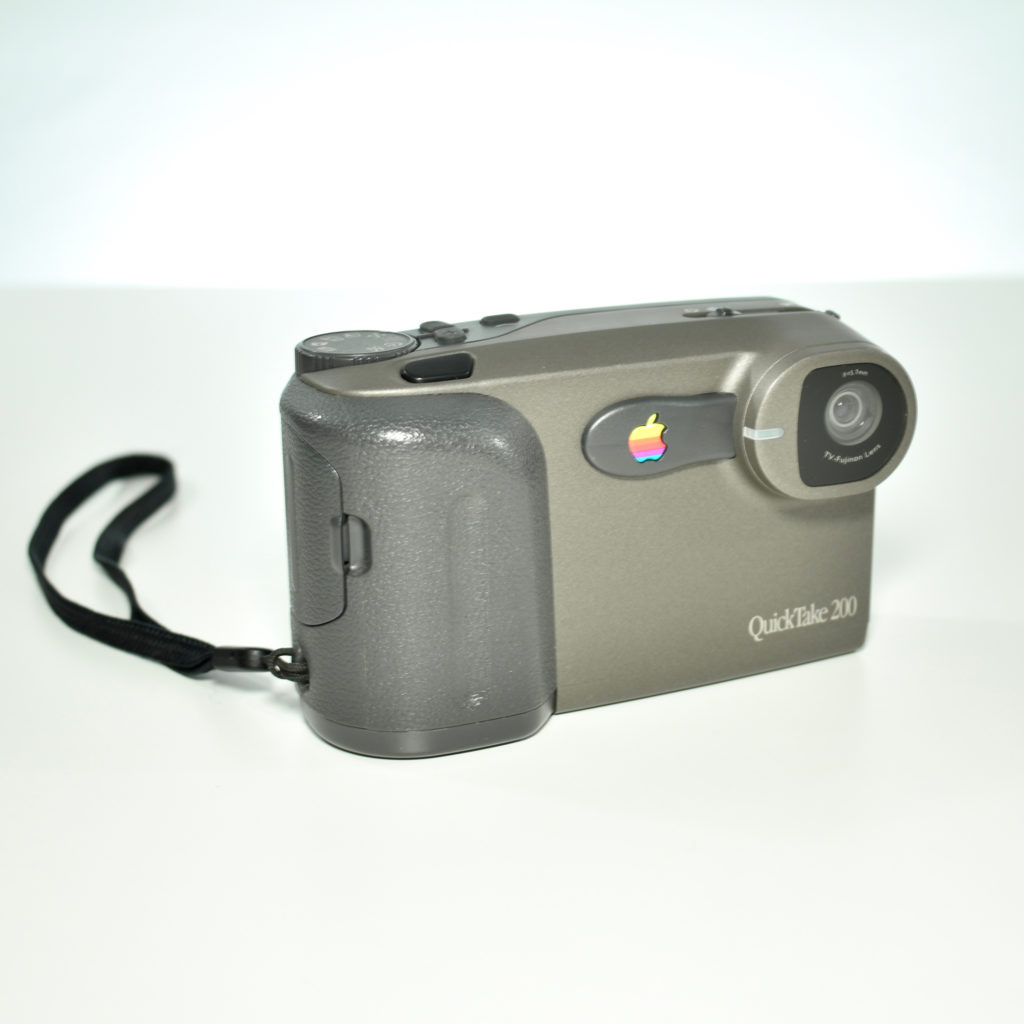
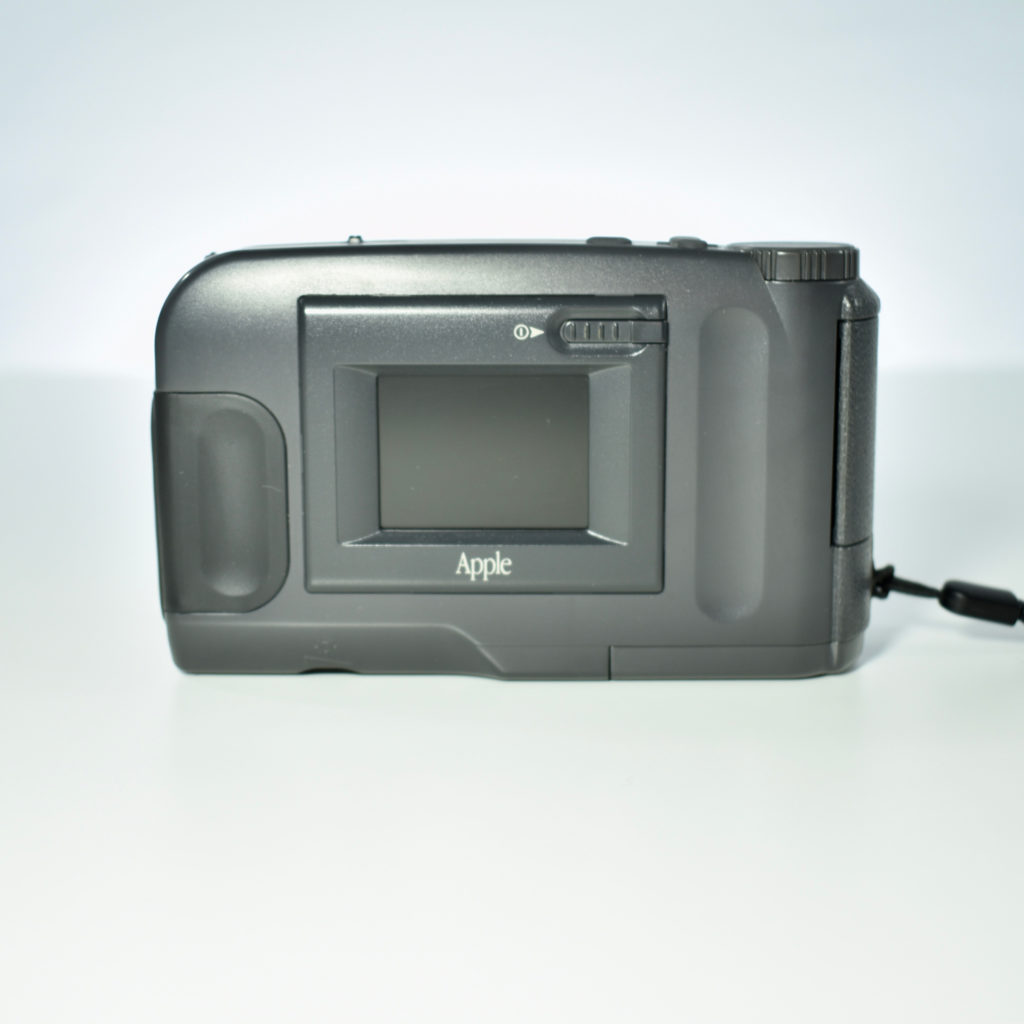
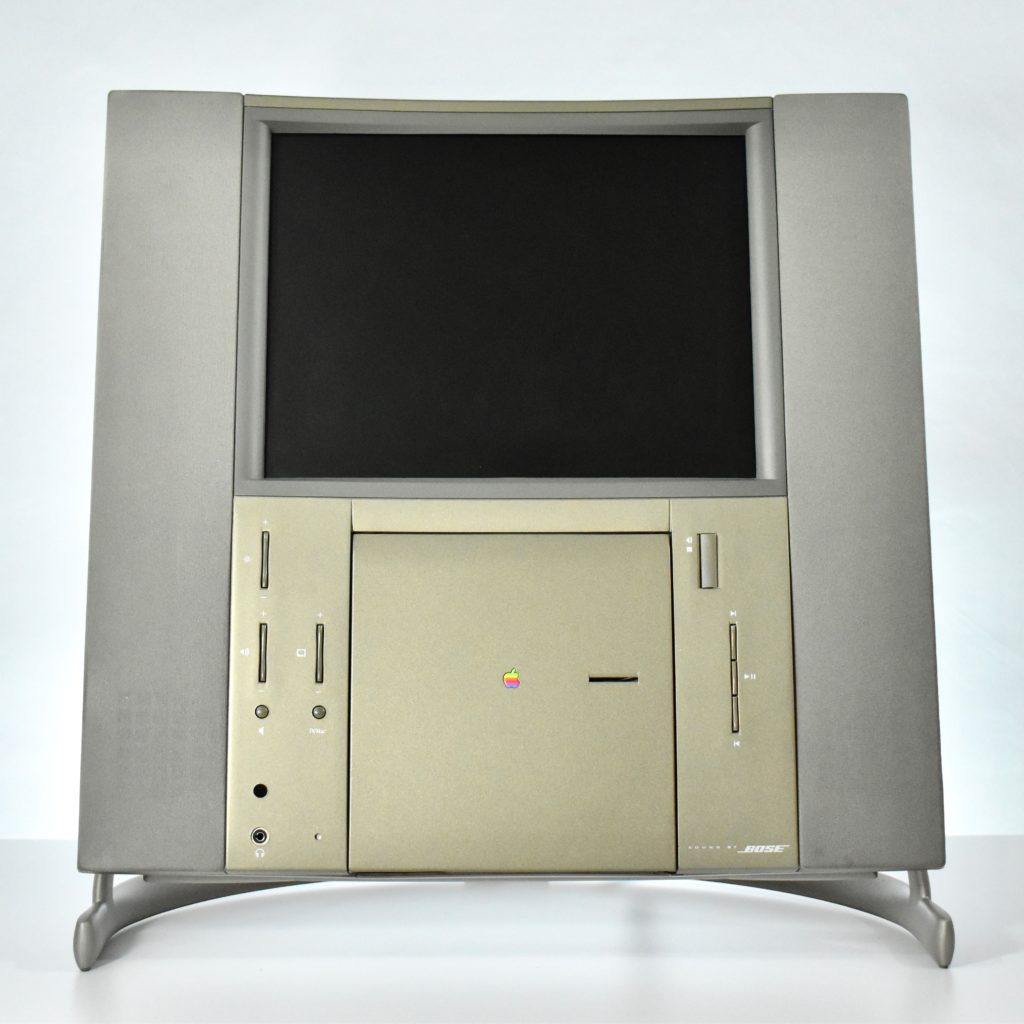
