When Phil Schiller introduced the iPhone 11 at a special event on September 10, 2019, he described the device:
“iPhone 11 is the next generation of iPhone, packed with great new capabilities in an incredible design, including new Ultra Wide and Wide cameras for gorgeous videos and photos, the power and ease of use of iOS 13, and A13 Bionic—the fastest chip ever in a smartphone that quickly handles the tasks that matter most to people every day.”
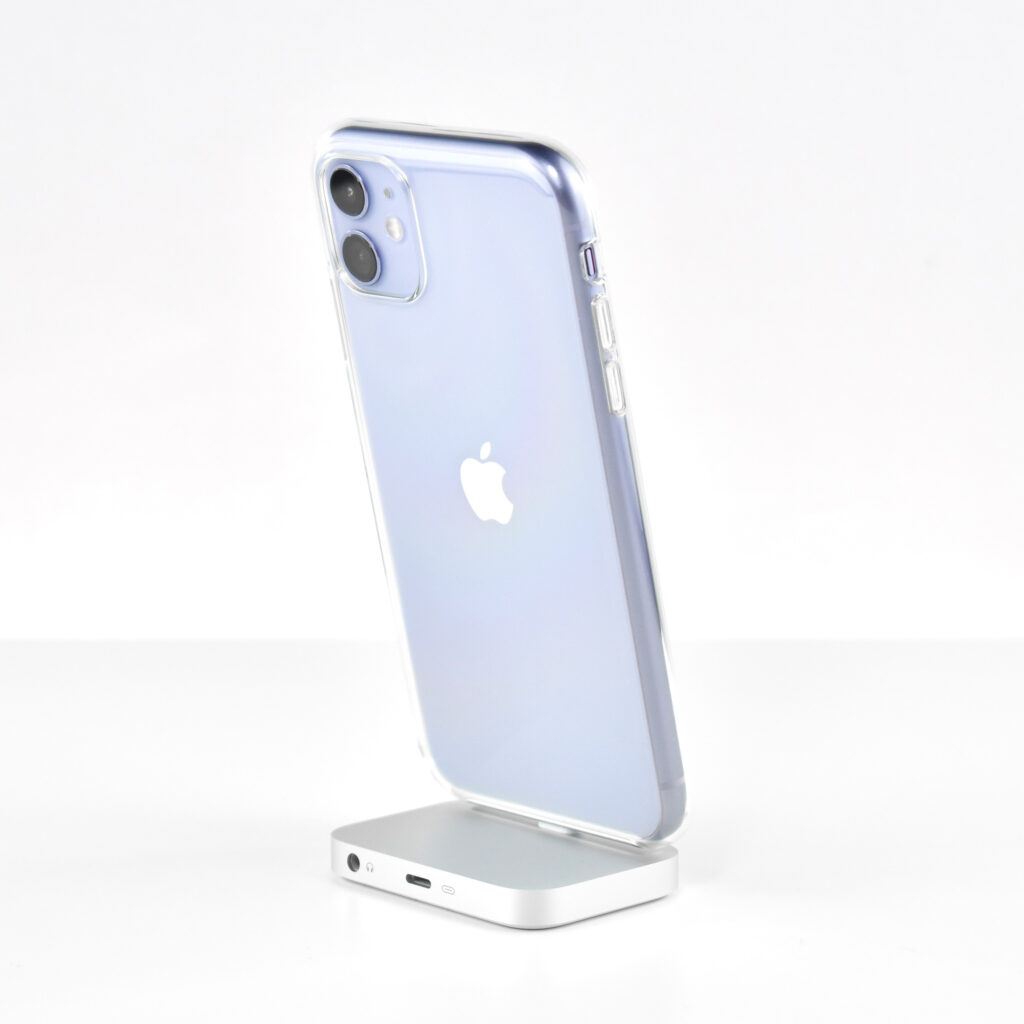
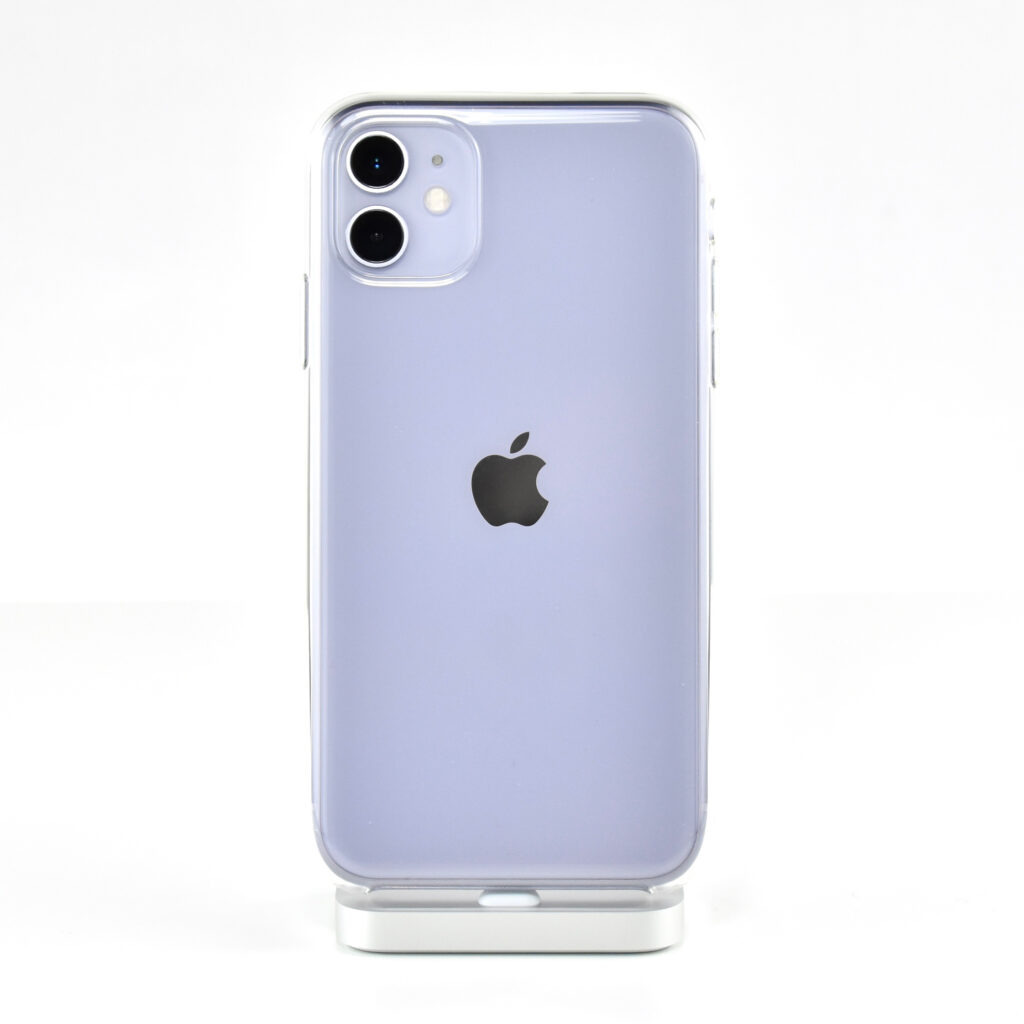
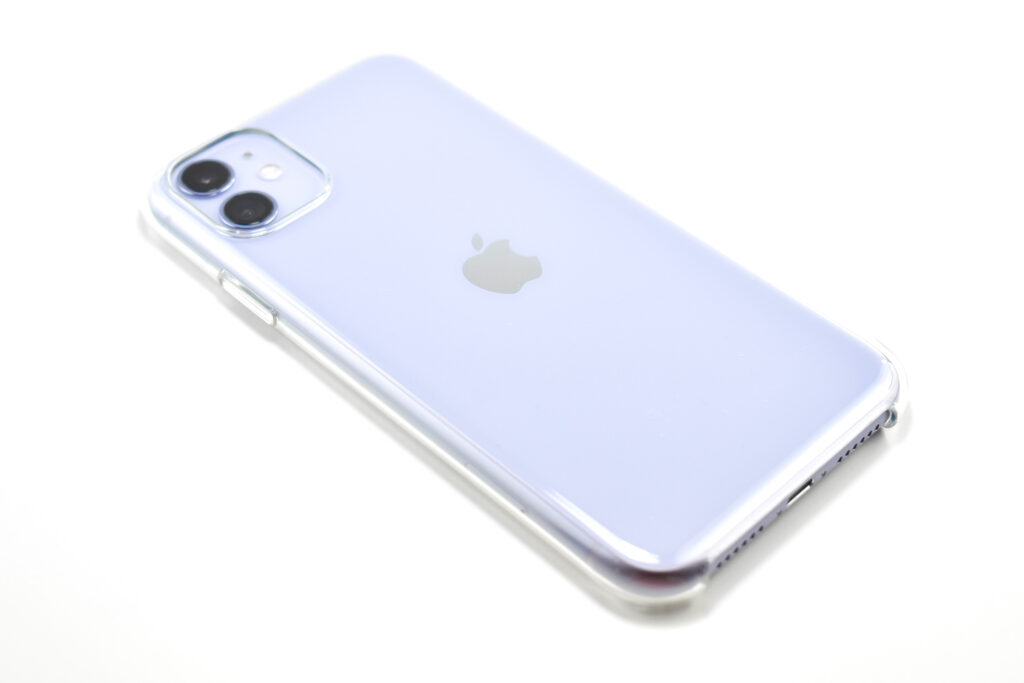
