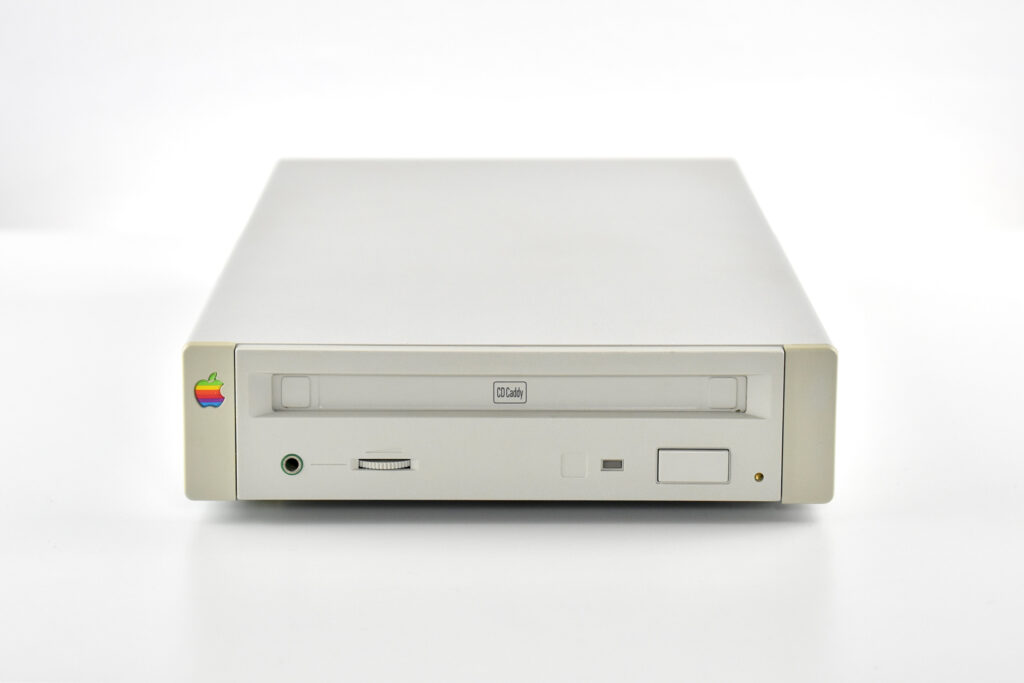
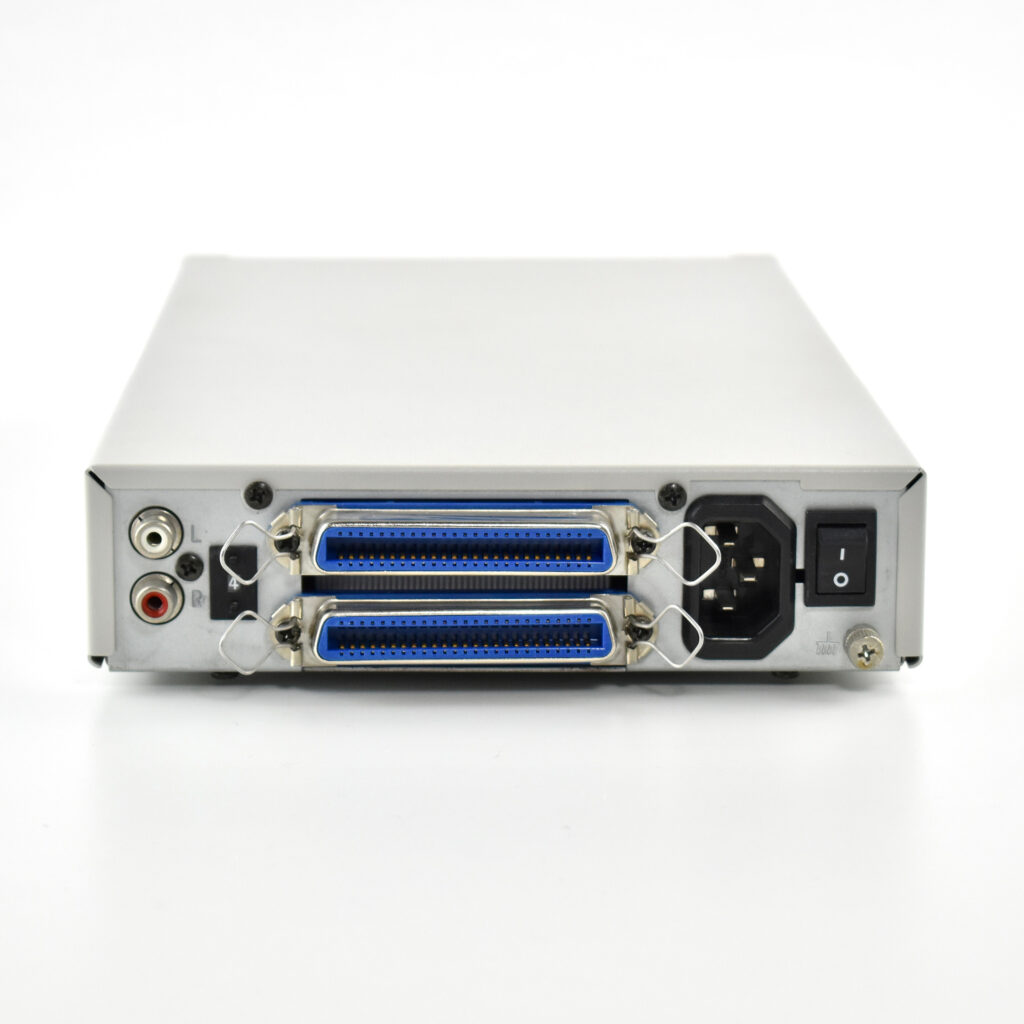
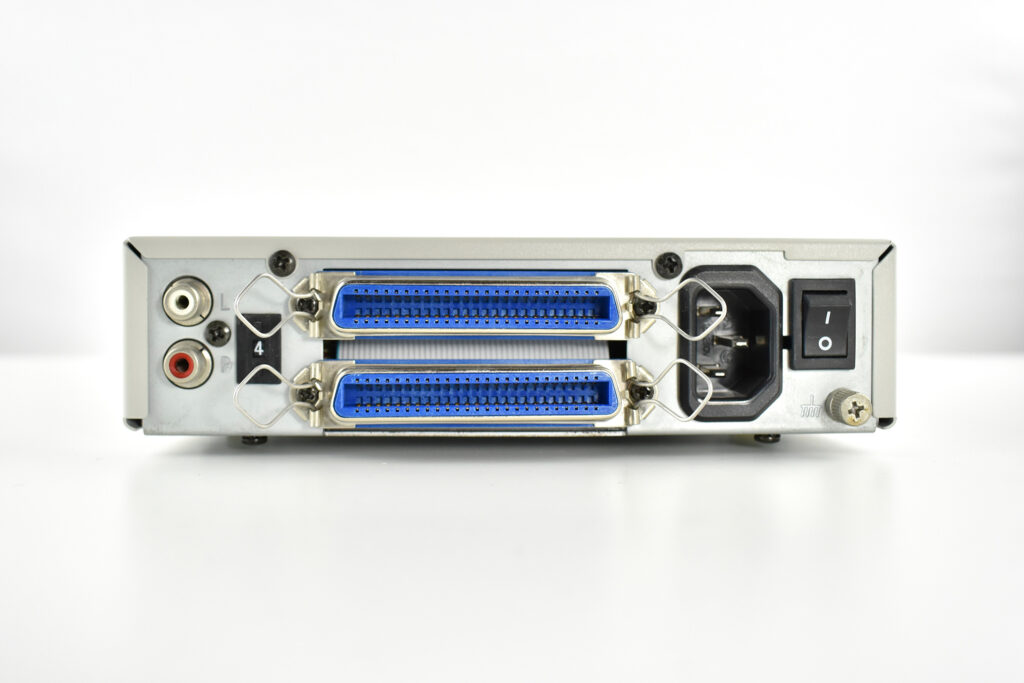
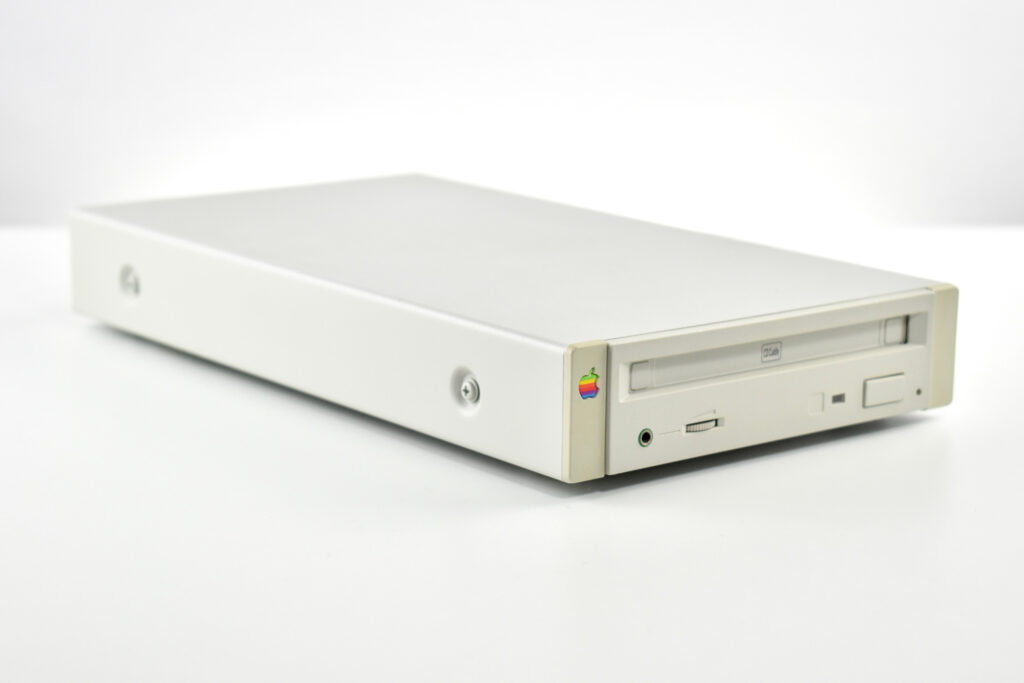
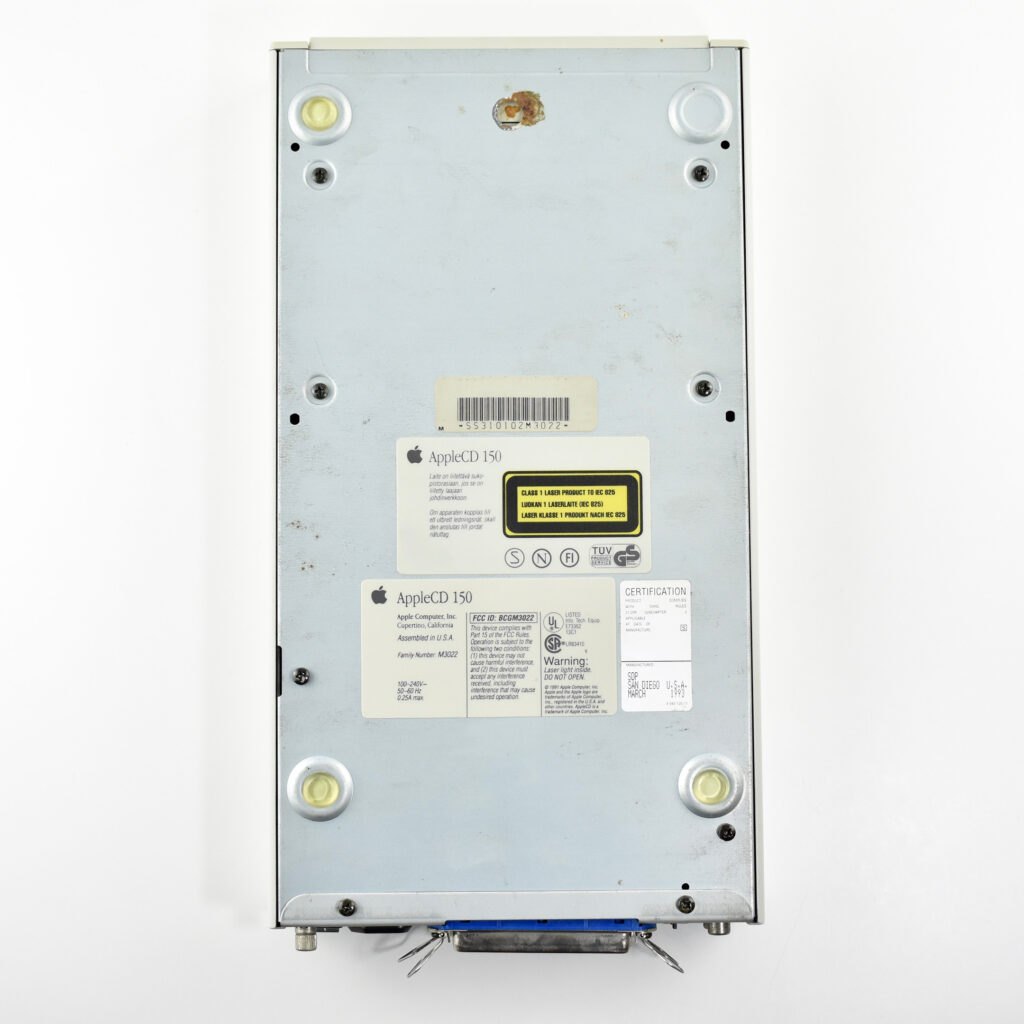
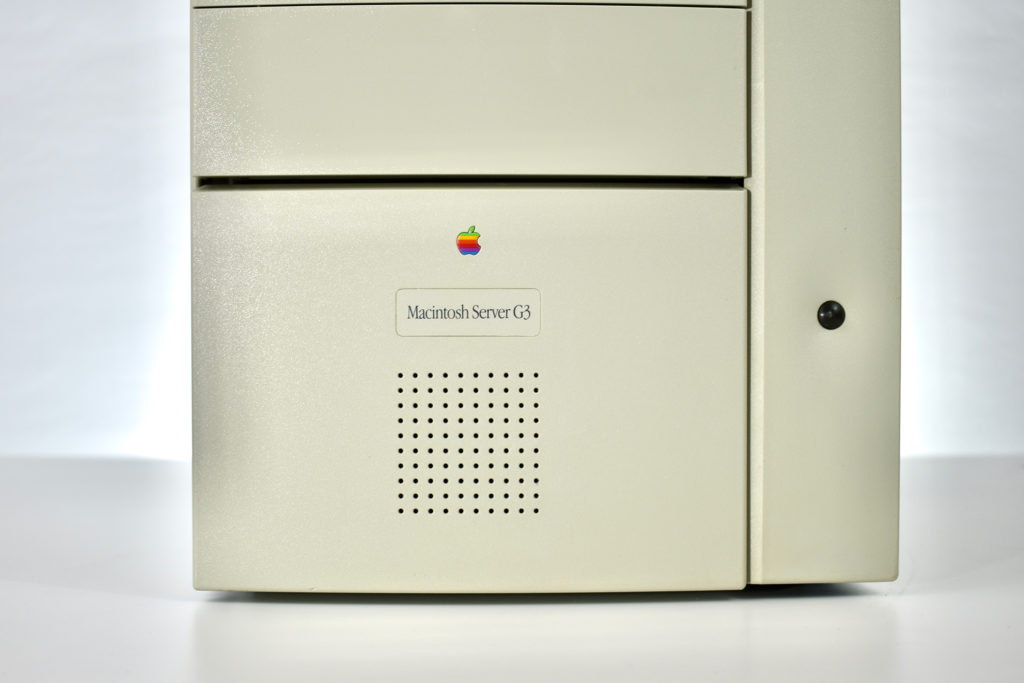