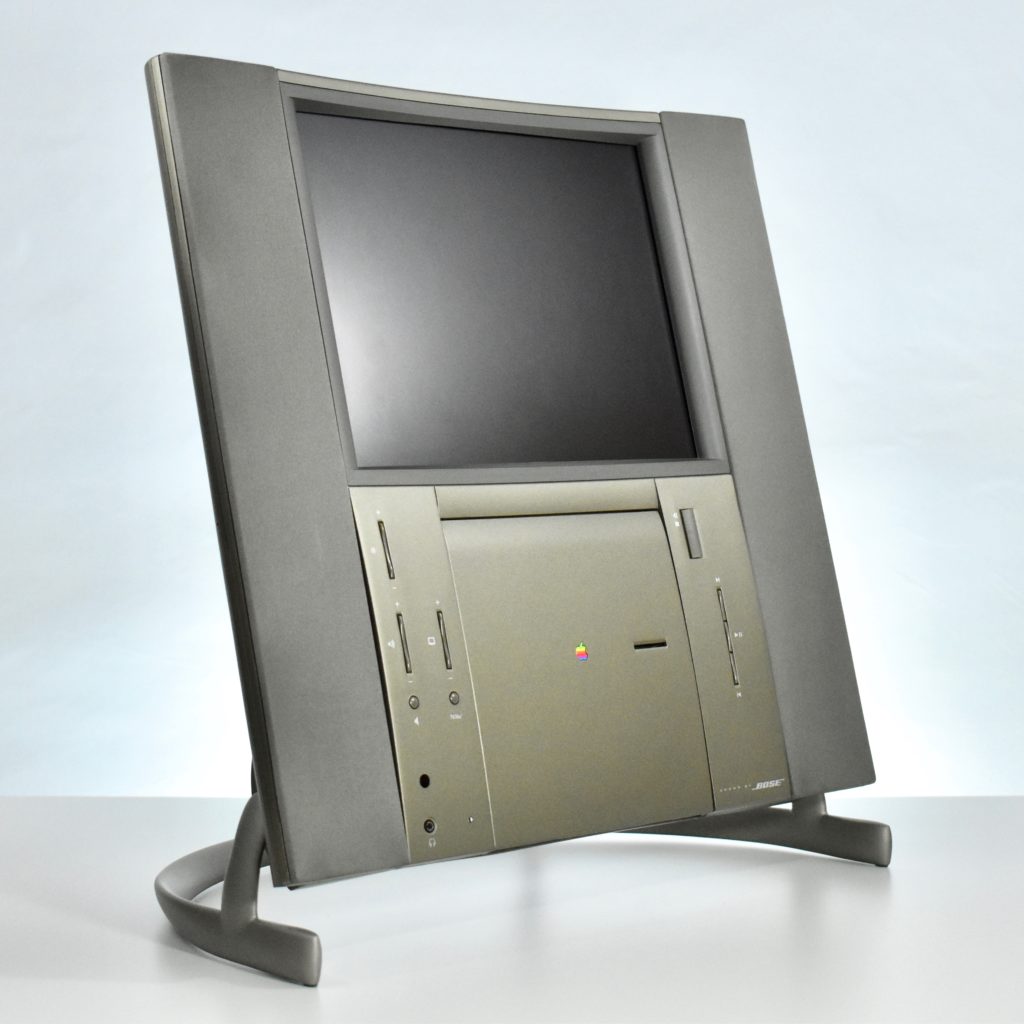
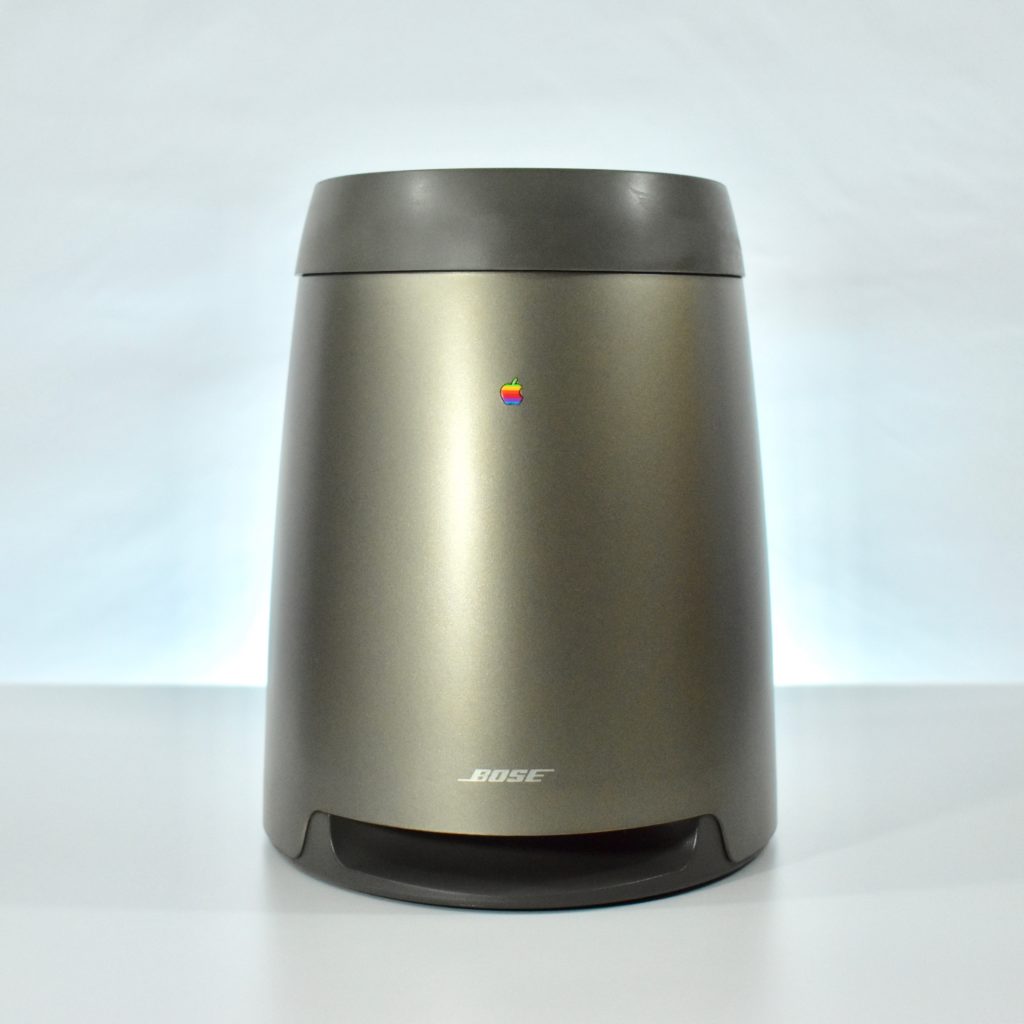
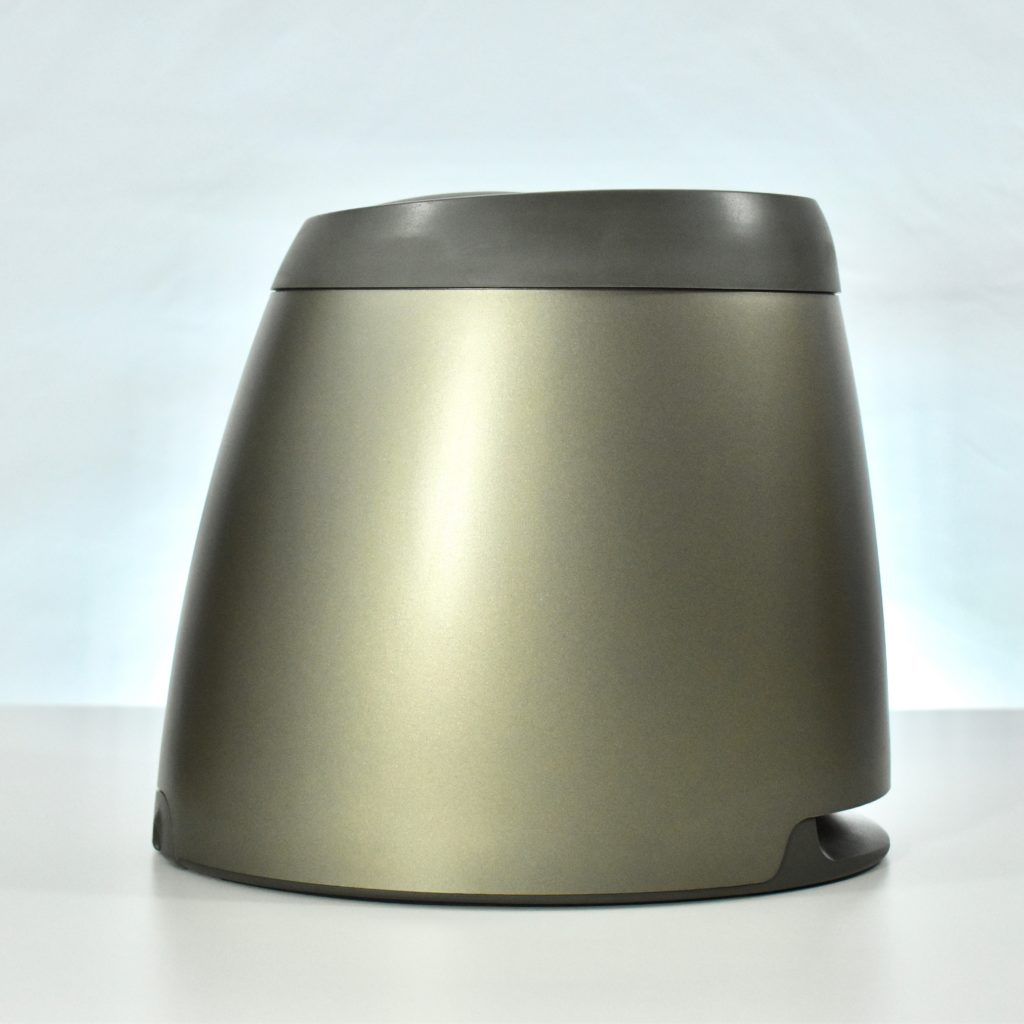