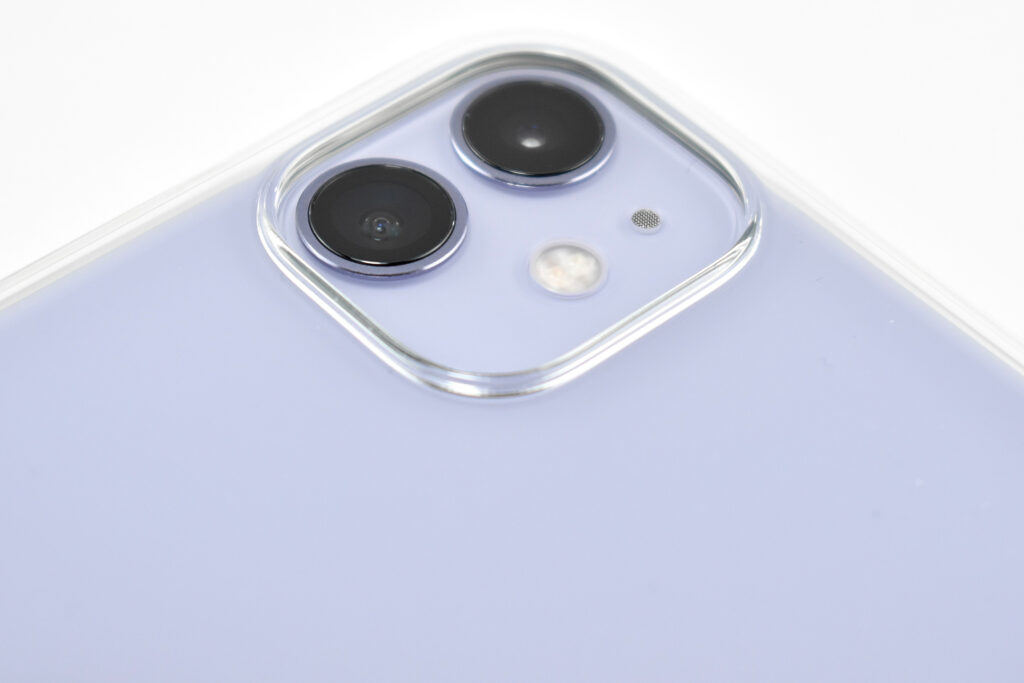
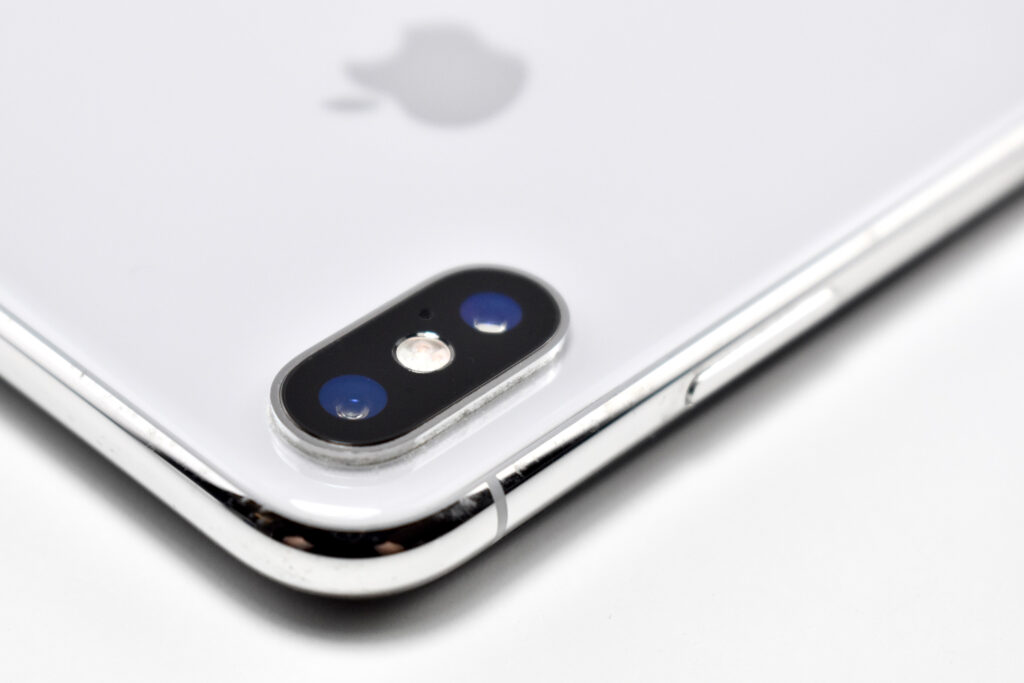
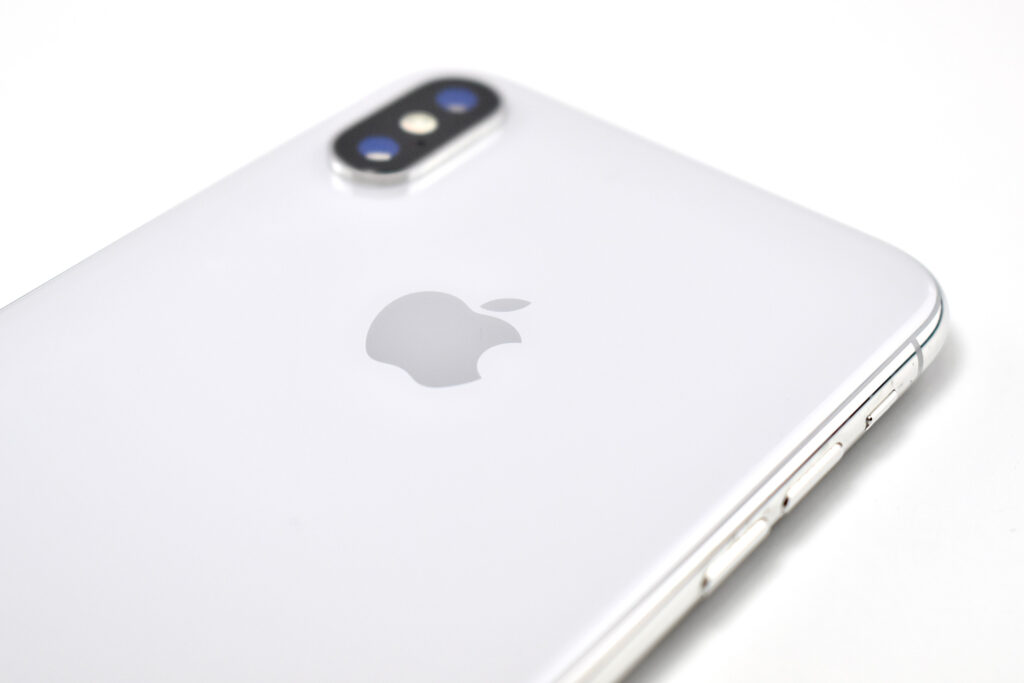
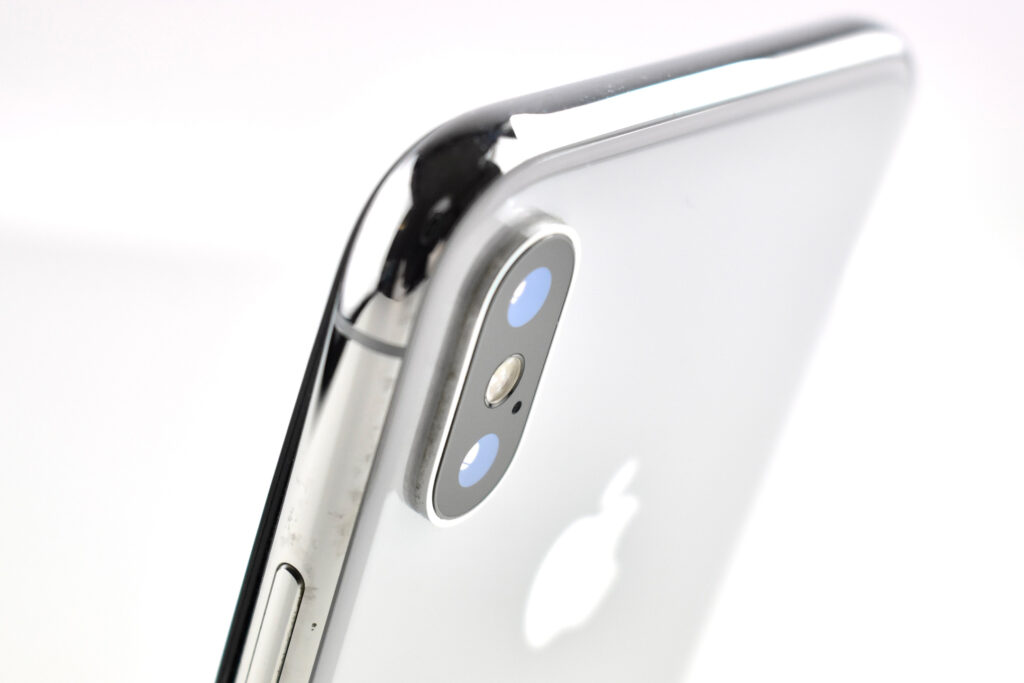
The iPhone 11 was the first of Apple’s base model phones to include a dual-camera system. Apple described the cameras in a press release:
“iPhone 11 introduces a dual-camera system with all-new Ultra Wide and Wide cameras that are deeply integrated into iOS 13, offering the highest quality video in a smartphone and major advancements in photography for the ultimate camera experience.”
Compared to previous models, the camera system was a major leap forward for iPhone. The camera system had two 12MP cameras (Ultra Wide and Wide). The A13 chip allowed Portrait mode with advanced bokeh and Depth Control, and Portrait Lighting included six effects: Natural, Studio, Contour, Stage, Stage Mono, and High-Key Mono. Panorama mode allowed photos of up to 63MP. Videos could be recorded at up to 4K (at 24, 25, 30, or 60 fps). Machine learning capabilities allowed Cinematic video stabilization (4K, 1080p, and 720p) and continuous autofocus video.