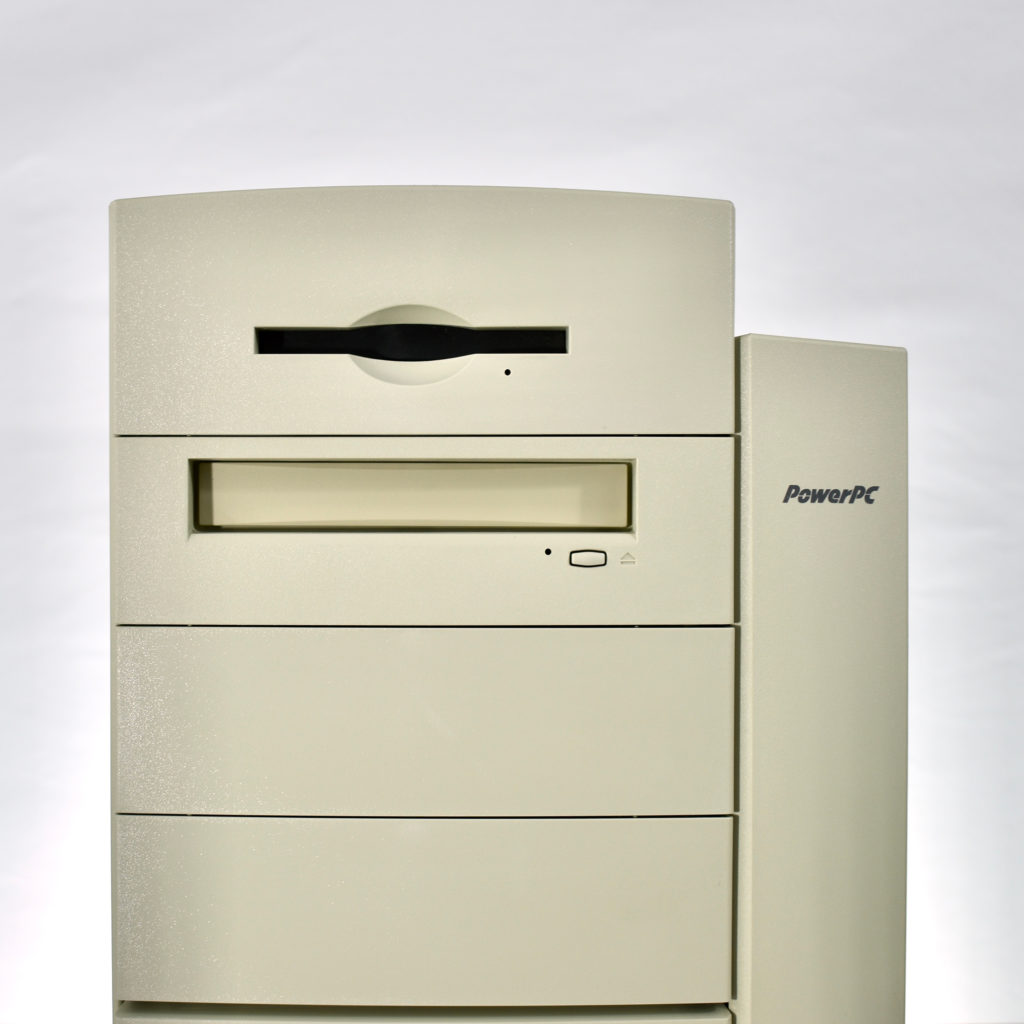
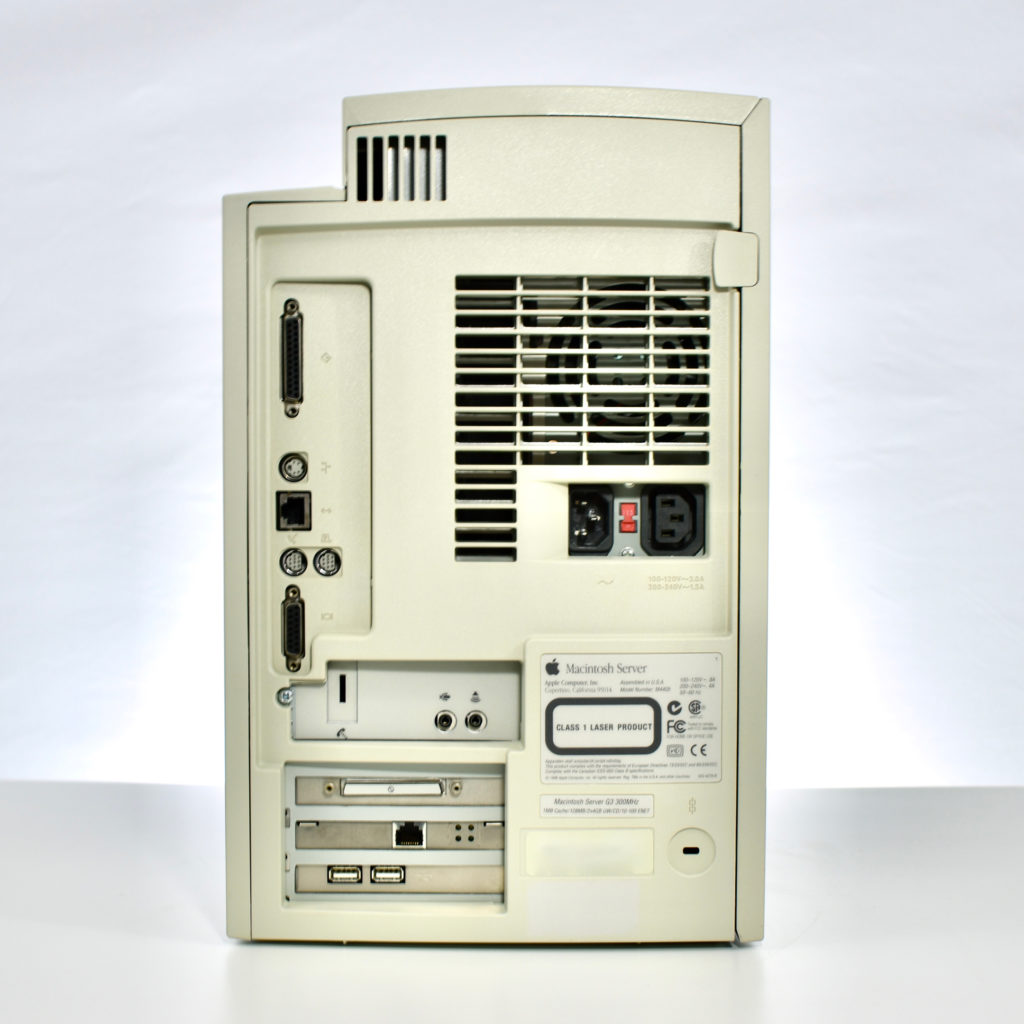
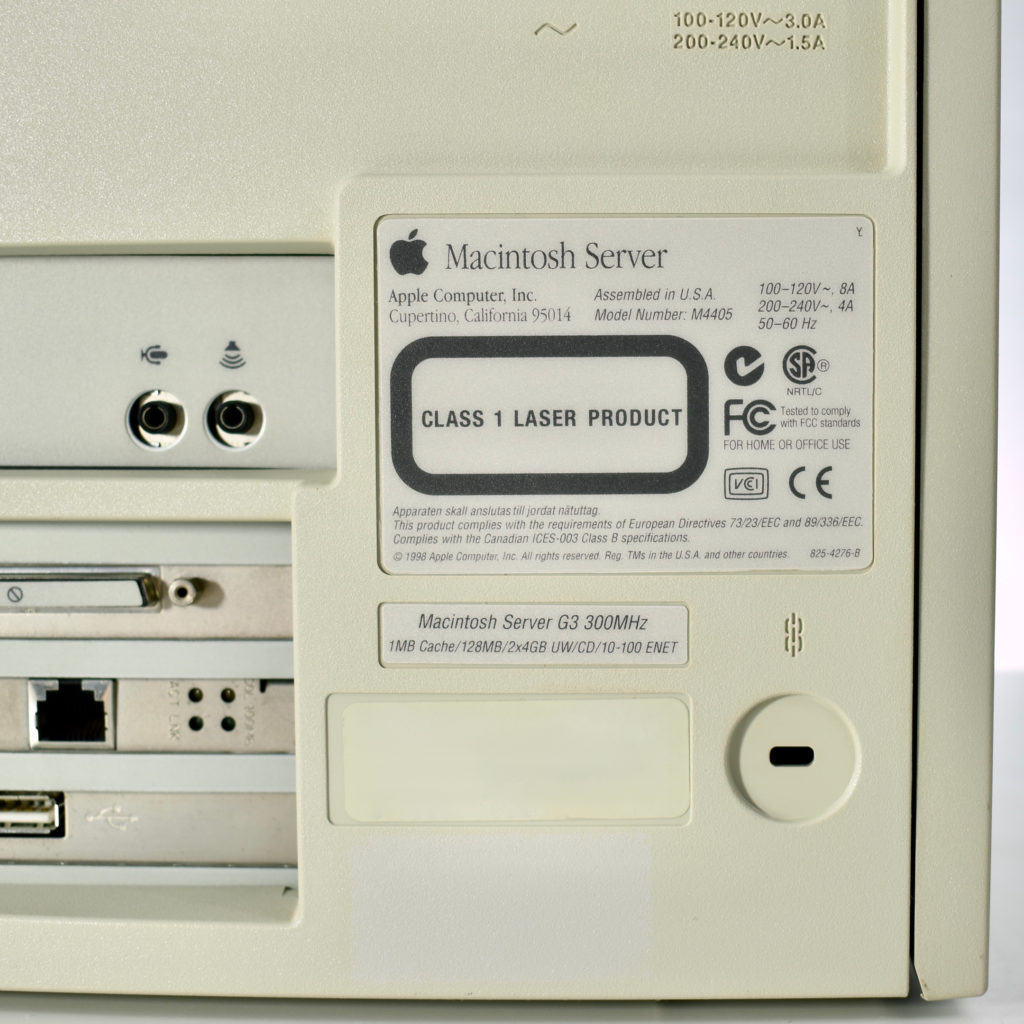
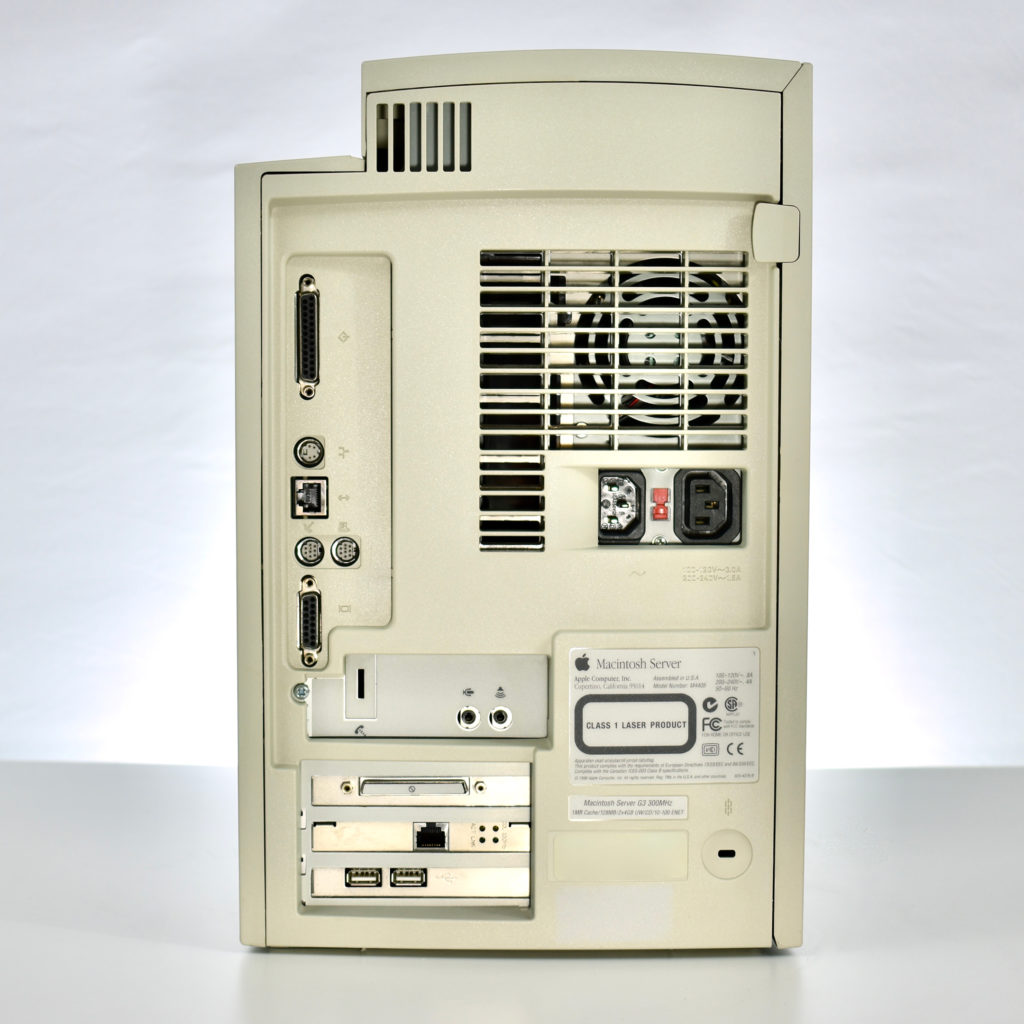
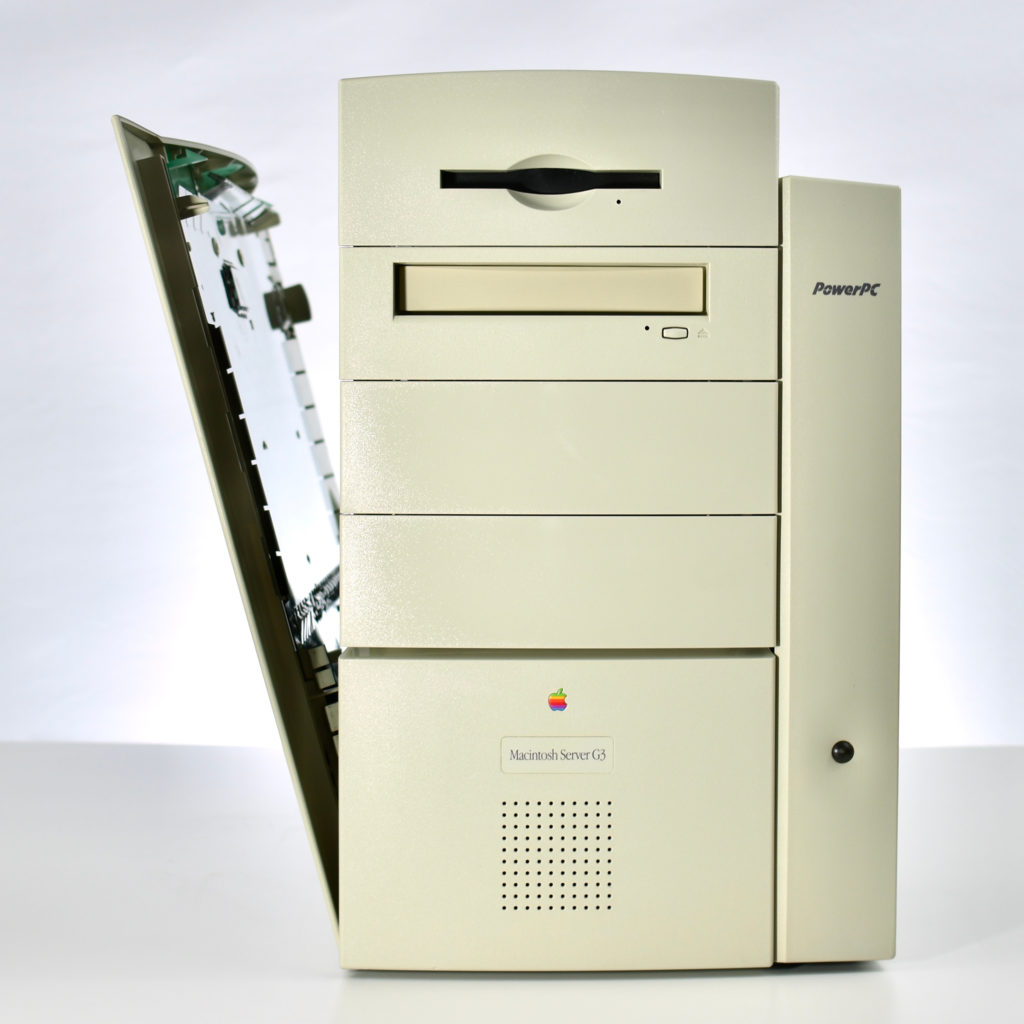
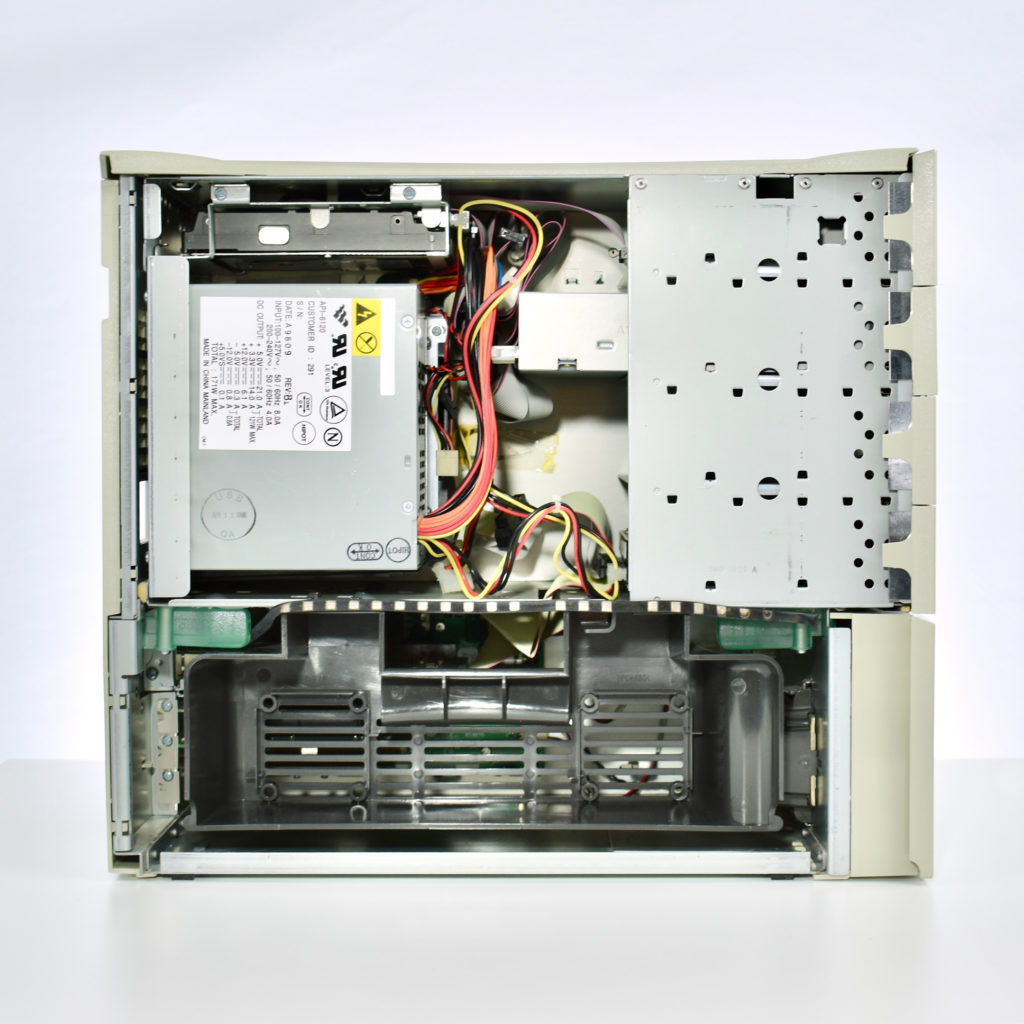