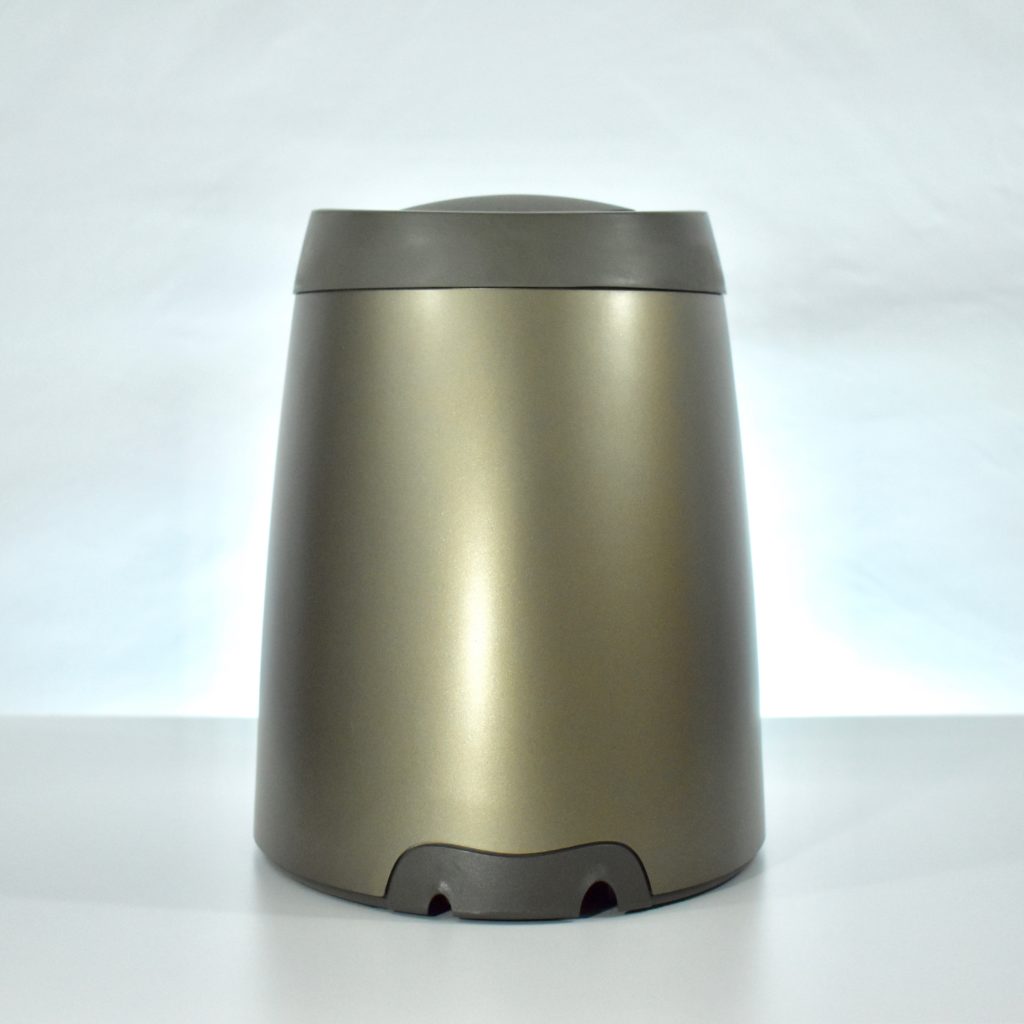
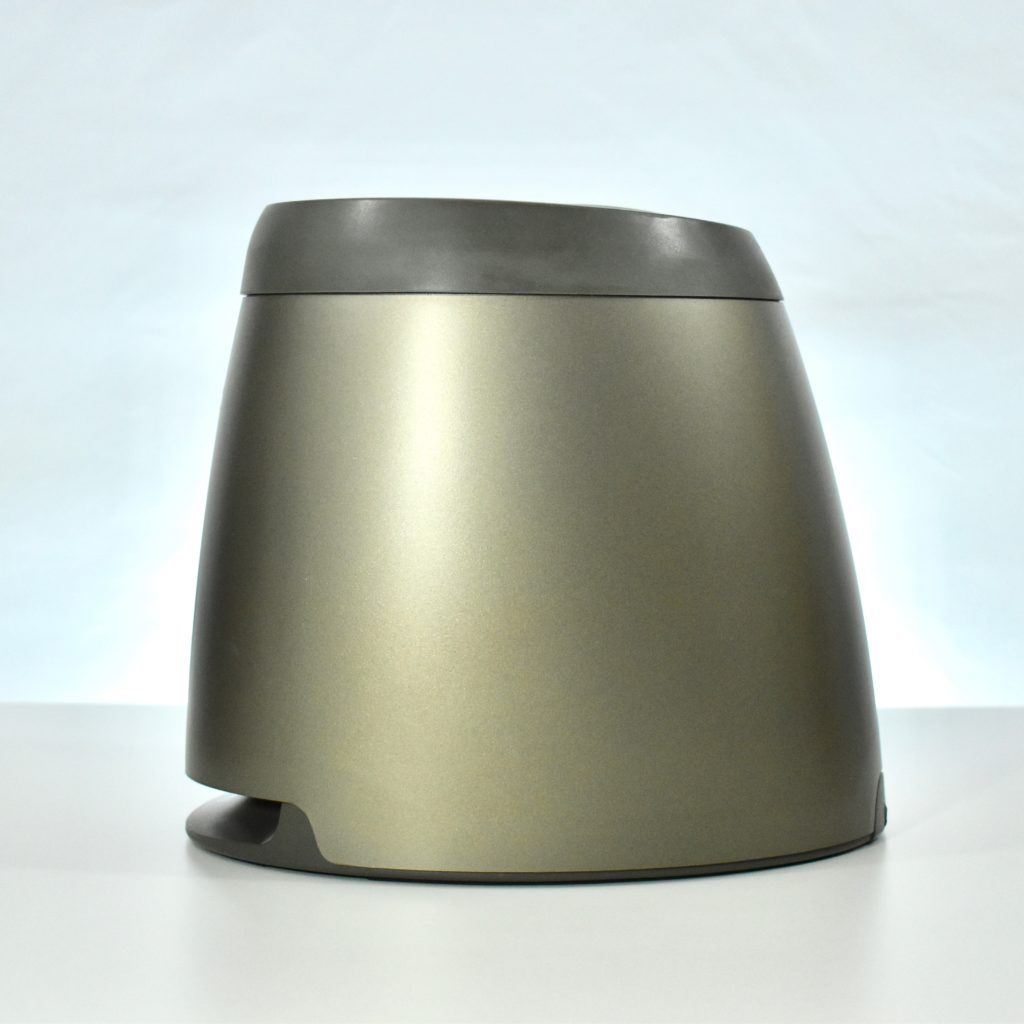
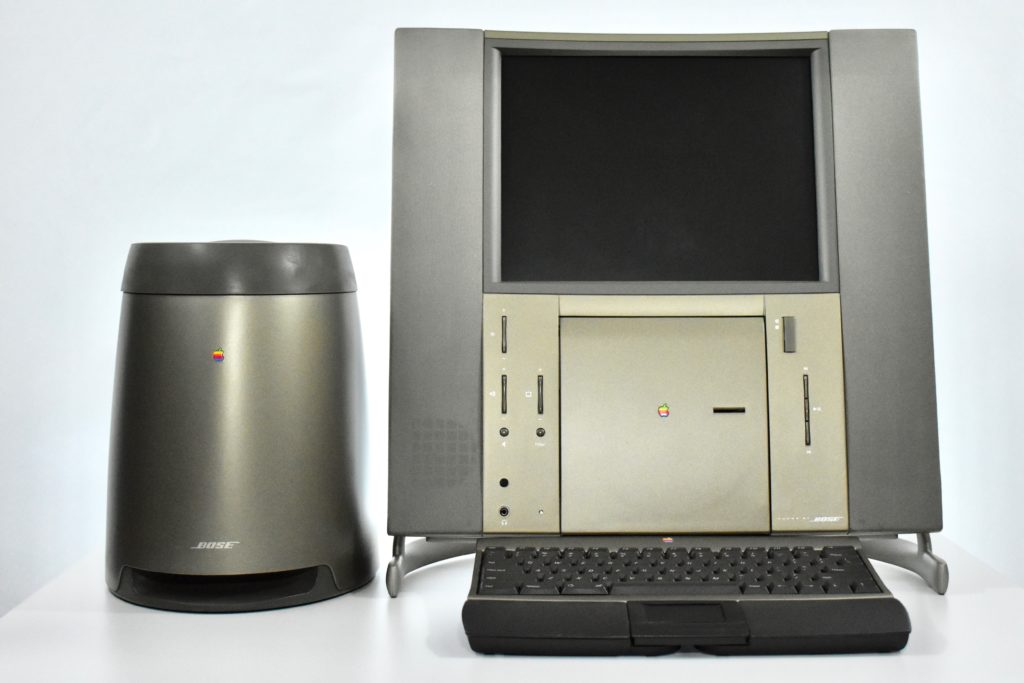
