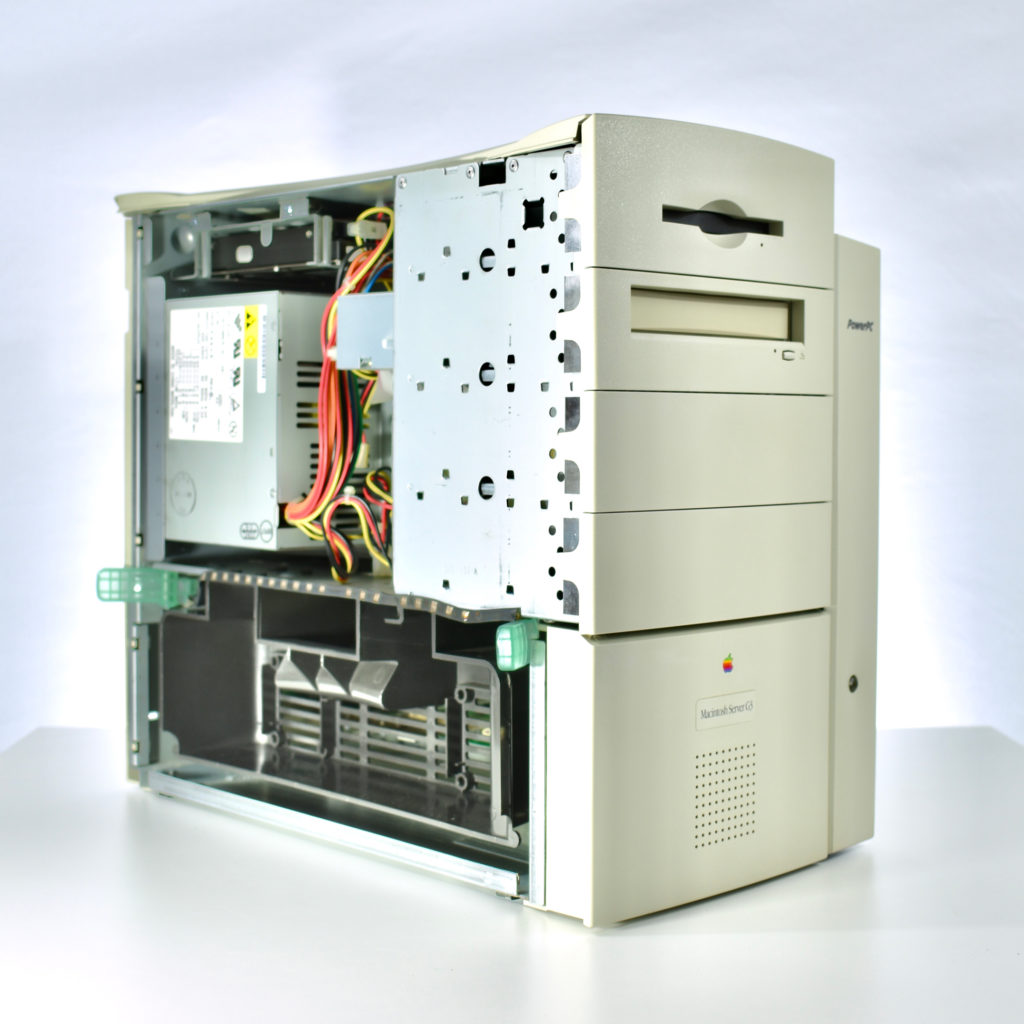
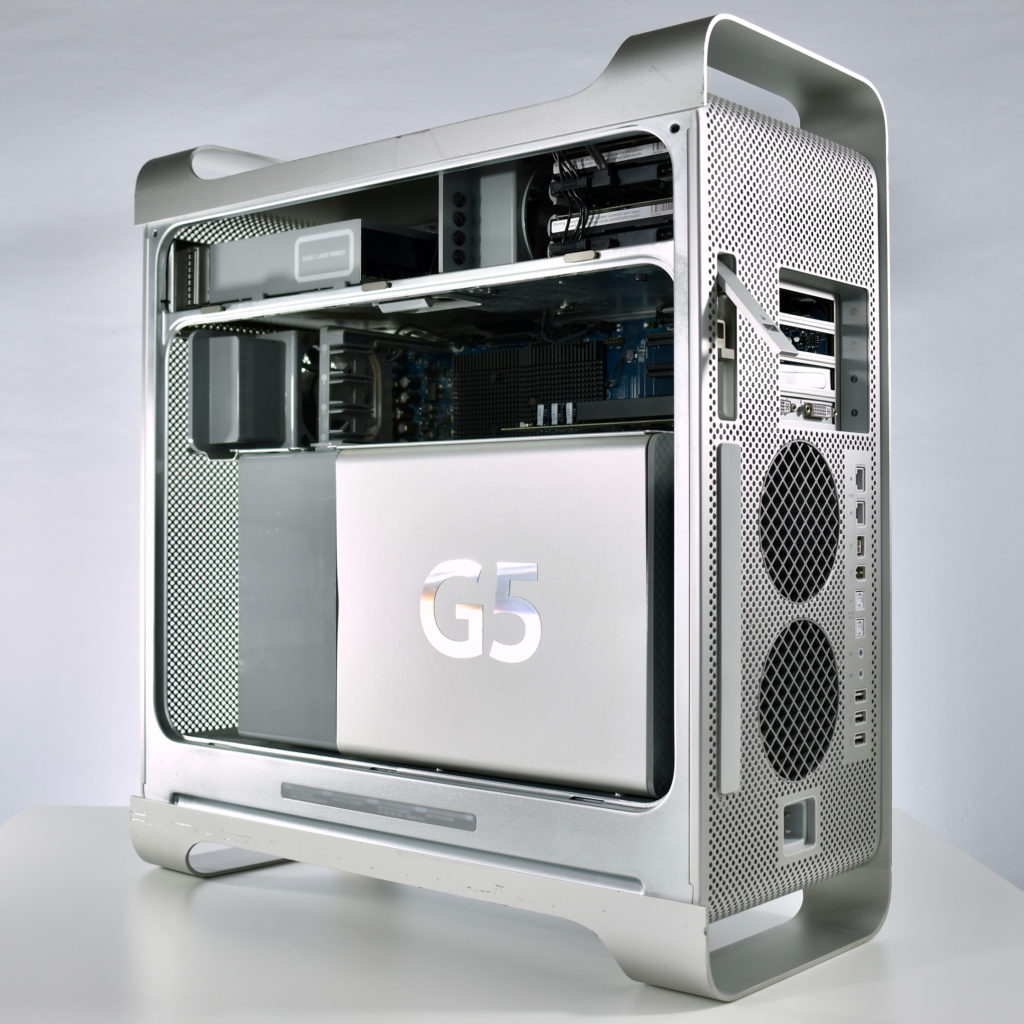
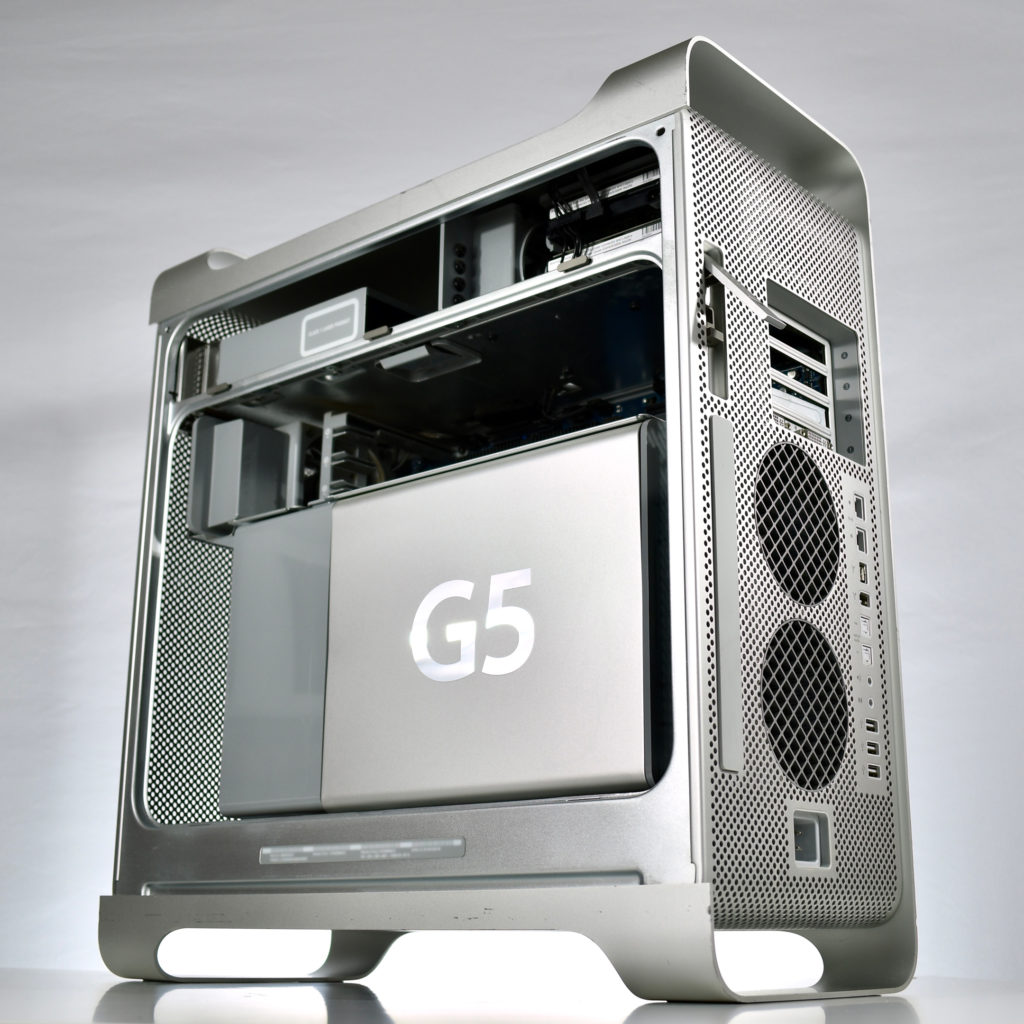
My collection of Apple CD and DVD media includes operating systems, applications, software collections that shipped with devices, promotional media, diagnostic tools, and educational content. In general, Apple-branded CD or DVD examples in original packaging have been presented separately, while single discs or collections of discs are presented chronologically.
Apple CDs and DVDs from 1997 include:
- eMate 300 Connectivity CD, Newtown (Version 1.1, 691-1630-A, 1997)
- Disney/Pixar A Bug’s Life DVD (video, original packaging, 1997)
- ClarisWorks 4.0 for Windows (1991–1997)