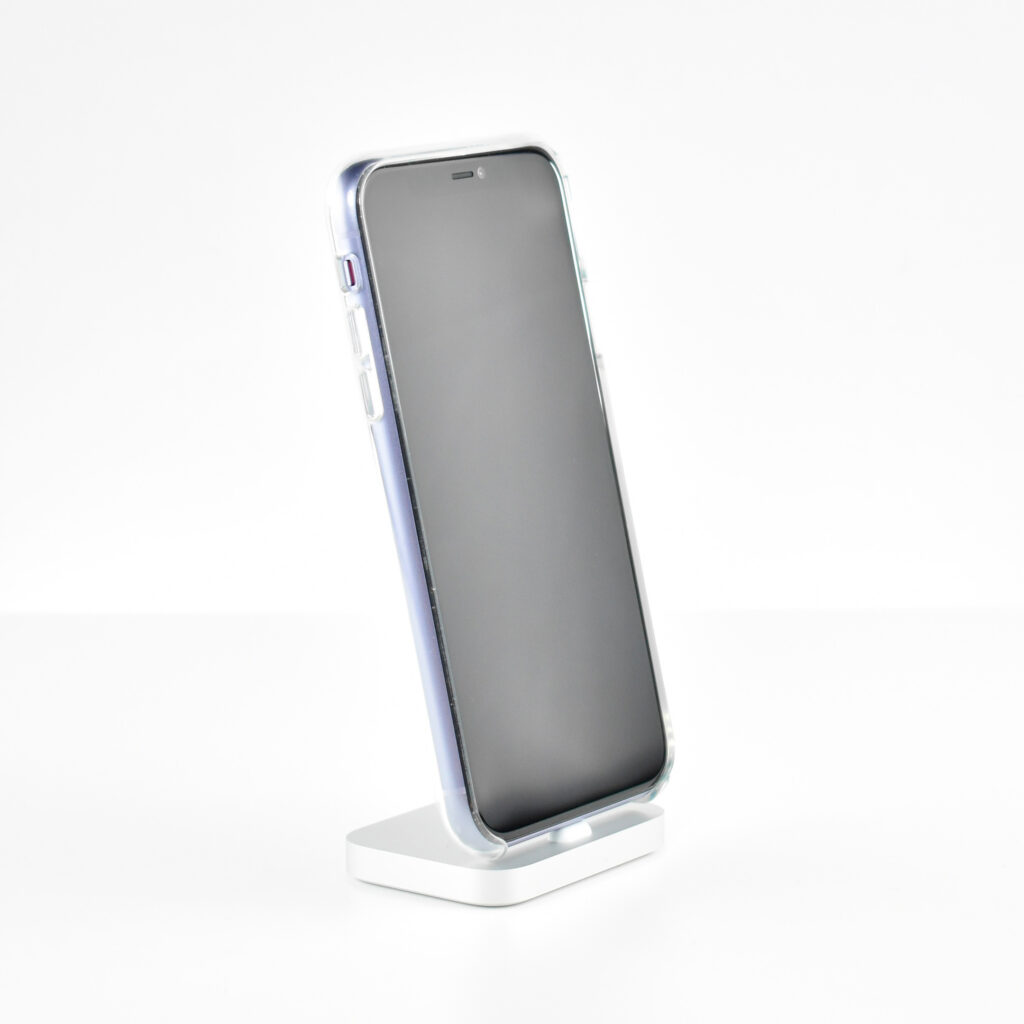
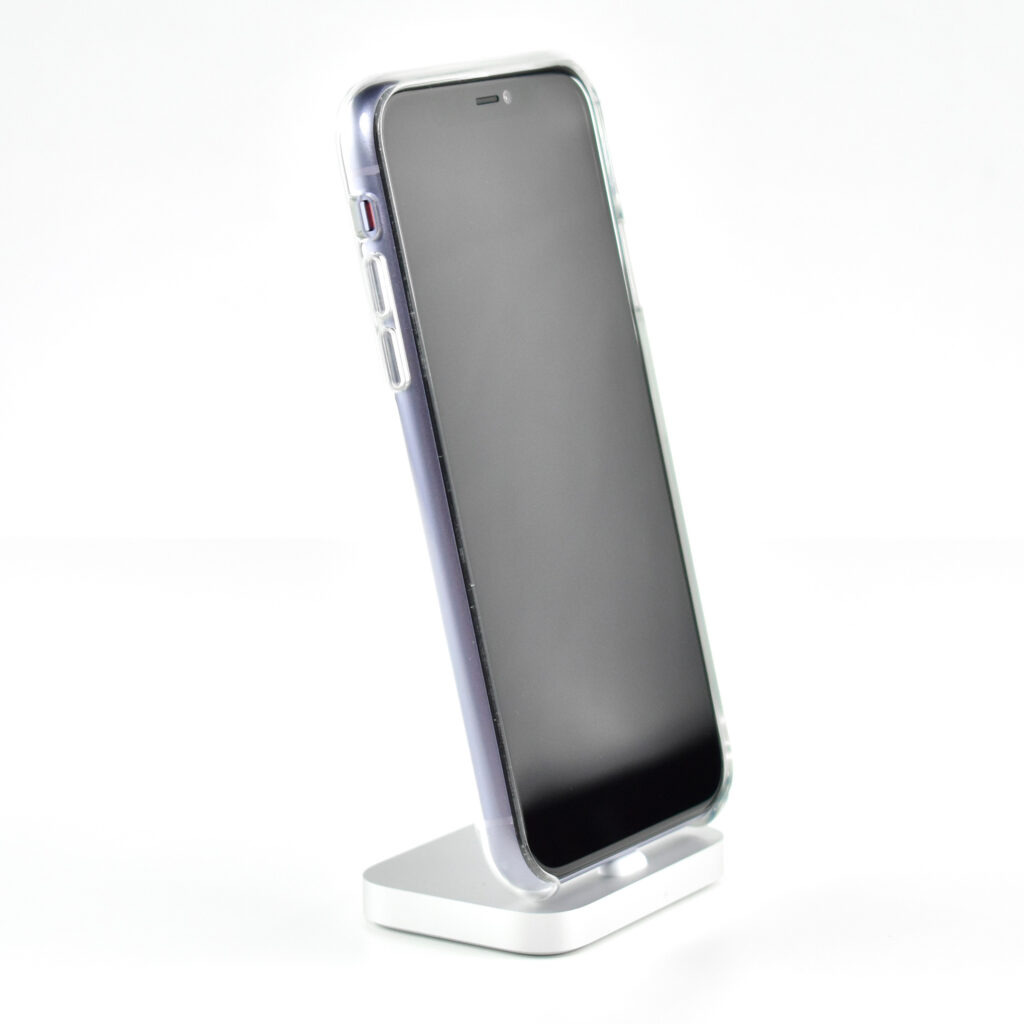
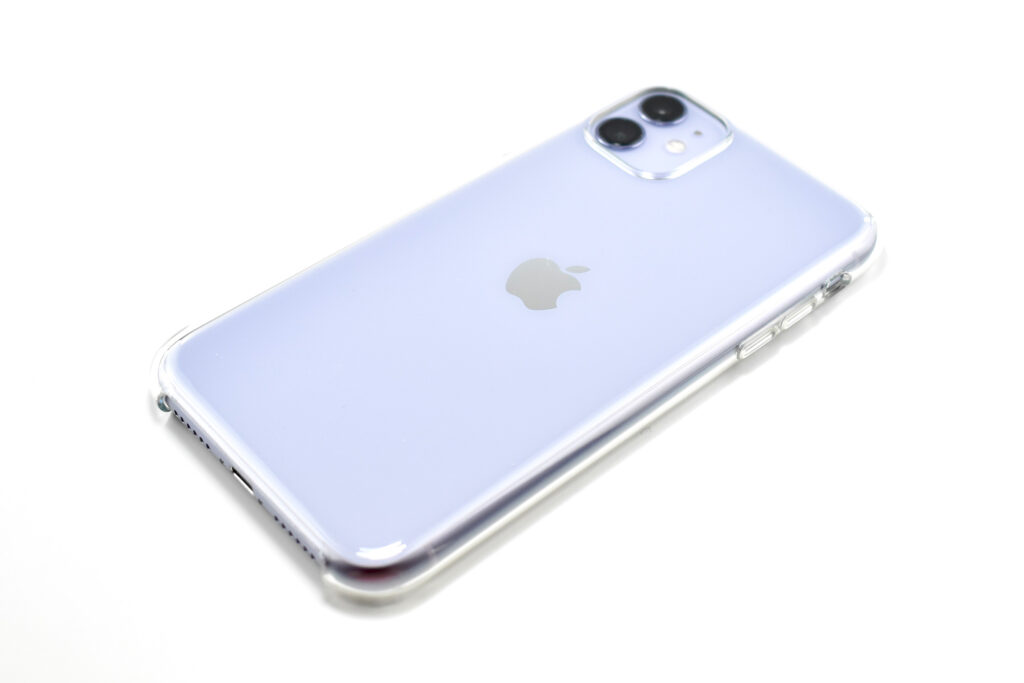
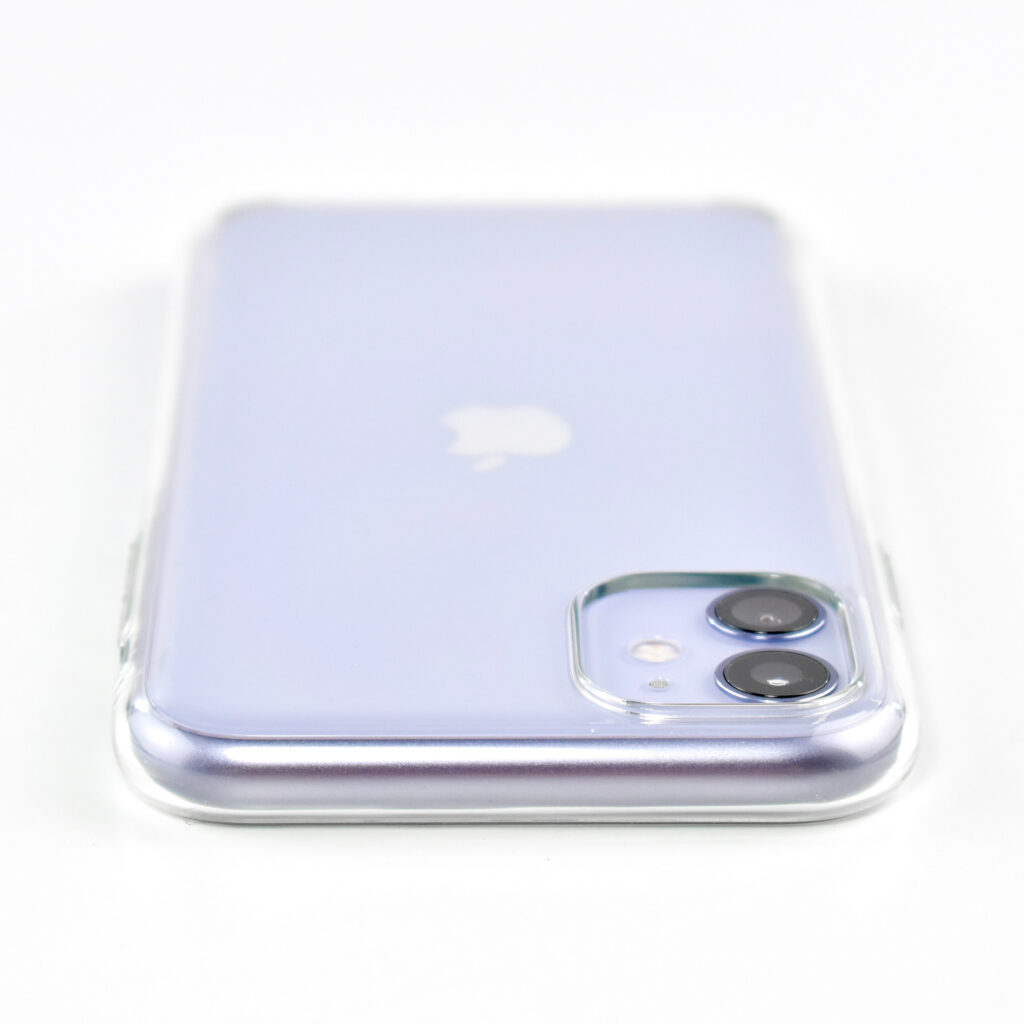
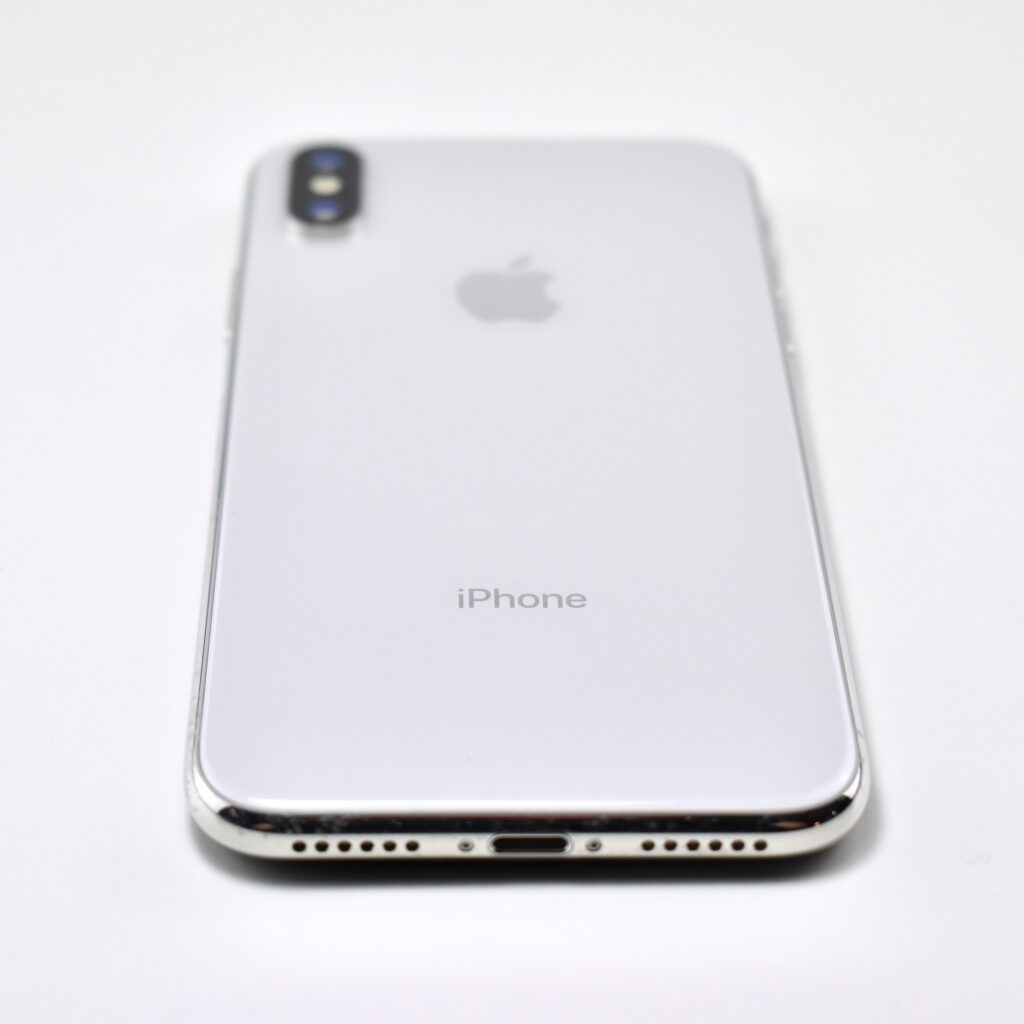
iPhone 11 was available in six “stunning colors” including purple, green, yellow, black, white and PRODUCT(RED). This example is purple, a lighter shade of purple sometimes referred to as “lilac.”