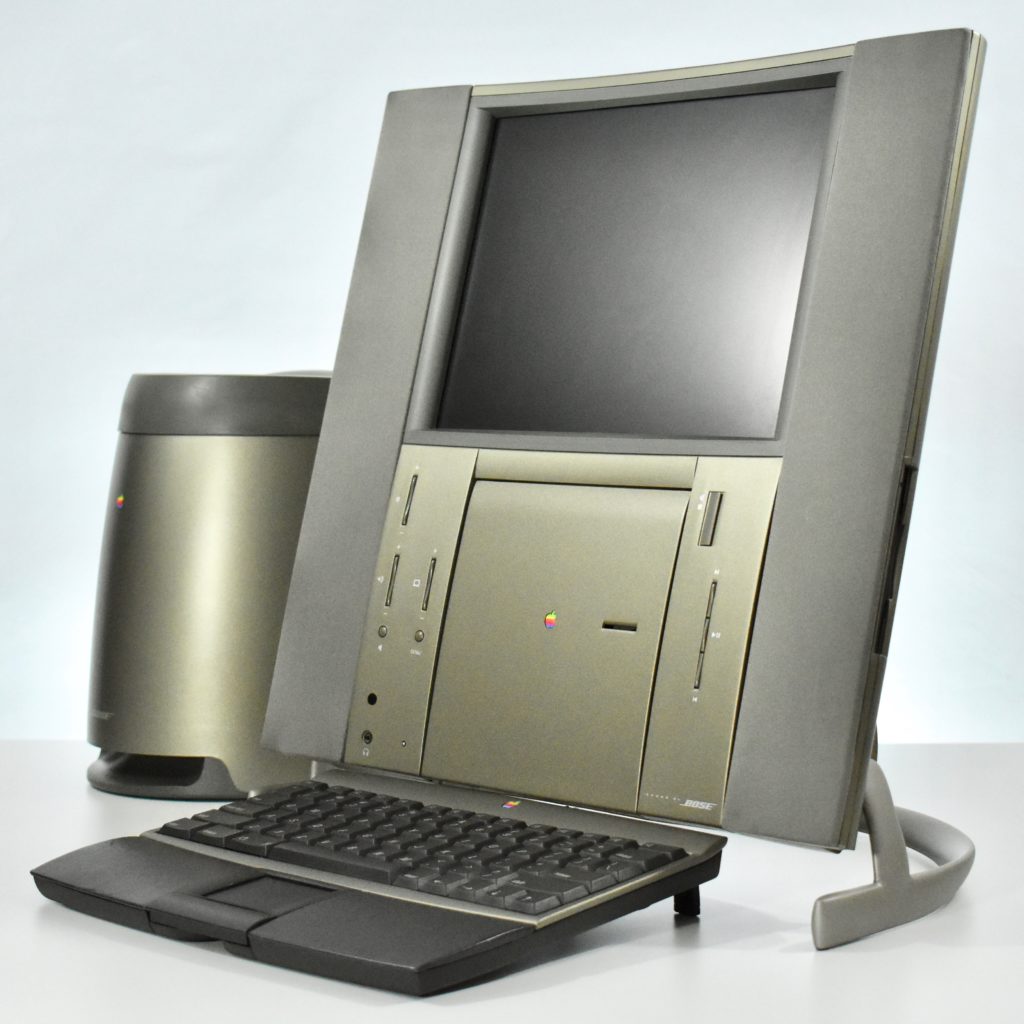
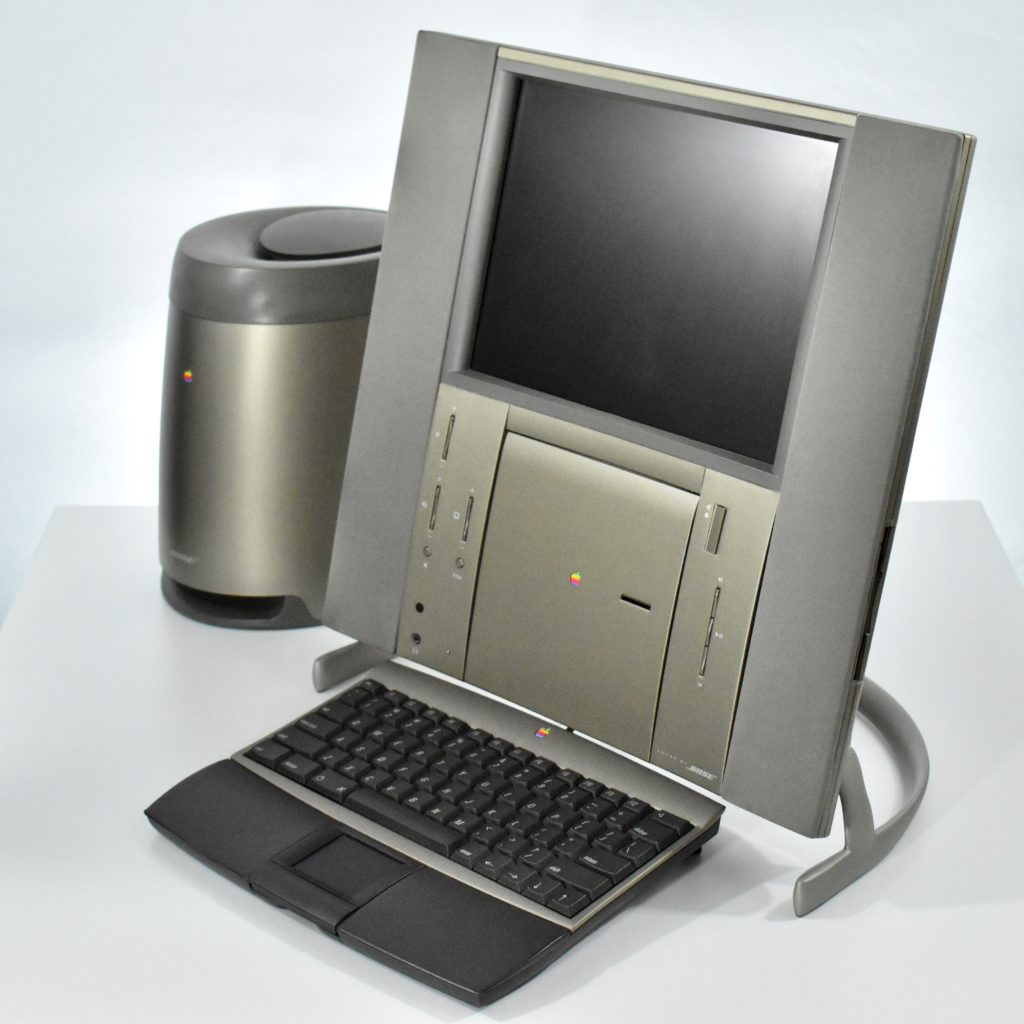
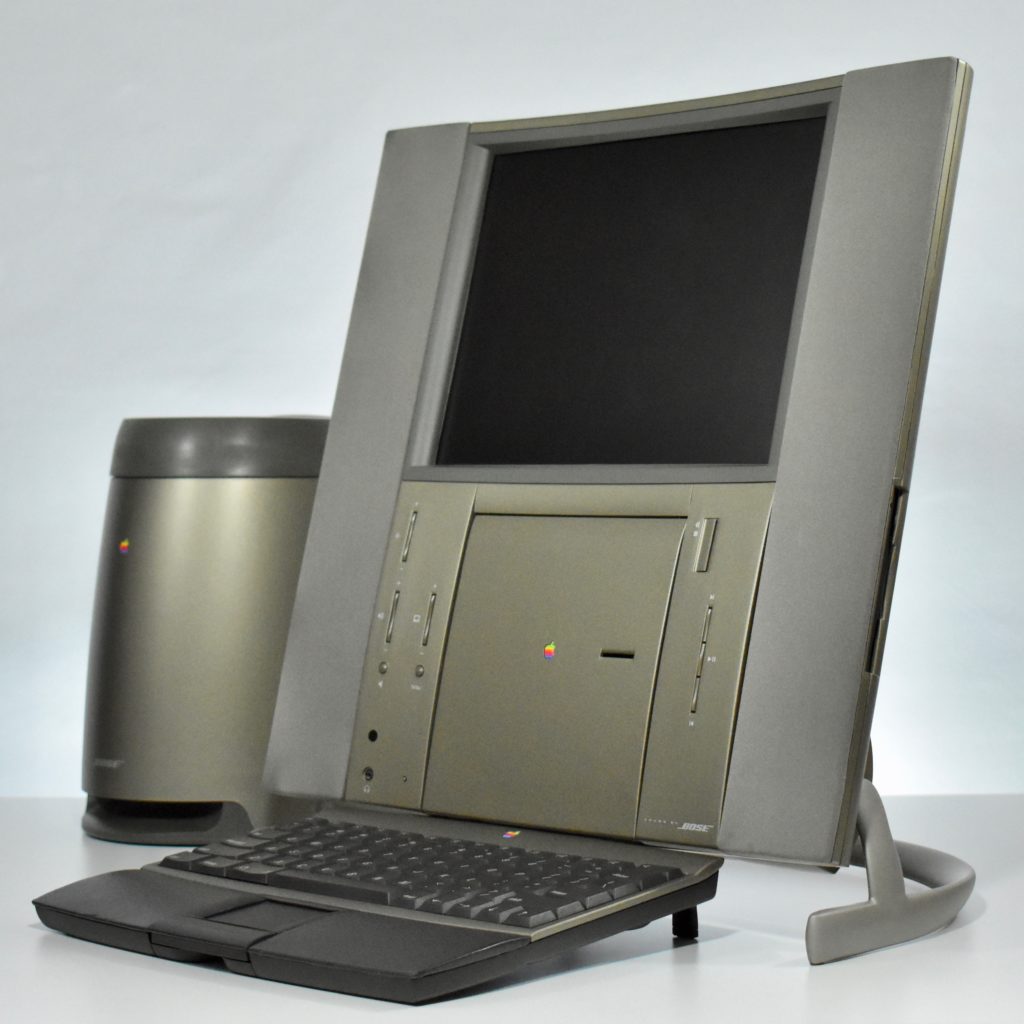
