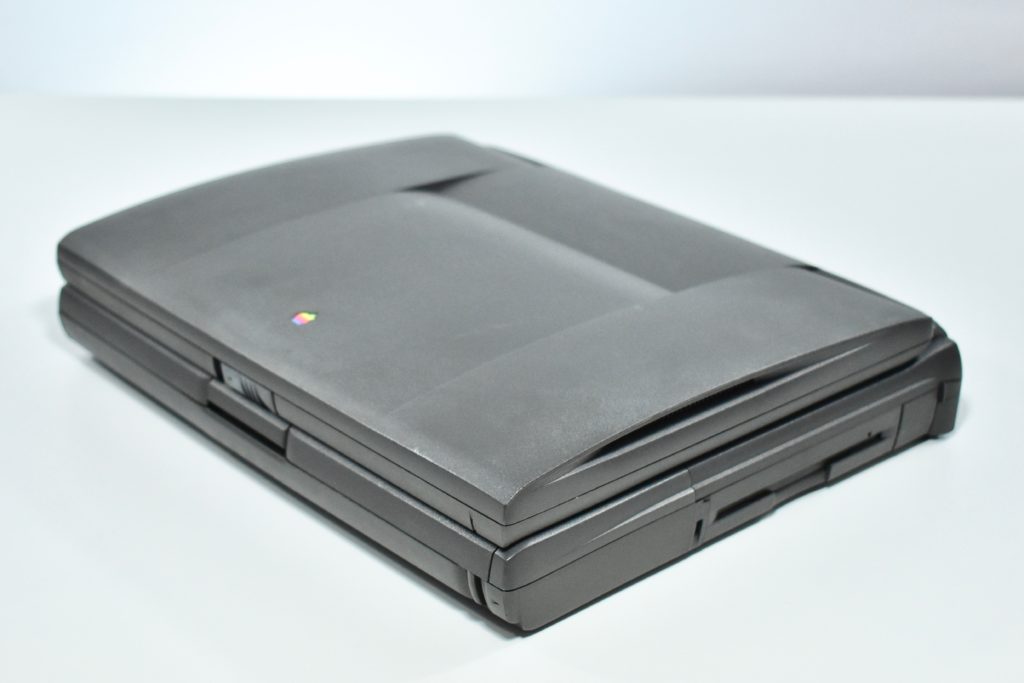
The case was a two-tone black design with both a hard plastic and a rubberized finish. The case was the same as the “Wallstreet” PowerBook that preceded it and included dual hot-swappable bays which could both hold batteries or expansion modules (the left used a a 3.5-inch bay and the right used a 5.25-inch bay).
While the “PDQ” PowerBook G3 Series had a fast processor and performed well for the time, the “PDQ” moniker described the simplification of its production process by offering one screen size instead of three and, therefore, solved supply issues “Pretty Darn Quick.”
Source: EveryMac.com