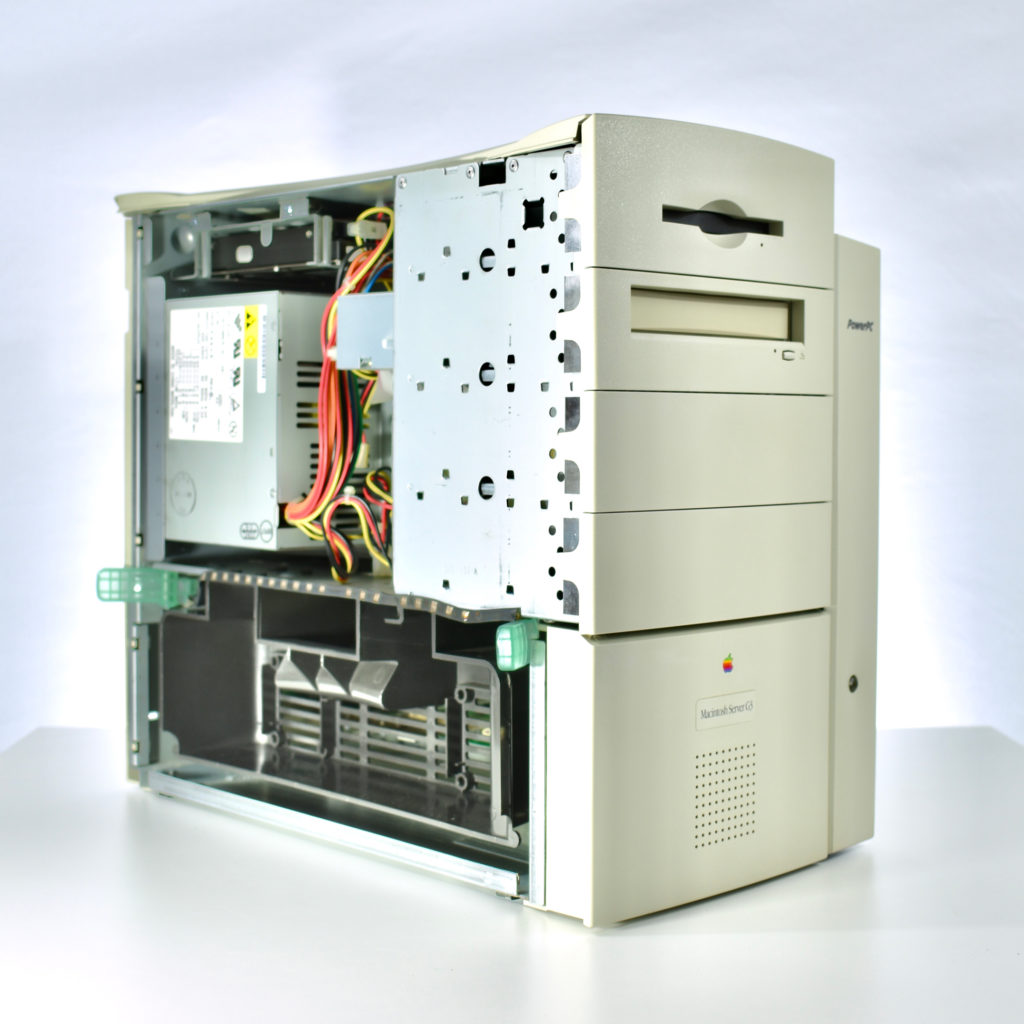
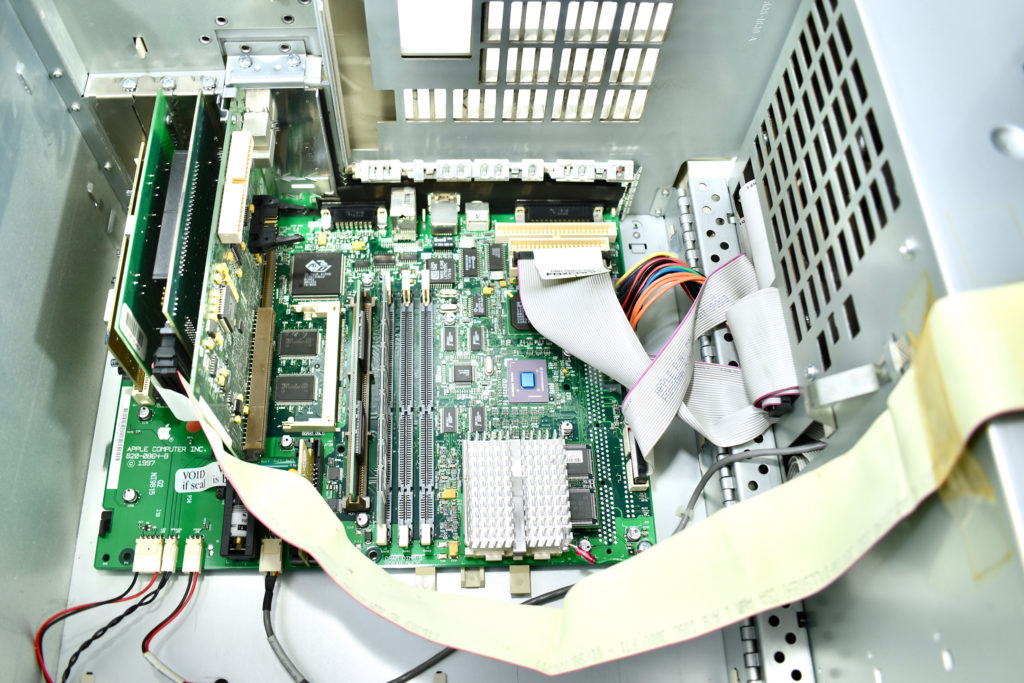
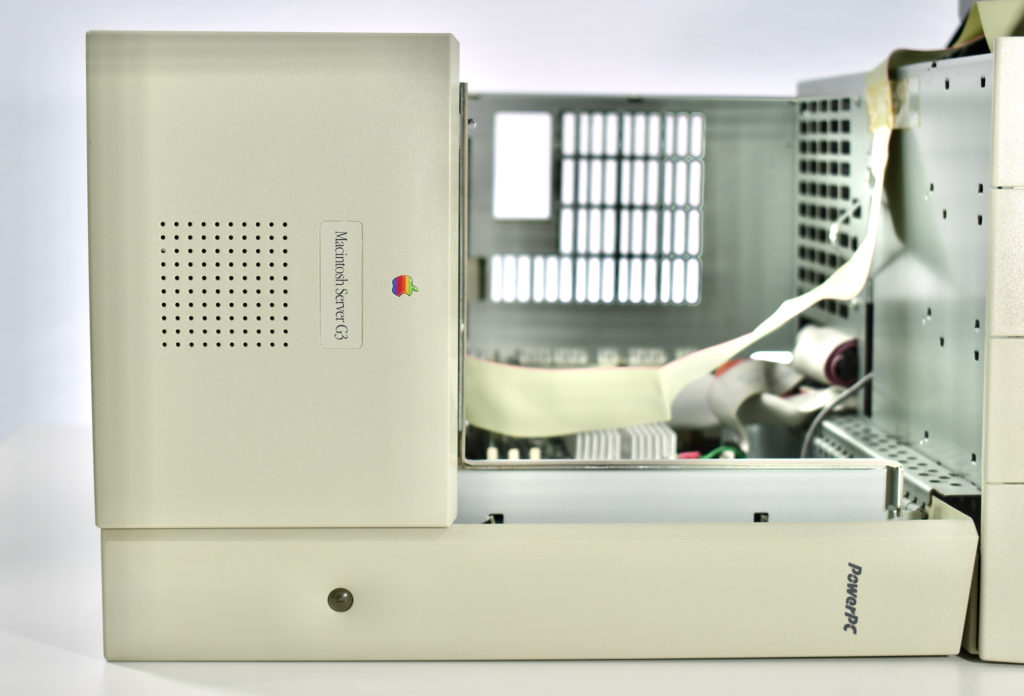
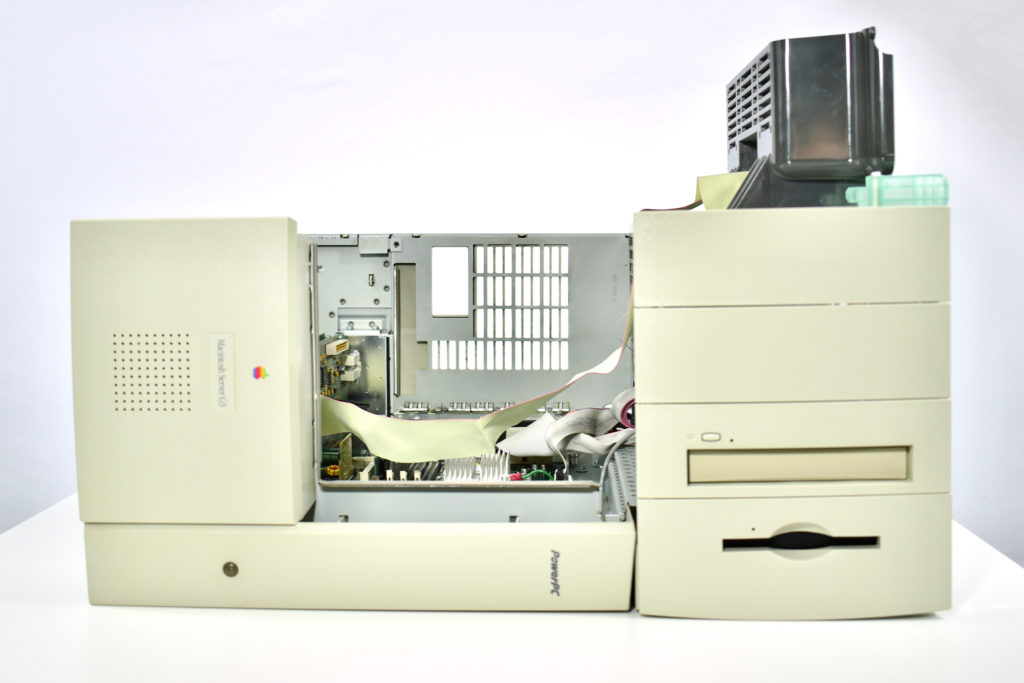
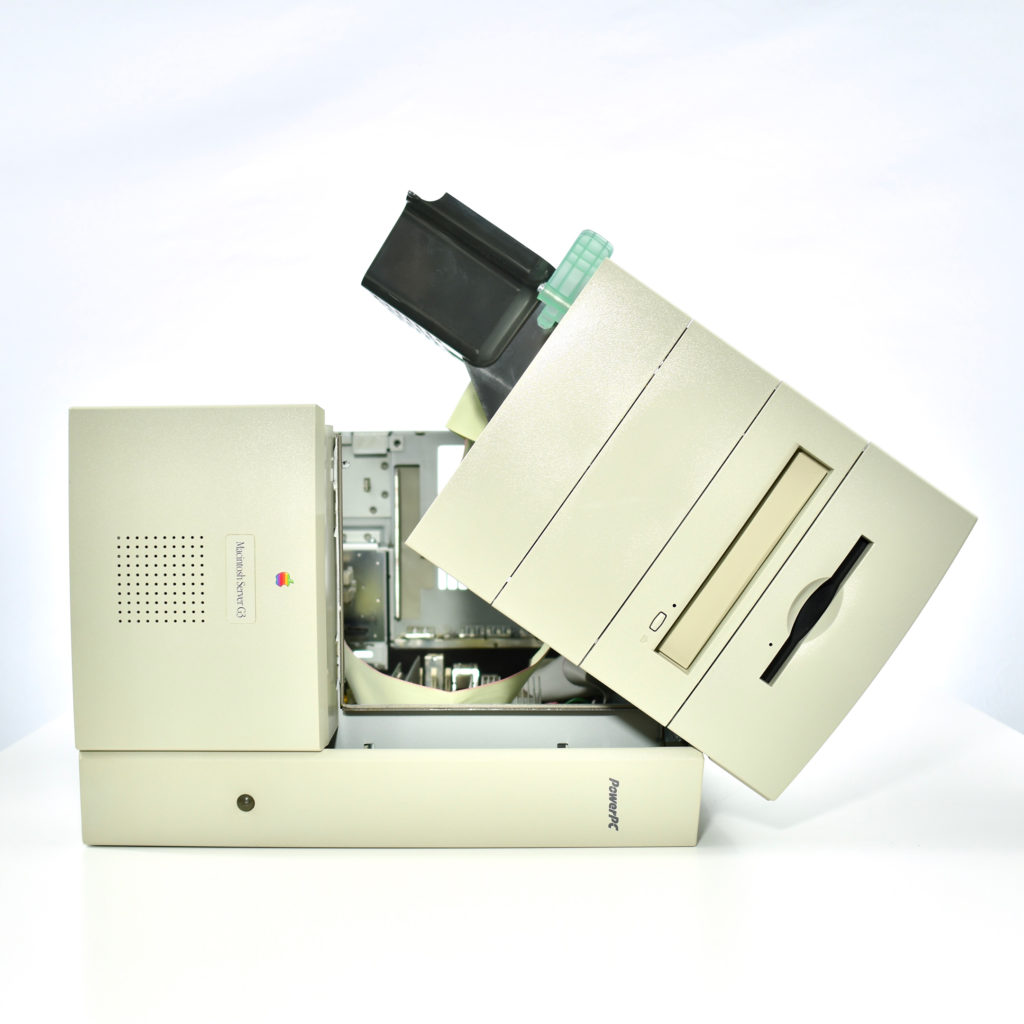
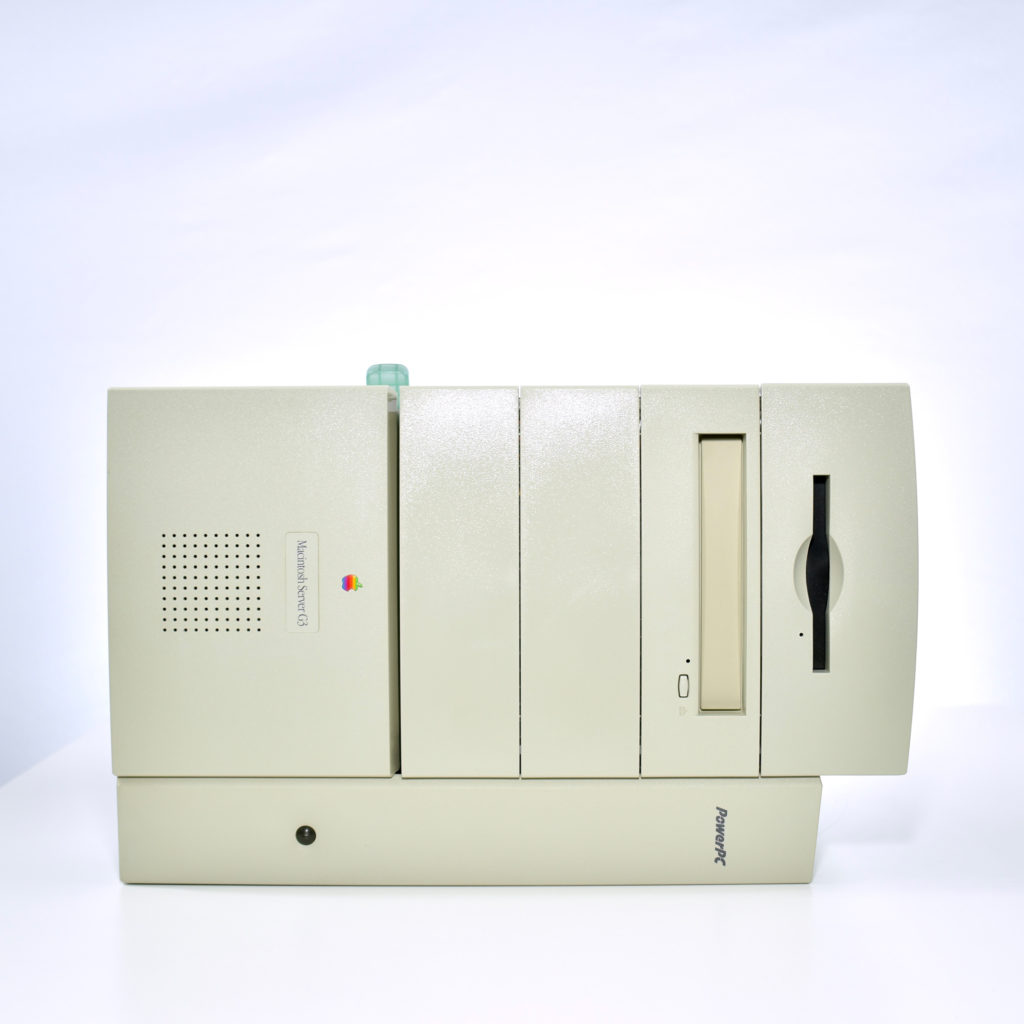
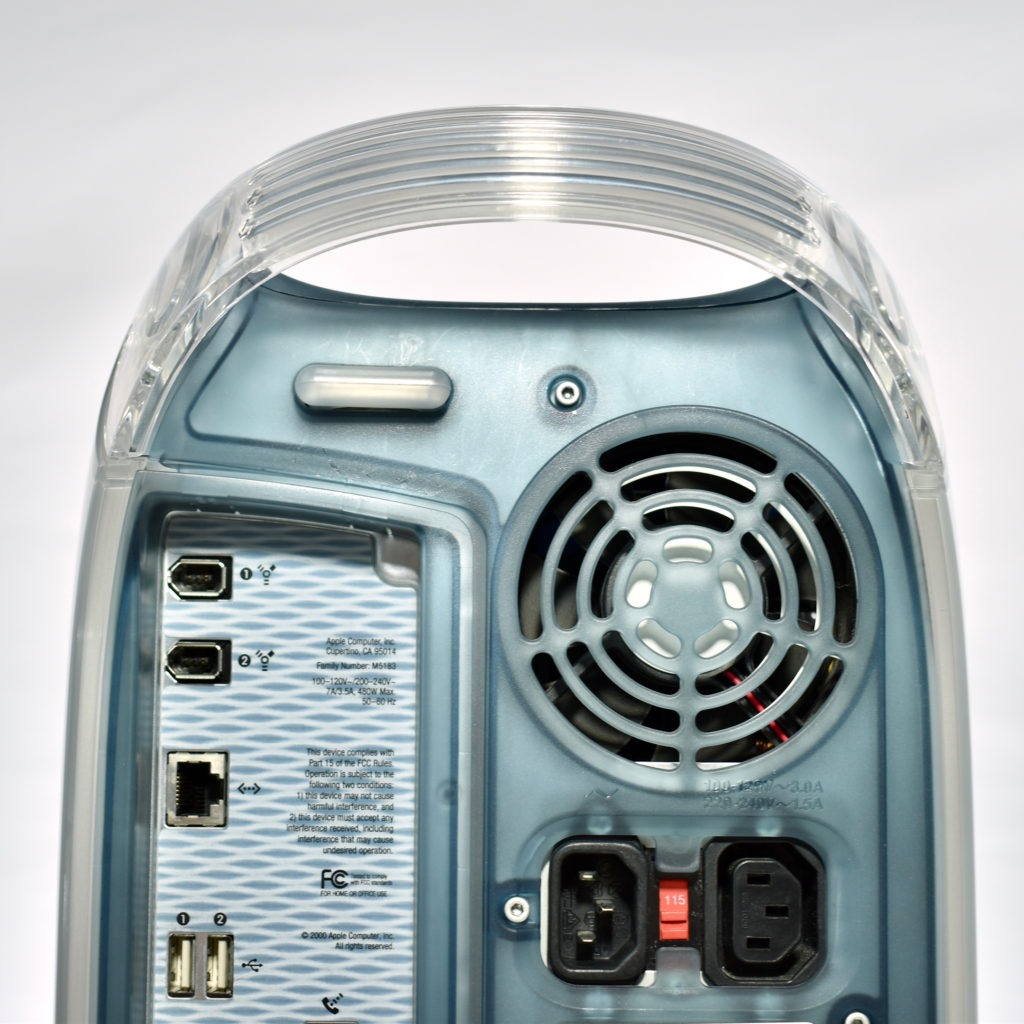