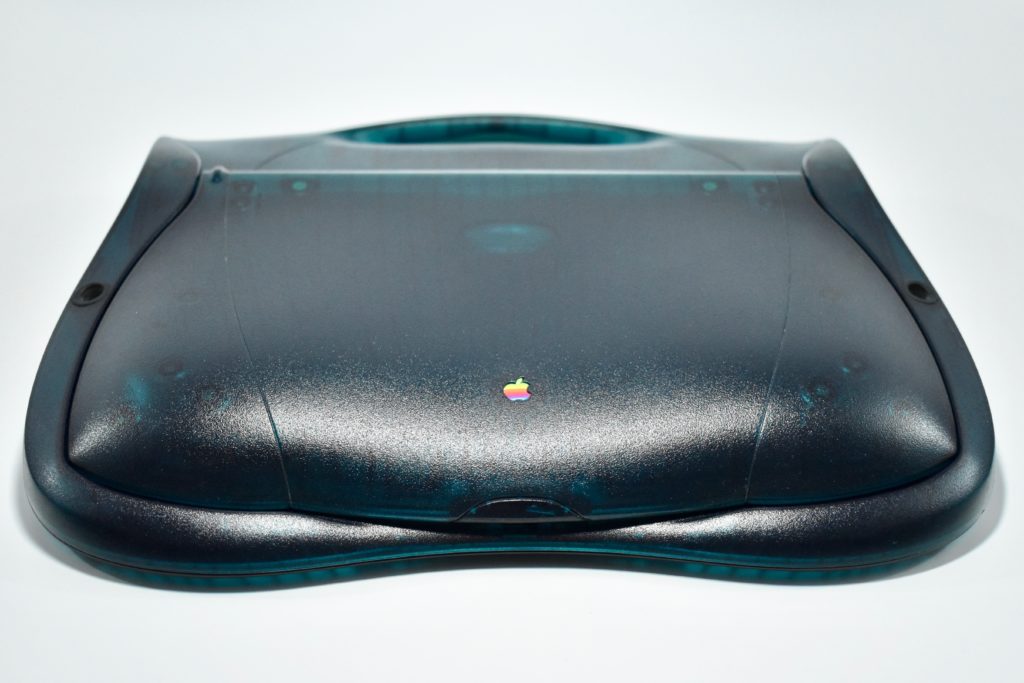
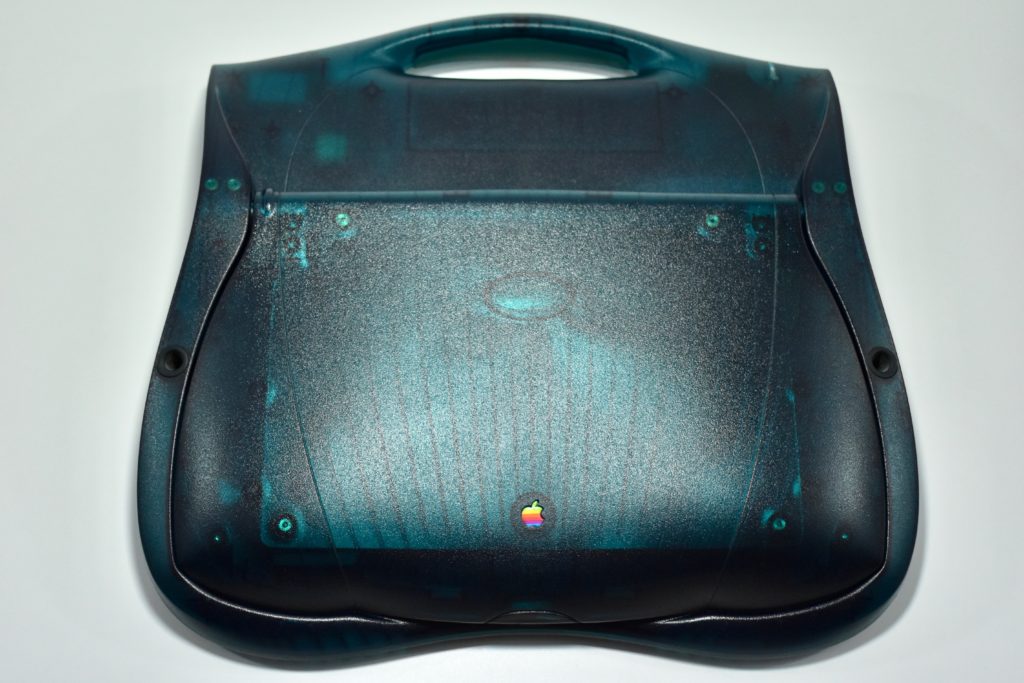
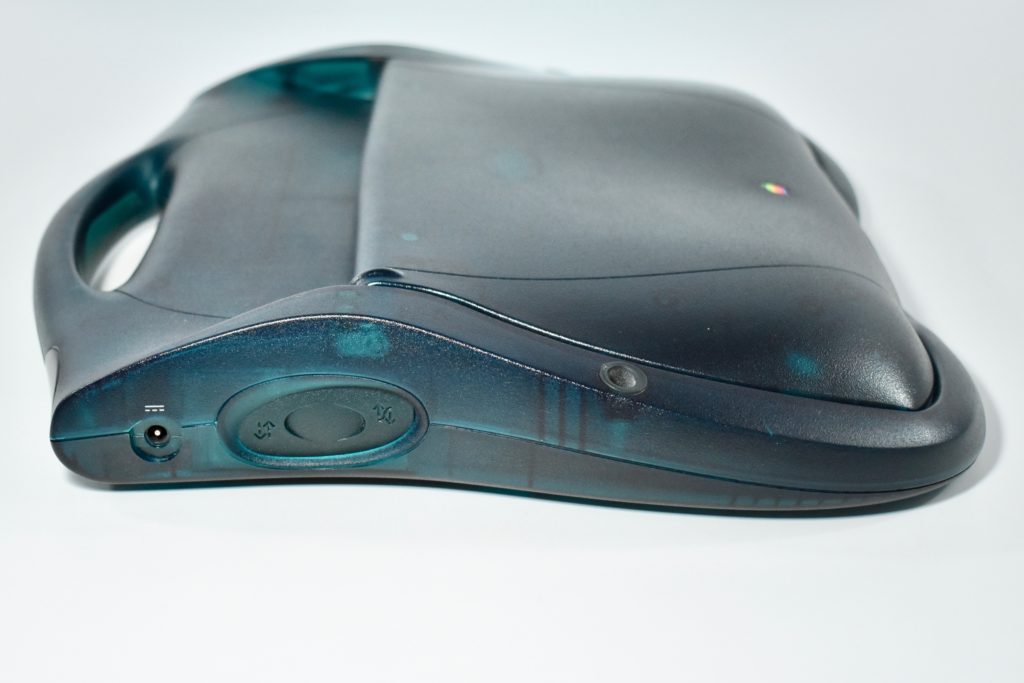