- Power Pack CD Power of 10 (templates for Ad Pad materials, 1997)
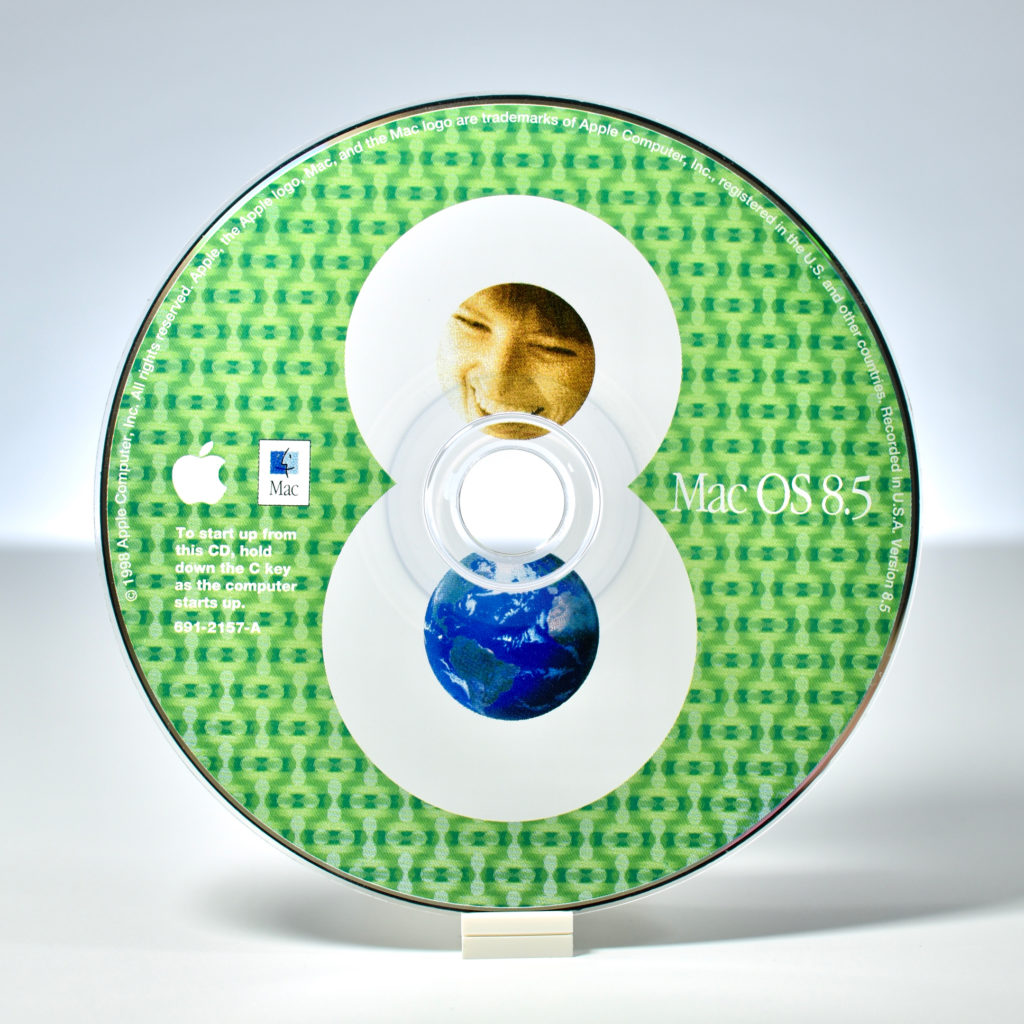
- Mac OS 8 (Version 8.0, 691-1773-A, U97073-049B, 1997)
- Mac OS 7.6.1 (Version 7.6.1 V1.0.2, Z691-2046-A, 1997)
- Drive Setup 1.3.1 (691-1796-A, U97073-131A, 1997)
- Apple QuickTake 200 Software For Mac OS (Version 1.0, 691-1338-A, 1997)
- The Apple Printer Software Collection for the Color StyleWriter 4500 (Version 1.0, 691-1415-A, 1997)
- The Apple Printer Software Collection for the Apple LaserWriter Series (original packaging, Version 1.1, 691-1522-B, 1997)
- Apple Macintosh CD, Power Macintosh G3 (SSW Version 8.0, CD Version 2-1.0, 691-1826-A, 1997)