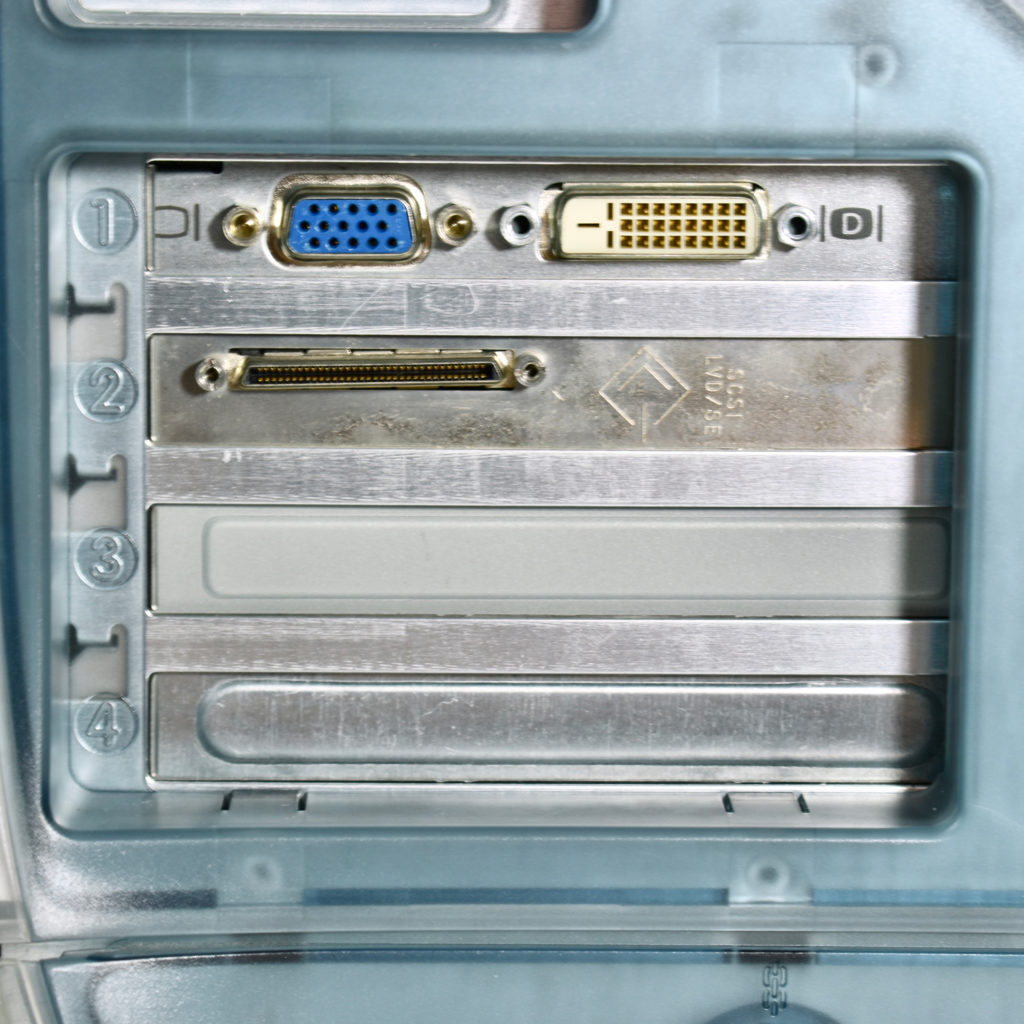
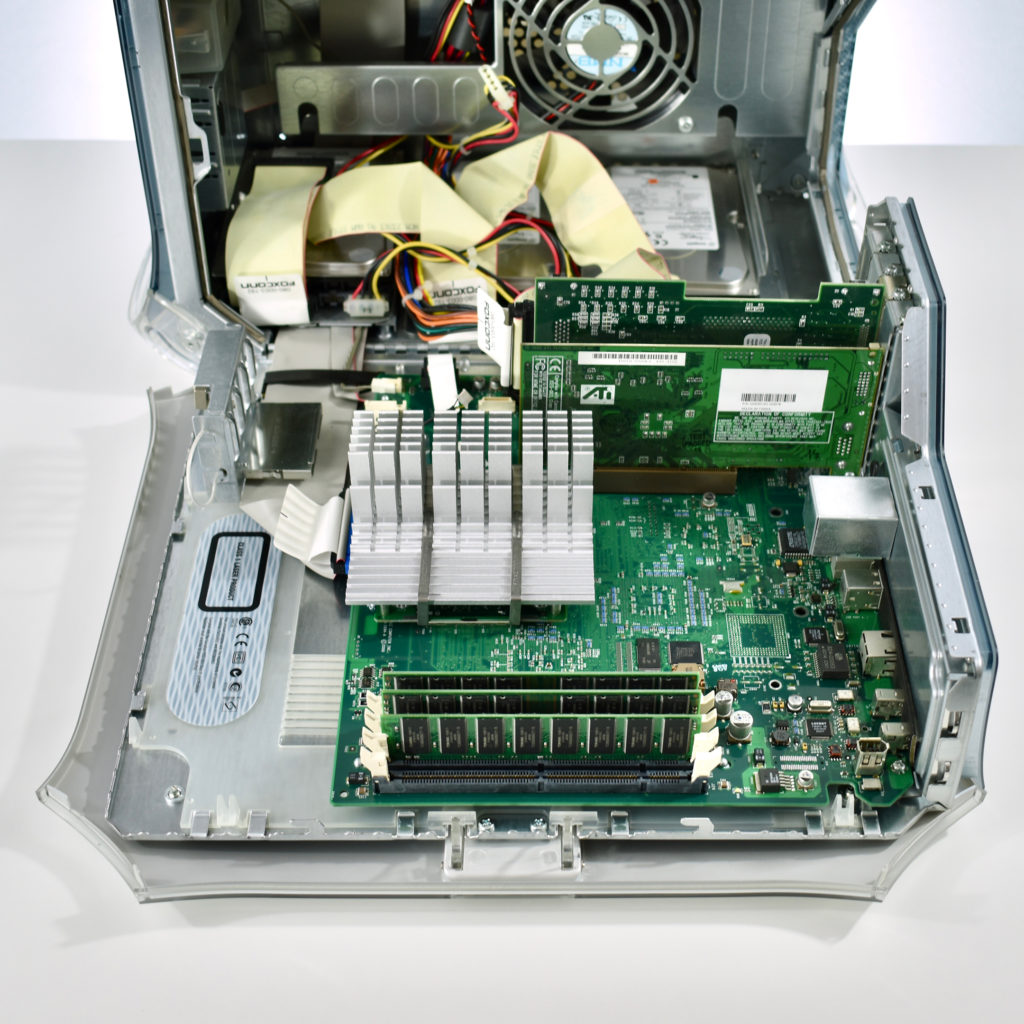
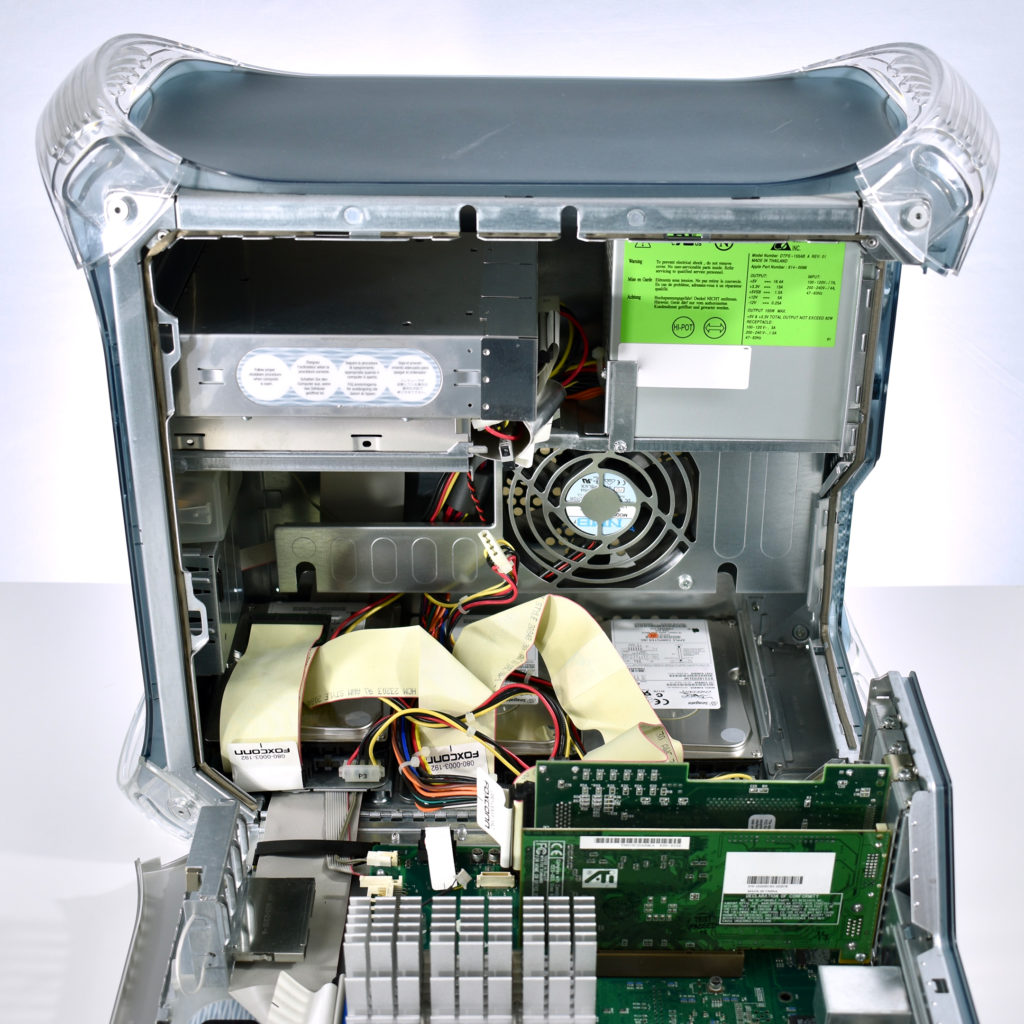
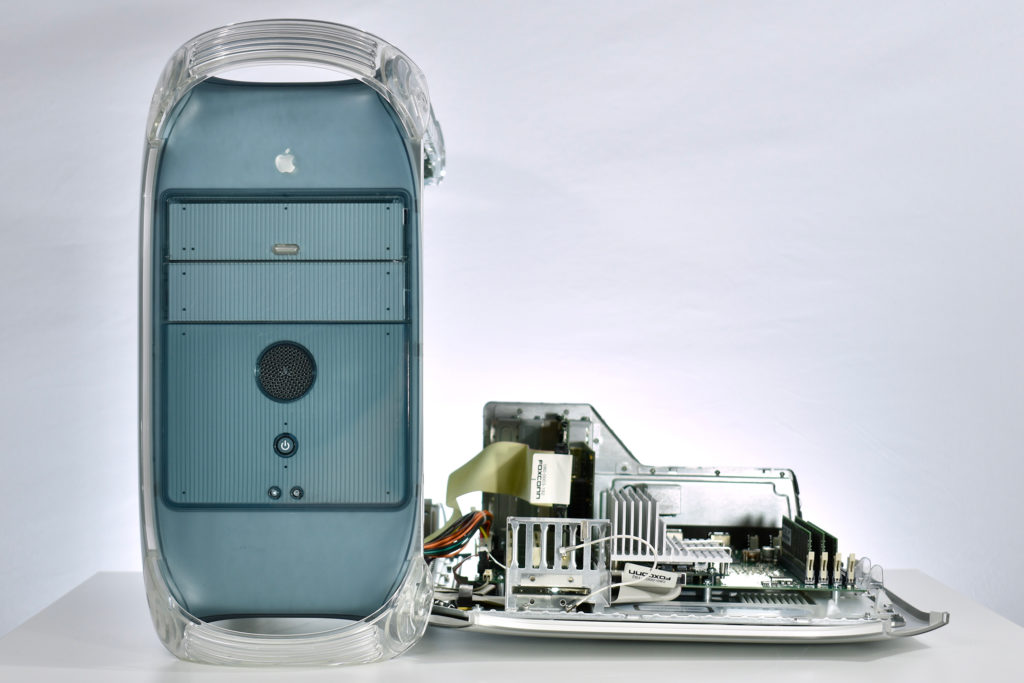
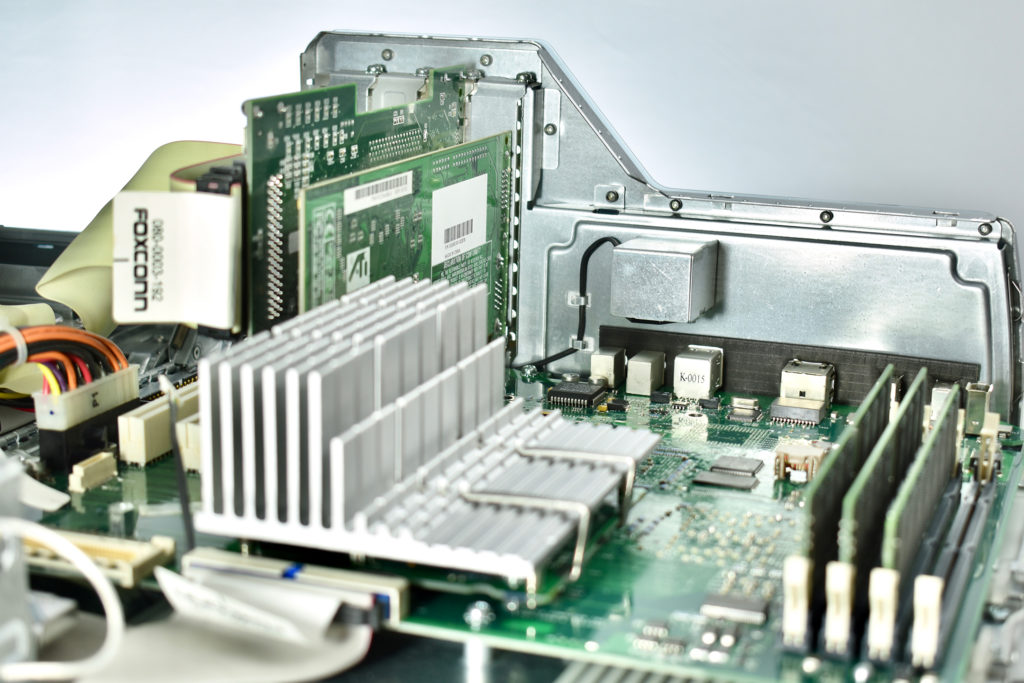
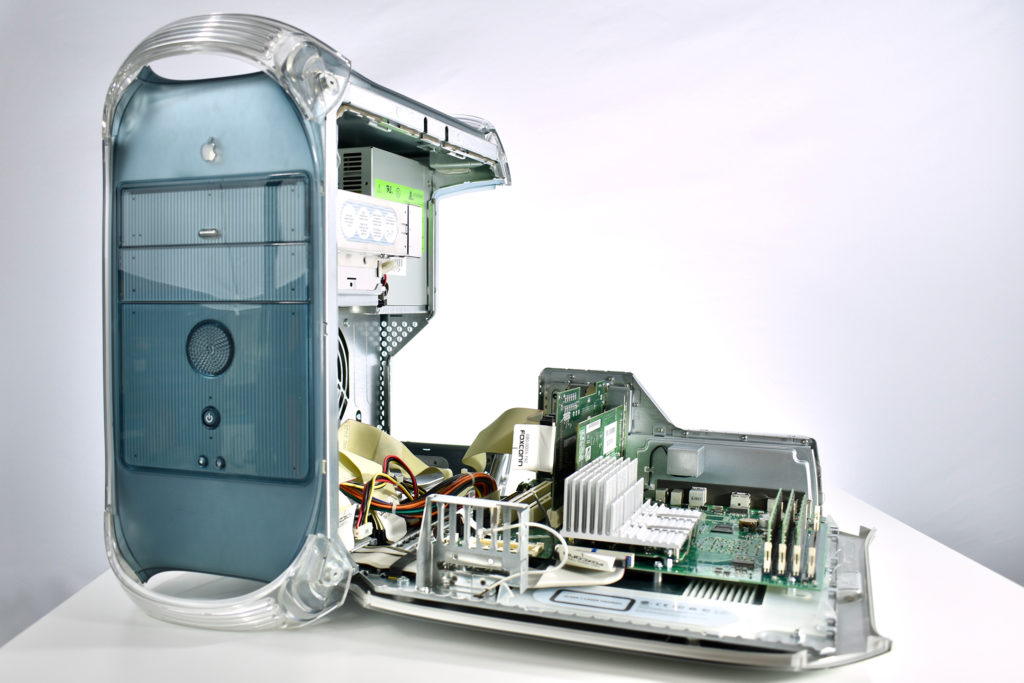