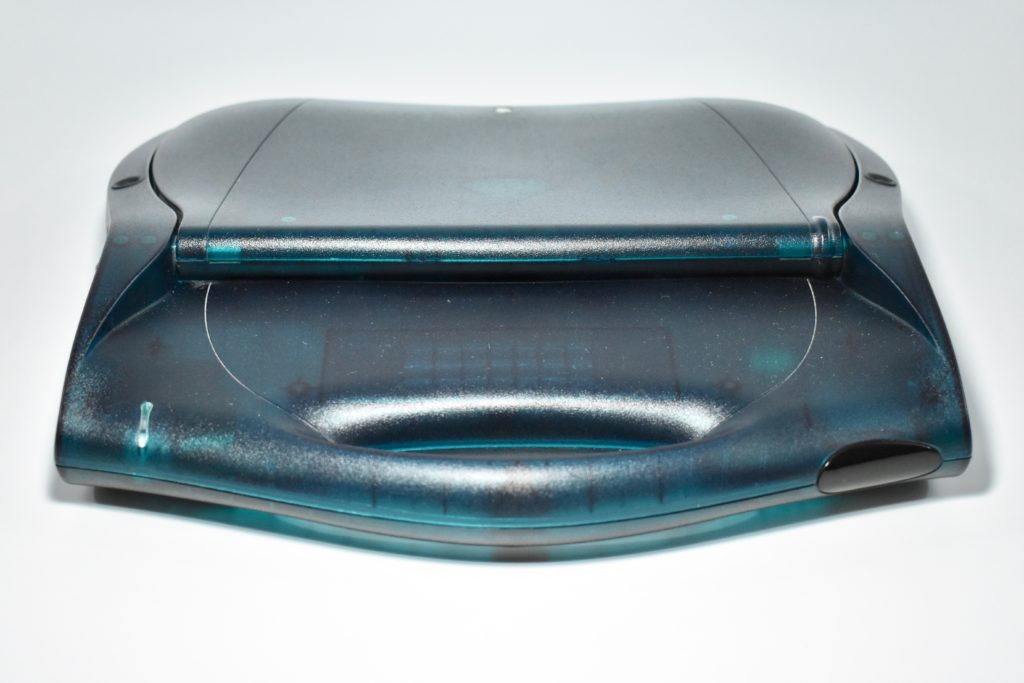
The Twentieth Anniversary Macintosh, sometimes referred to as the “TAM,” is a truly unique Macintosh.