- Apple Macintosh CD, Power Macintosh 5400, 5500, and 6500 series (SSW Version 7.6.1, CD Version 1.0, 691-1559-A, 1997)
- Apple Macintosh CD, Power Macintosh 9600 and 8600 series (SSW Version 7.6.1, CD Version 1.0, 691-1623-A, 1997)
- AppleVision Software (Version 1.2, 691-1462-A, 1997)
- AppleVision Software (Version 1.3, 691-1665-A, 1997)
- AppleShare IP 5.0 CD (bundle, 1997)
- AppleShare IP 5.0 (Version 5.0.2, Z97073-108A, 1997)
- AppleShare IP 5.0 Companion CD (Version 5.0, Z96073-104A, 1997)
- AppleShare IP 5.0 CD (bundle, 1997)
- Mac OS 7.6 (Version 7.6, Z97073-038A, 1997)
- AppleShare IP 5.0 (Version 5.0.1, Z96073-103B, 1997)
- Apple Network Administrator Toolkit 2.0 (U96073-026B, 1997)
- Mac OS 8 Tour (Mac OS 8 Demo Tour)
- Mac OS 8, What a difference 8 makes. Version 8.0, Not for resale
In 1997 Macintosh computer system software was able to fit on a single CD. For Macintosh computers, Apple used a standard white CD envelope with a white cloth-like back and a clear plastic front. Since Macintosh servers required several CDs, Apple used a clear plastic CD book with space for a thin, square book at the front and pages with white backs and clear plastic covers. Each page held a single CD. The design of Apple CDs began to change in 1997 from the older black and silver design (with red accents) to a design with a single background color, black or white text, and with some CDs using few additional accent colors.