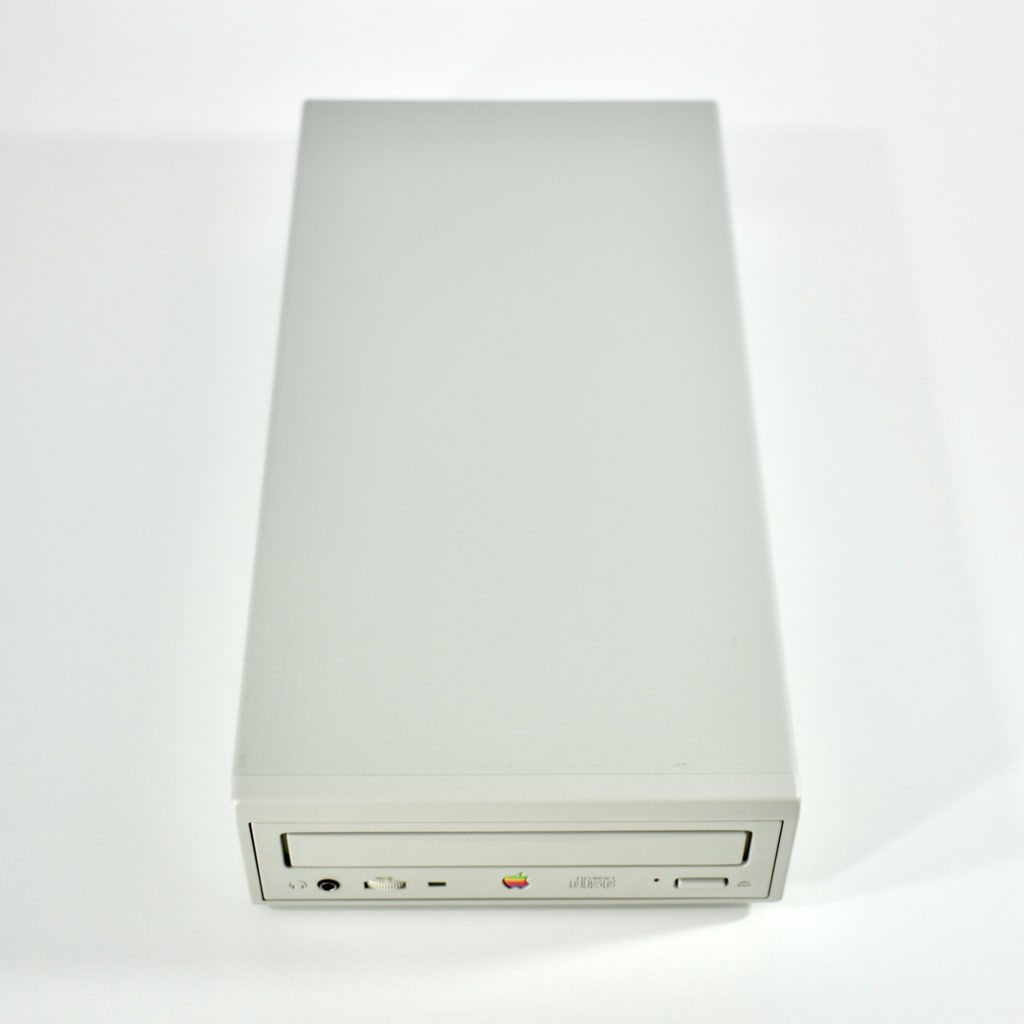
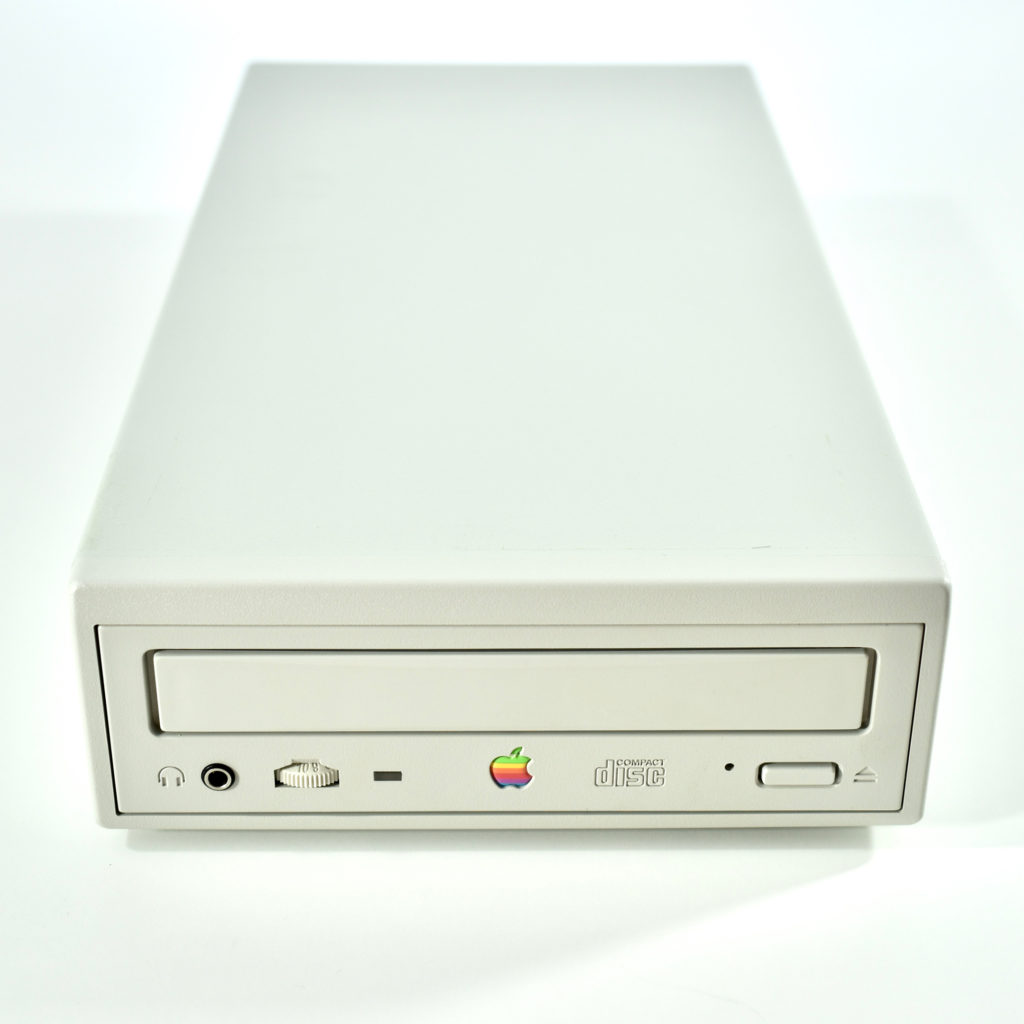
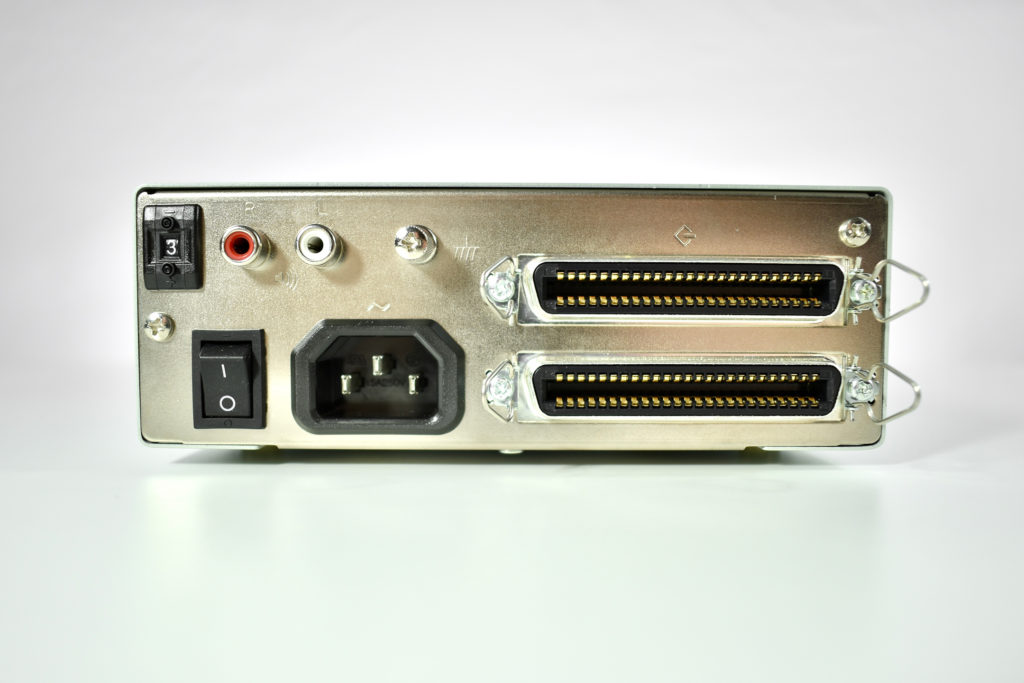
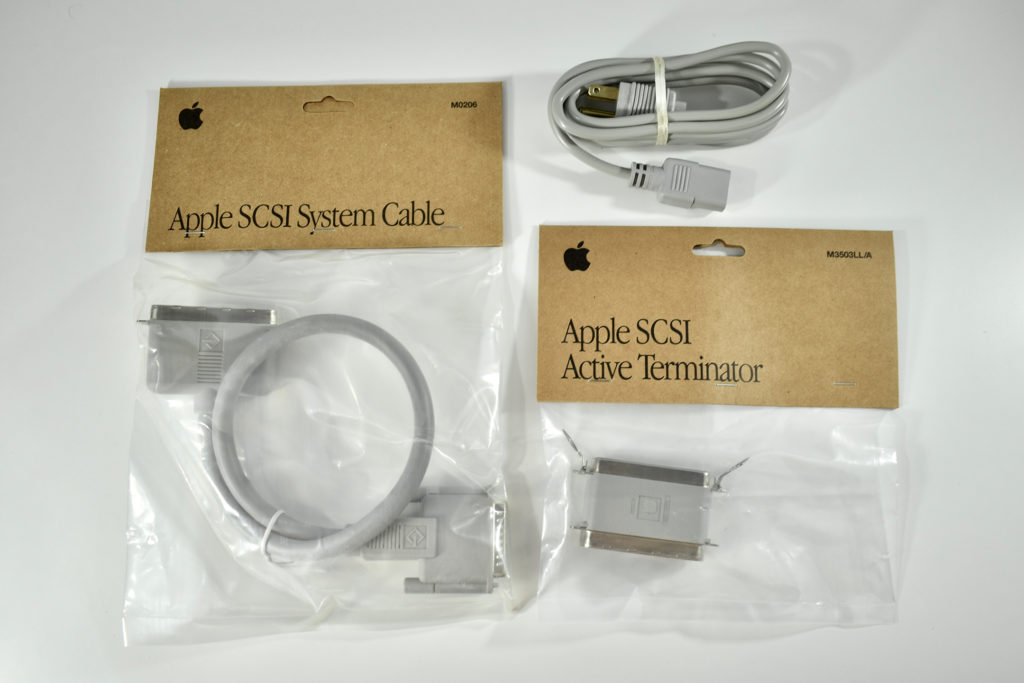
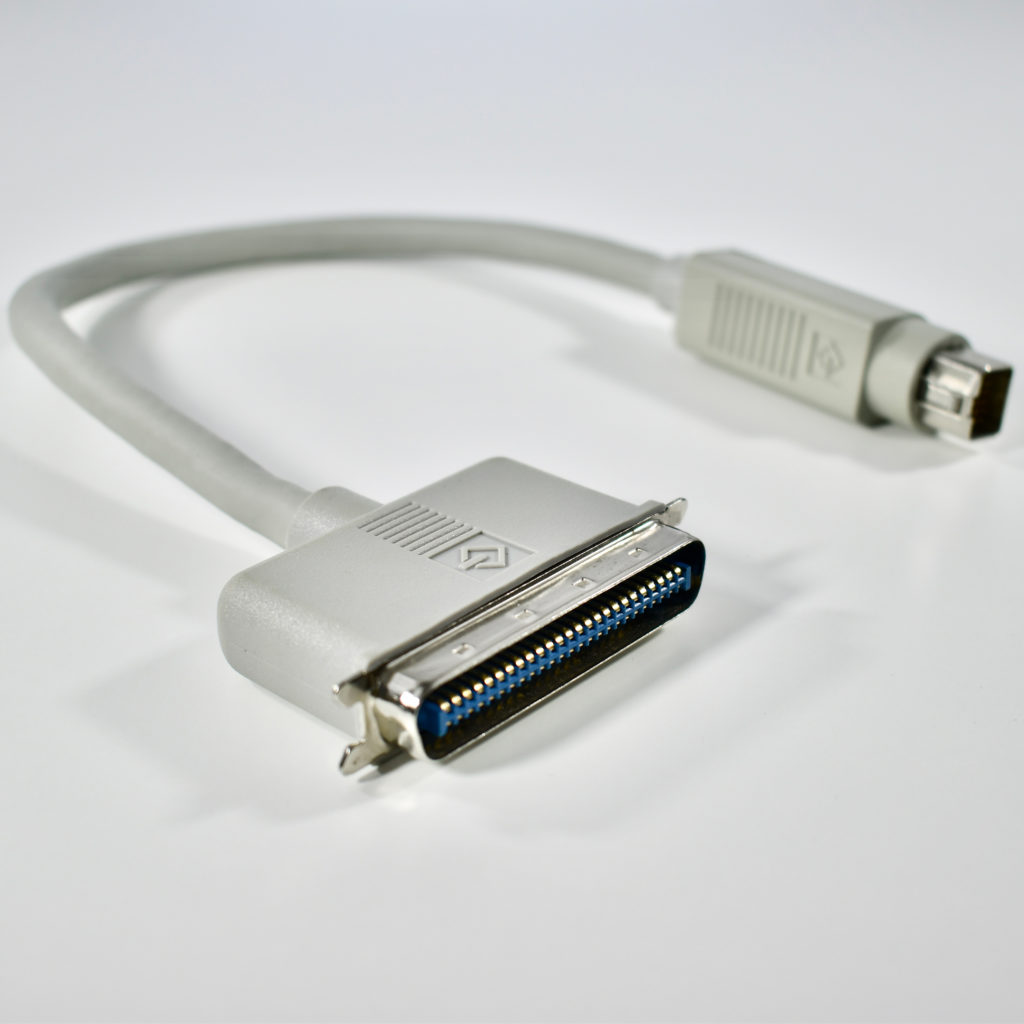
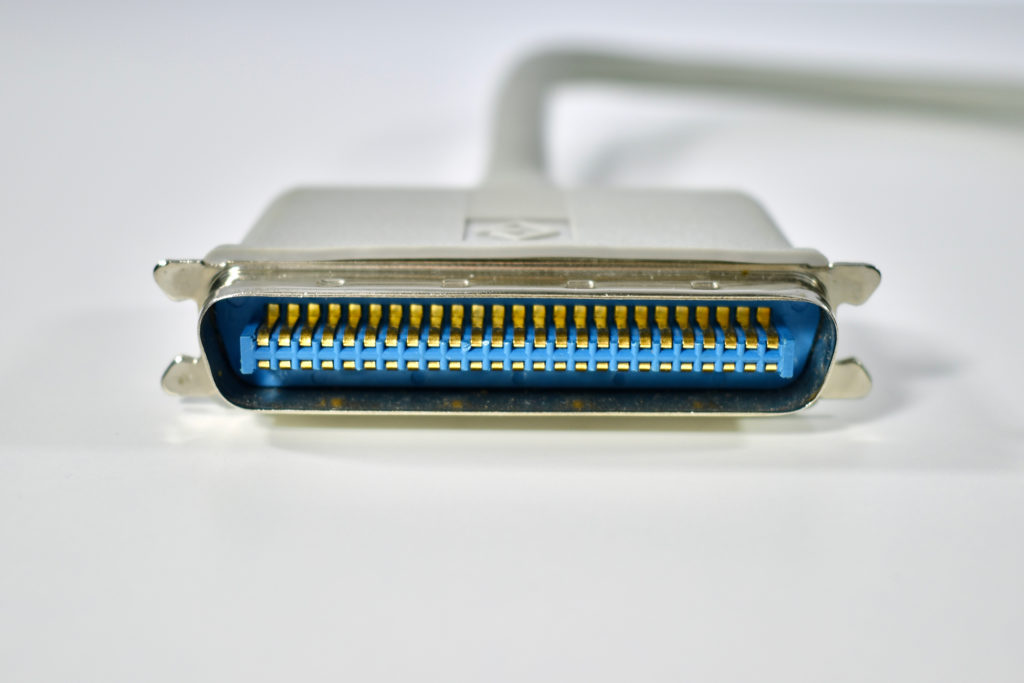