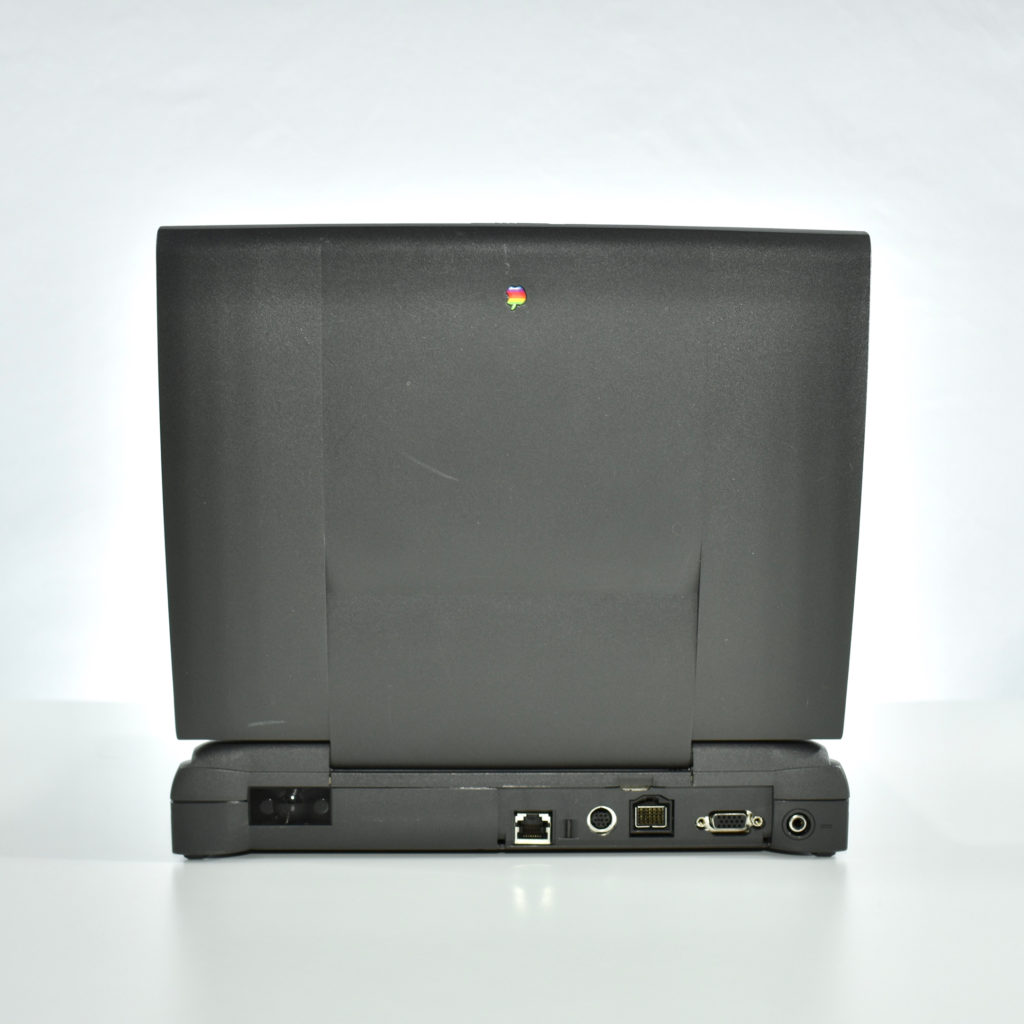
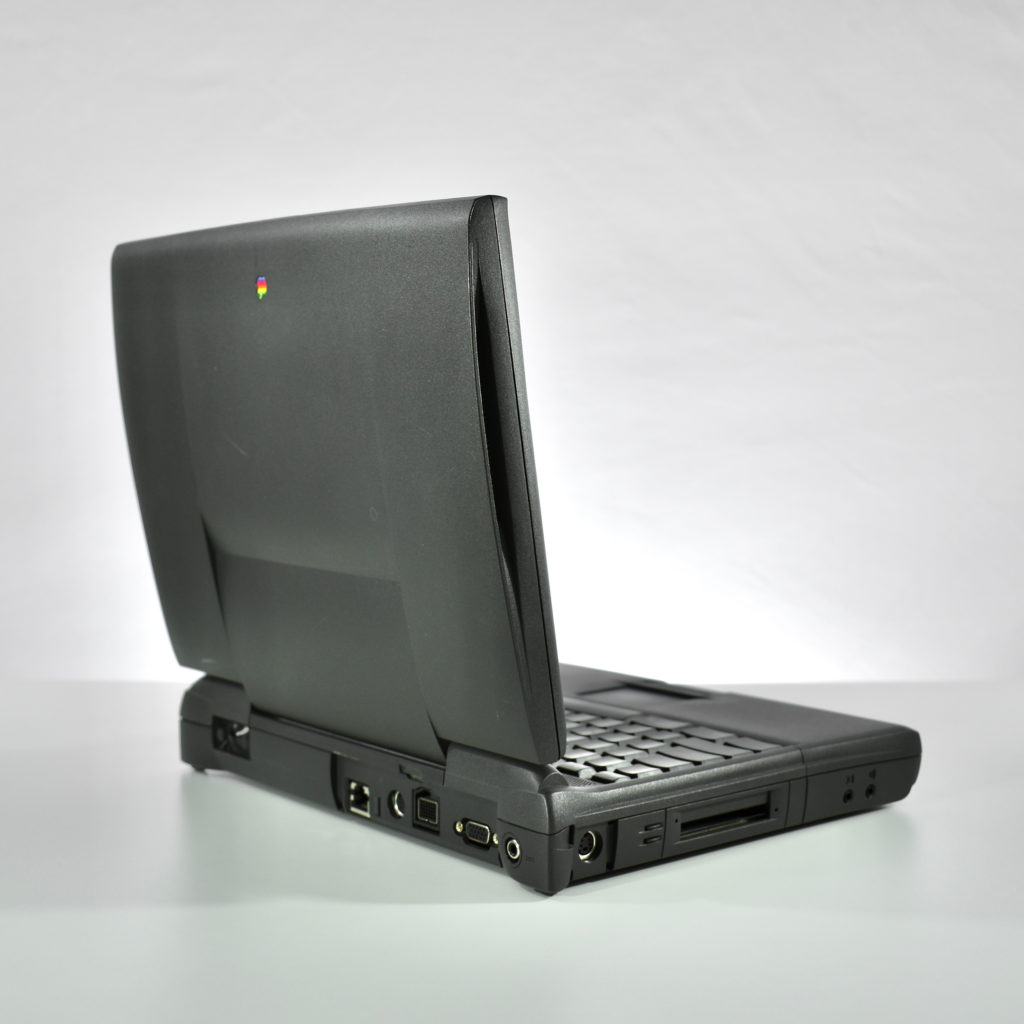