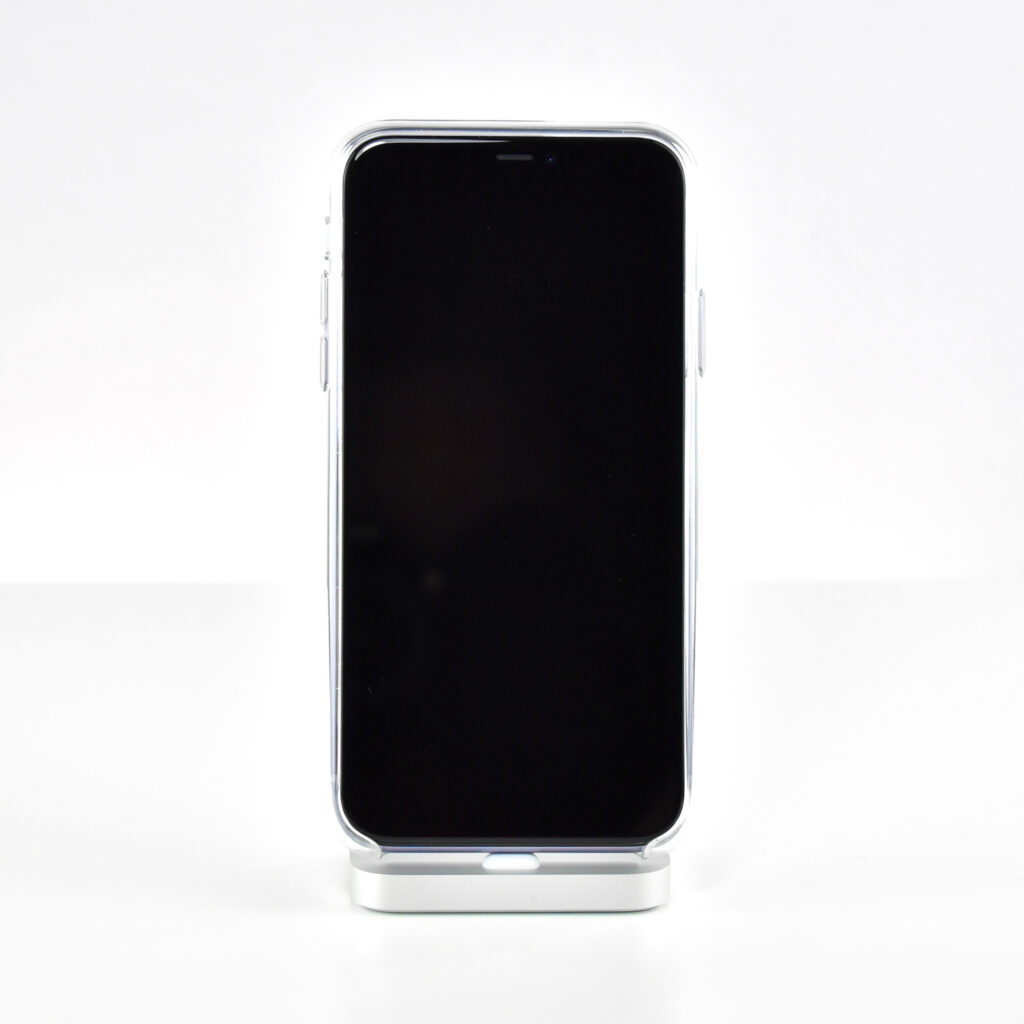
This phone had a Liquid Retina HD display that measured 6.1‑inch (diagonal) display at 1792 x 828‑pixel resolution (326 ppi). The A13 Bionic chip allowed for “the best machine learning platform in a smartphone” at the time of its release. It used a 6-core CPU with 2 performance and 4 efficiency cores, a 4-core GPU, and an 8-core Neural Engine.