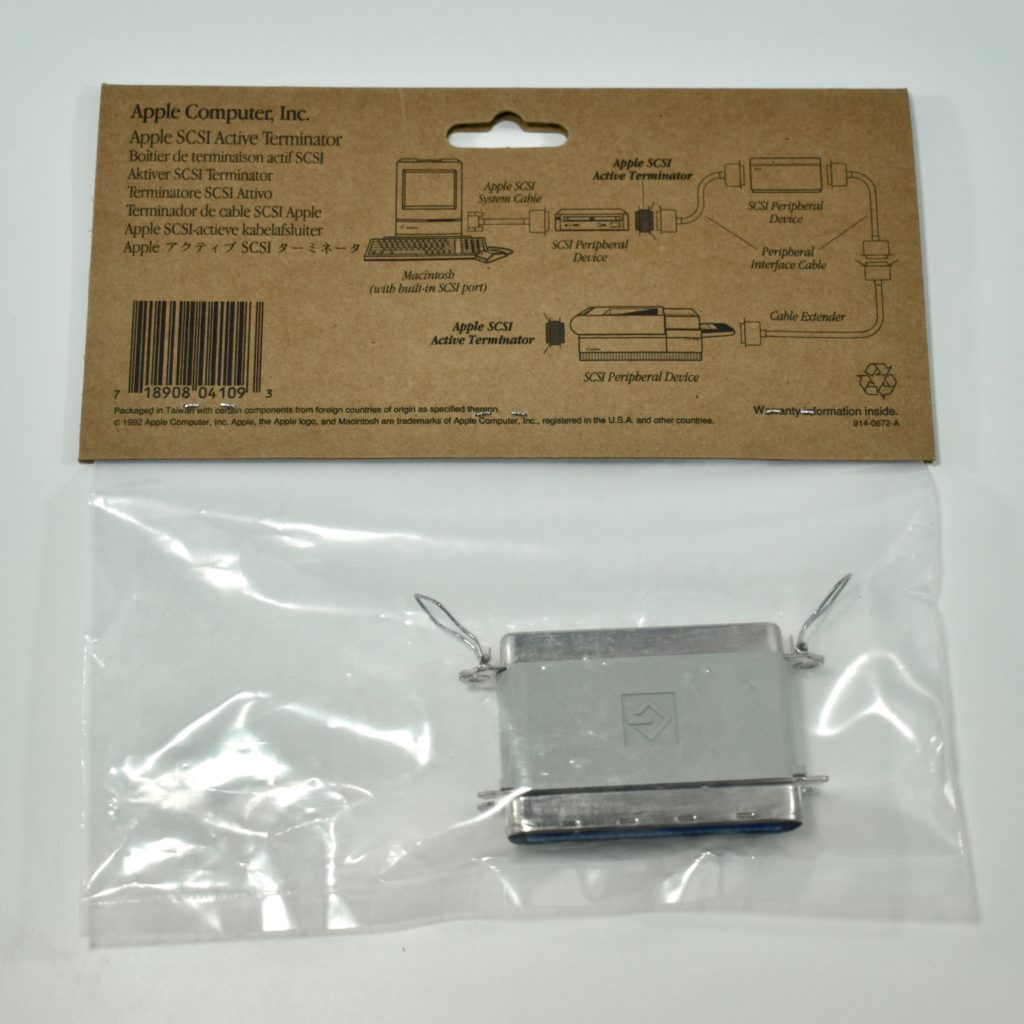
The AppleCD 150 was among a few nearly identical SCSI-connected external CD-ROM drives manufactured by Apple. All AppleCD models used a SCSI (Small Computer System Interface, pronounced “scuzzy”) connection. According to PC Magazine, SCSI was “used in mainframes, servers and storage arrays in the late 1980s and 1990s… The SCSI bus connects up to 15 devices in a daisy chain topology, and any two can communicate at one time: host-to-peripheral and peripheral-to-peripheral.”