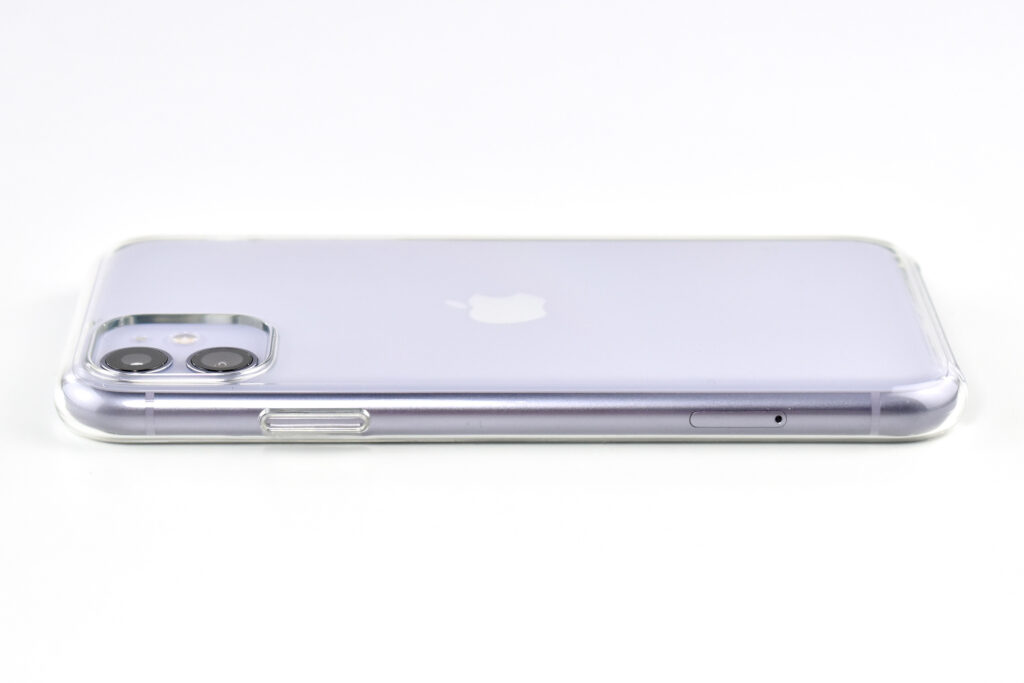
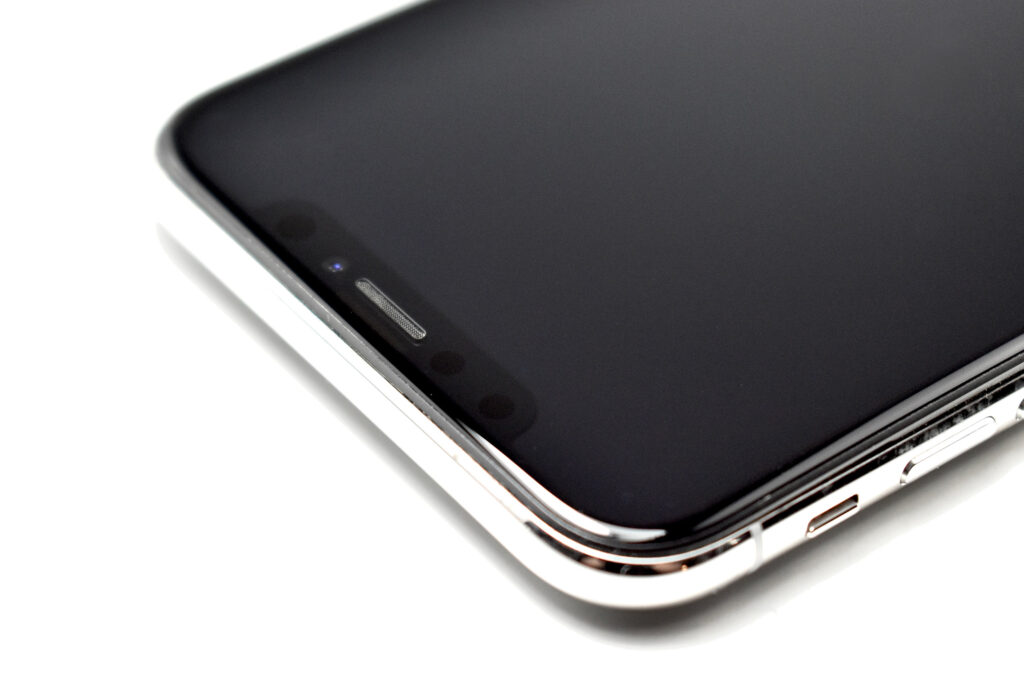
The iPhone 11 was also the first base iPhone to lack a Home button. Its six sensors included Face ID, barometer, 3‑axis gyro, accelerometer, proximity sensor, and an ambient light sensor.
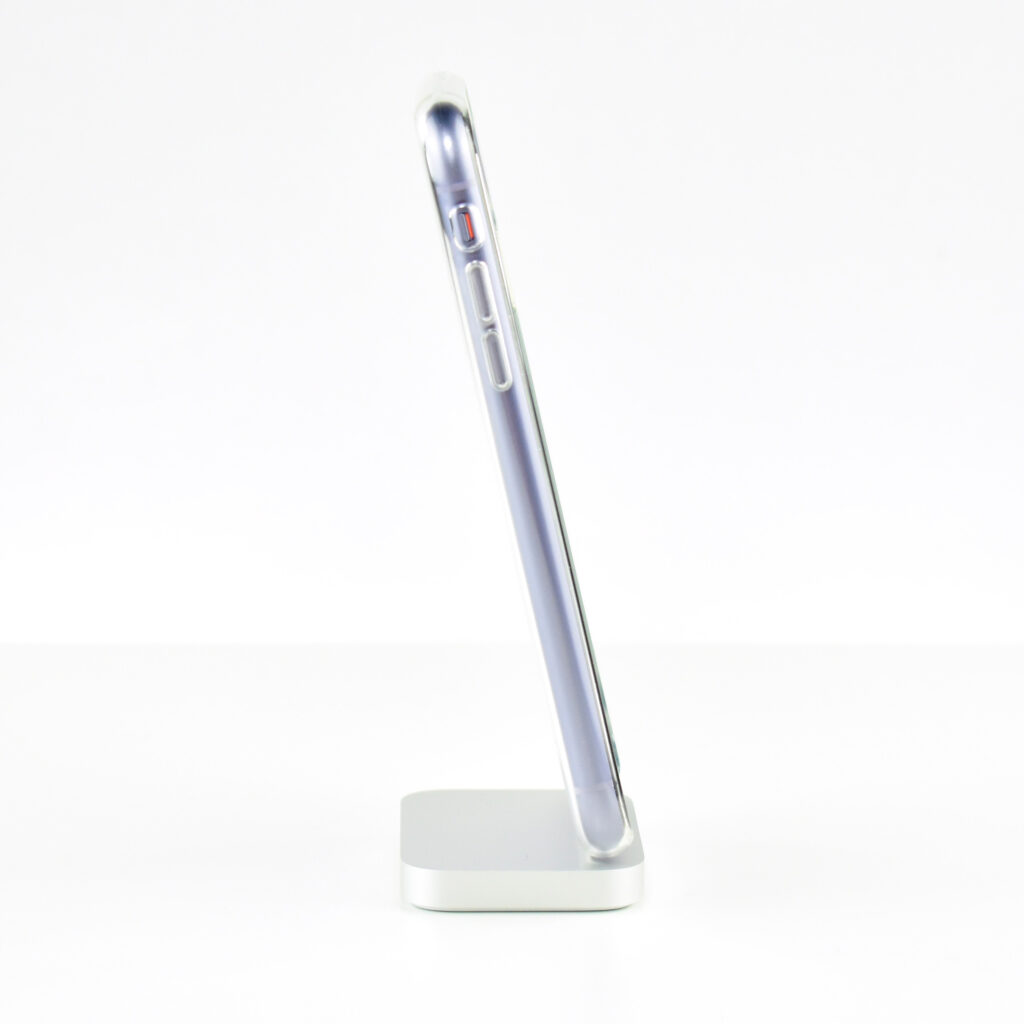
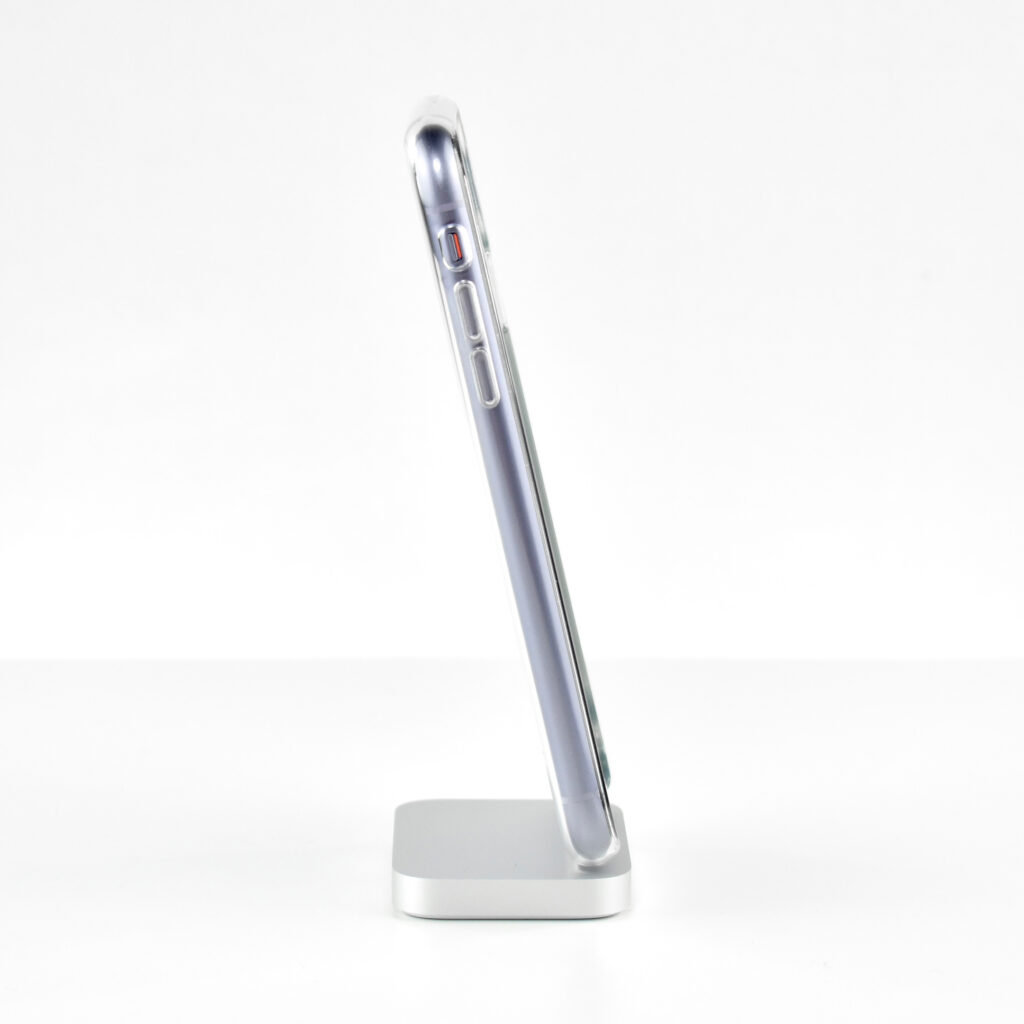
The design of the iPhone 11 included rounded edges and the front and back were made of glass. Apple noted, “With a back design that is precision milled and sculpted from a single piece of glass, iPhone 11 features the toughest glass ever in a smartphone.”
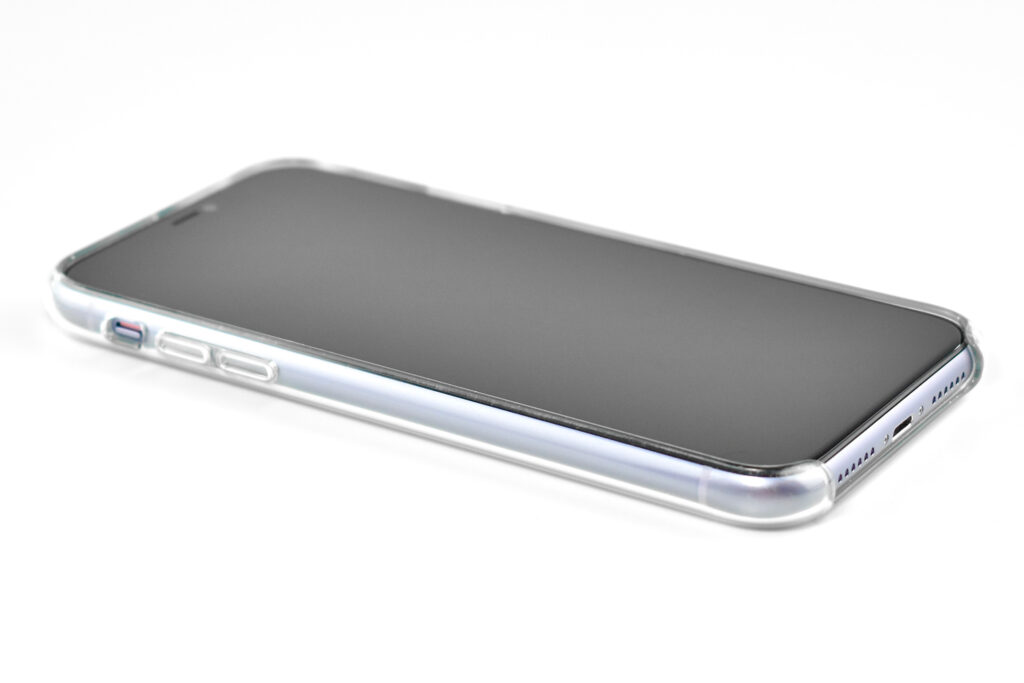
This iPhone is shown in an iPhone 11 Clear Case. Apple described the case as “Thin, light, and easy to grip.” According to Apple’s website:
“Made from a blend of optically clear polycarbonate and flexible TPU materials, the iPhone 11 Clear Case provides a solid, comfortable feel. The back is designed to be sturdy, while the sides are made from a softer, more flexible material that fits right over the buttons for an improved grip. And when it’s time to wirelessly charge, just leave the case on and set your iPhone on your Qi-certified charger. On the surface, a scratch-resistant coating has been applied to both the interior and exterior. And all materials and coatings are optimized to prevent yellowing over time.”
Sources: Apple (specs, Newsroom)