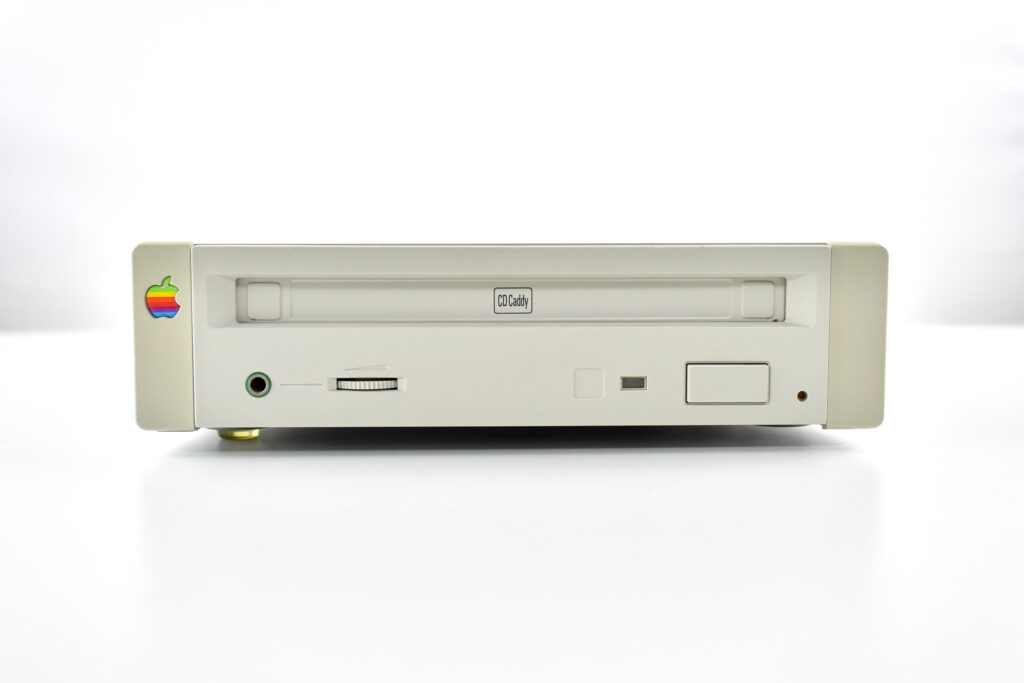
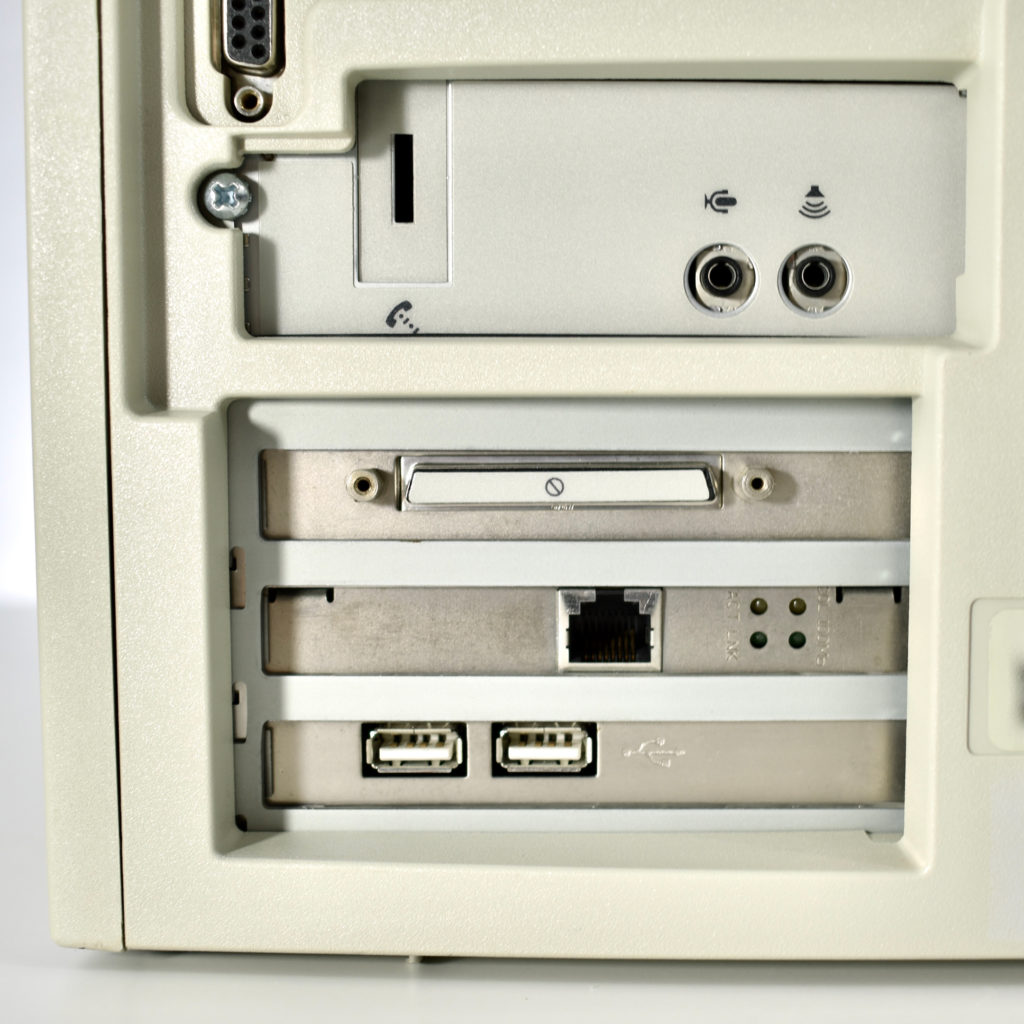
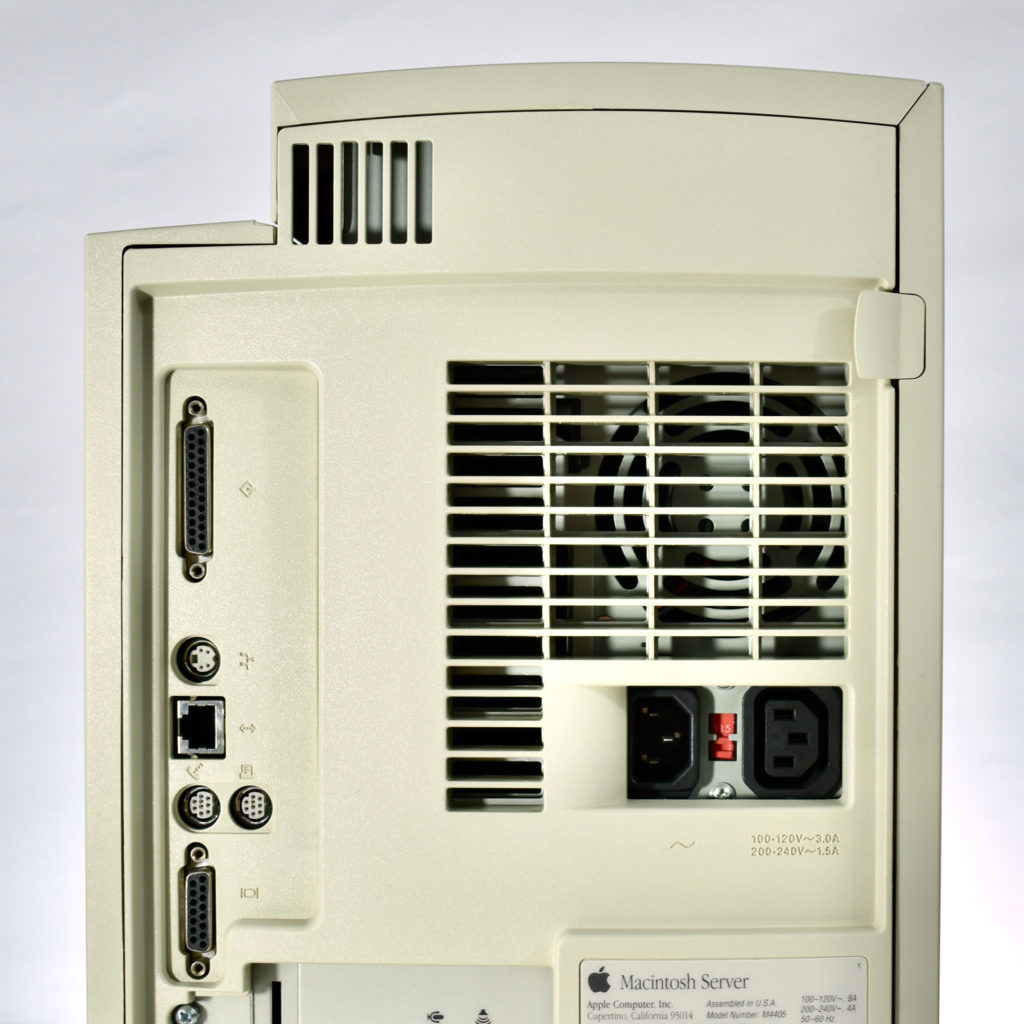
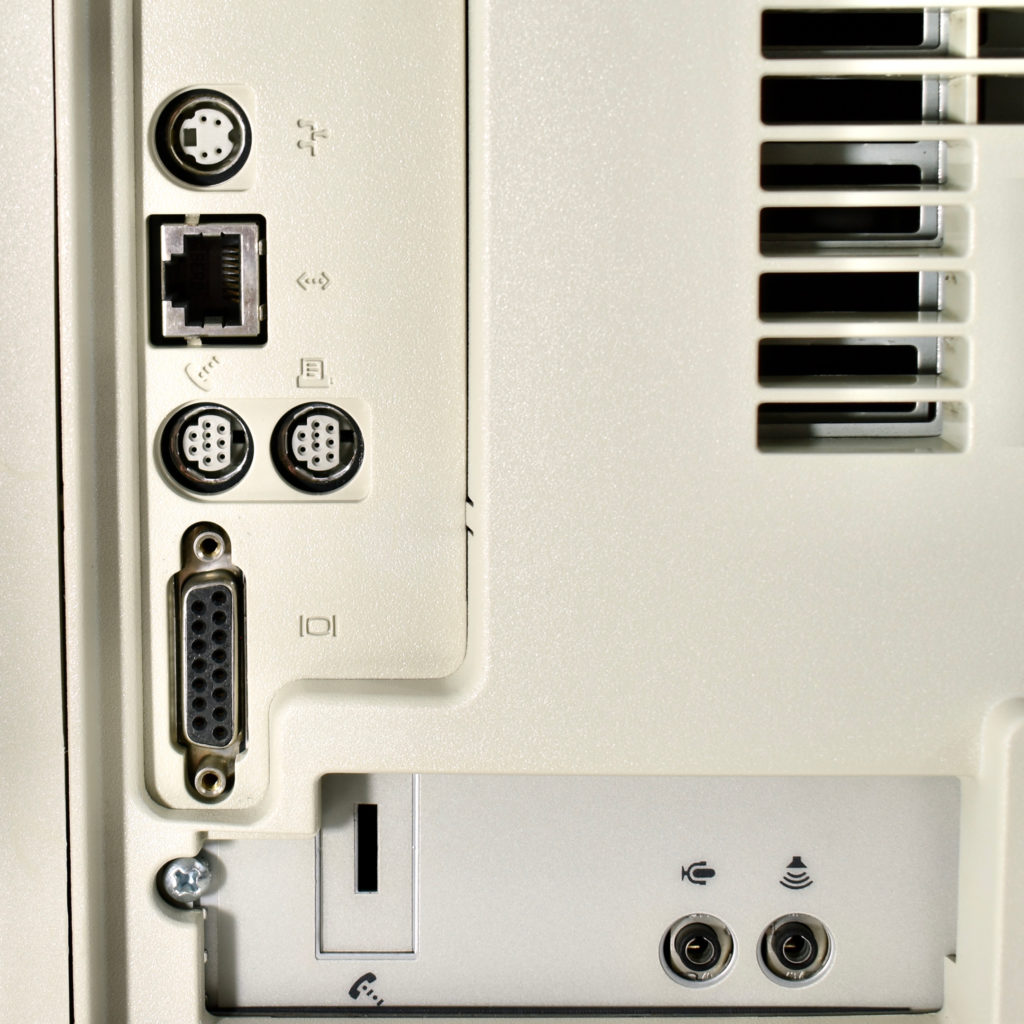
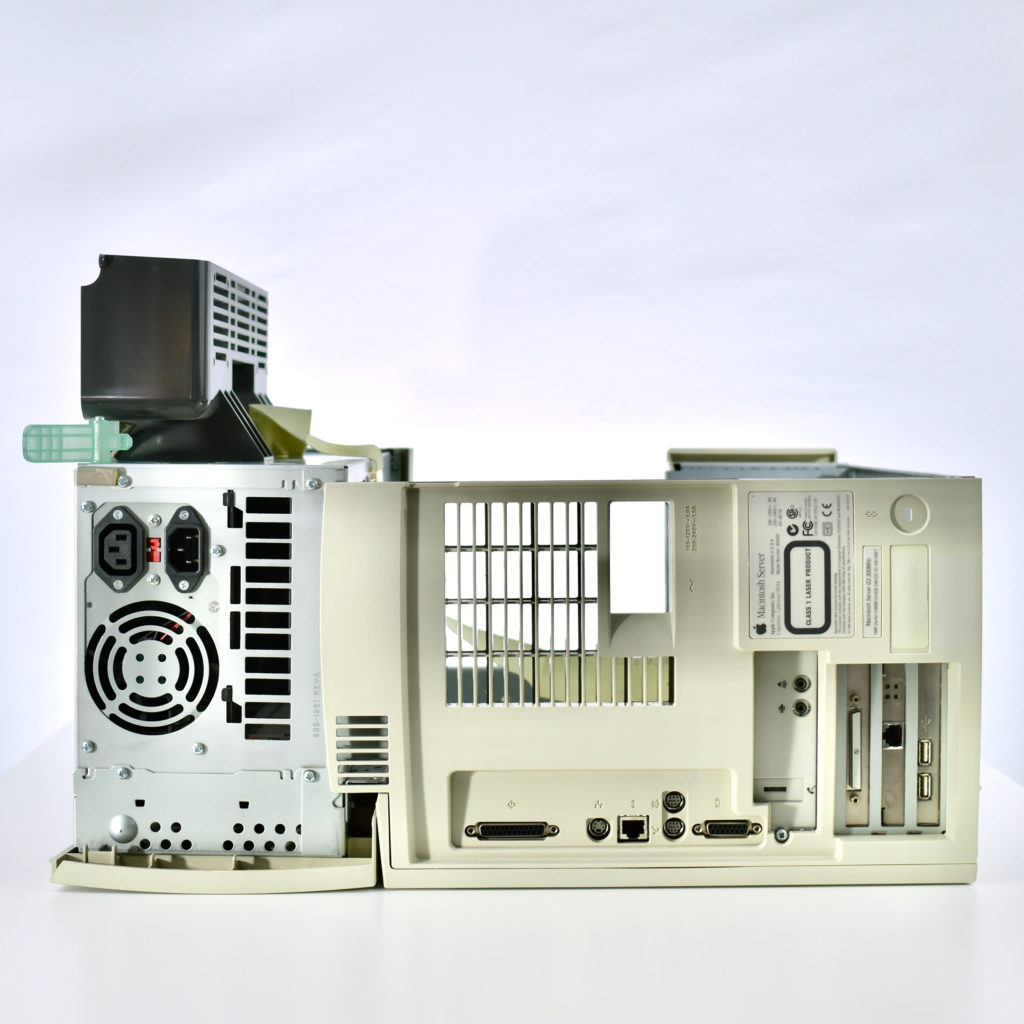
The AppleCD had a 1x Read-Only CD-ROM that could read CDs with with up to 750 MB of data. Ports on the back of the device included two 50-pin Centronics SCSI connectors, red and white audio RCA connectors, and device power input. A front input included a mini-headphone audio jack. The AppleCD could read five CD formats: CD-Audio, CD-ROM, HFS, ProDOS, and High Sierra.
To insert a CD in the AppleCD 150, a “CD Caddy” was required. The CD Caddy was a tray that slid out of the CD-ROM drive and required the user to pinch the edges of the tray to open a clear plastic hinged lid, insert the CD-ROM, and then slide the tray into the drive so it could be read by the drive.
Several models of the AppleCD drive were made, including the SC, SC Plus, 150, 300, 300e, 300i plus, 600i, 600e plus, and 1200i.