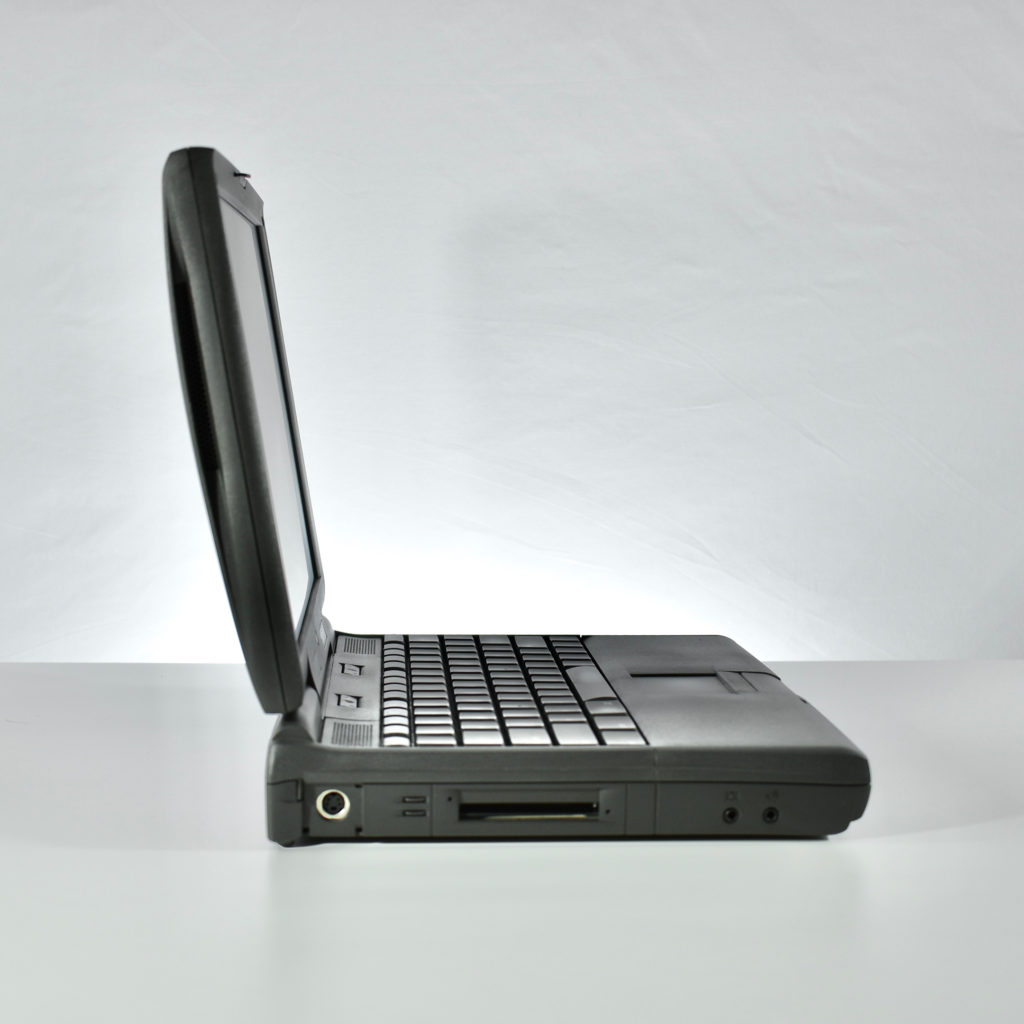
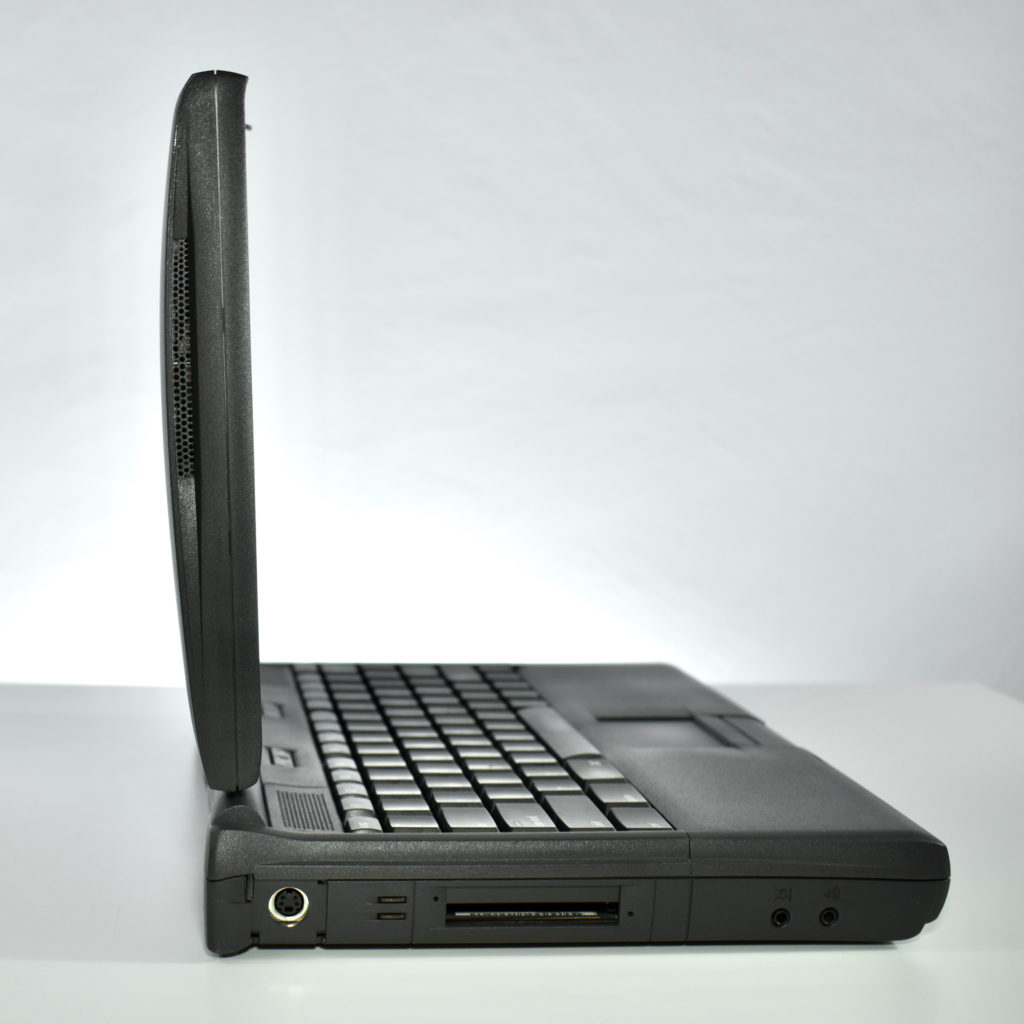
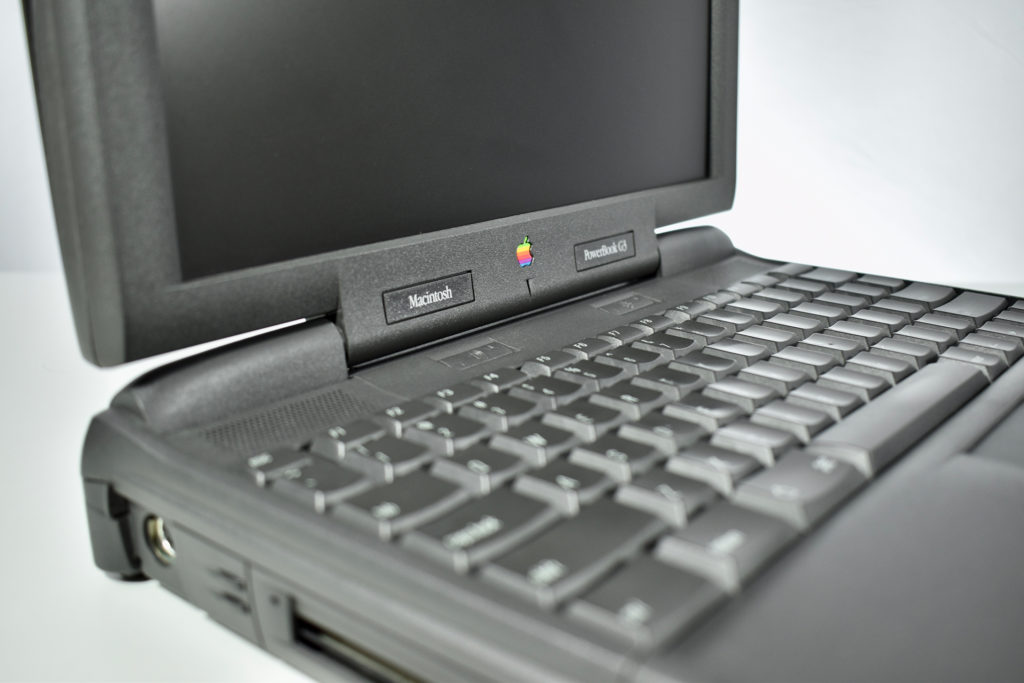
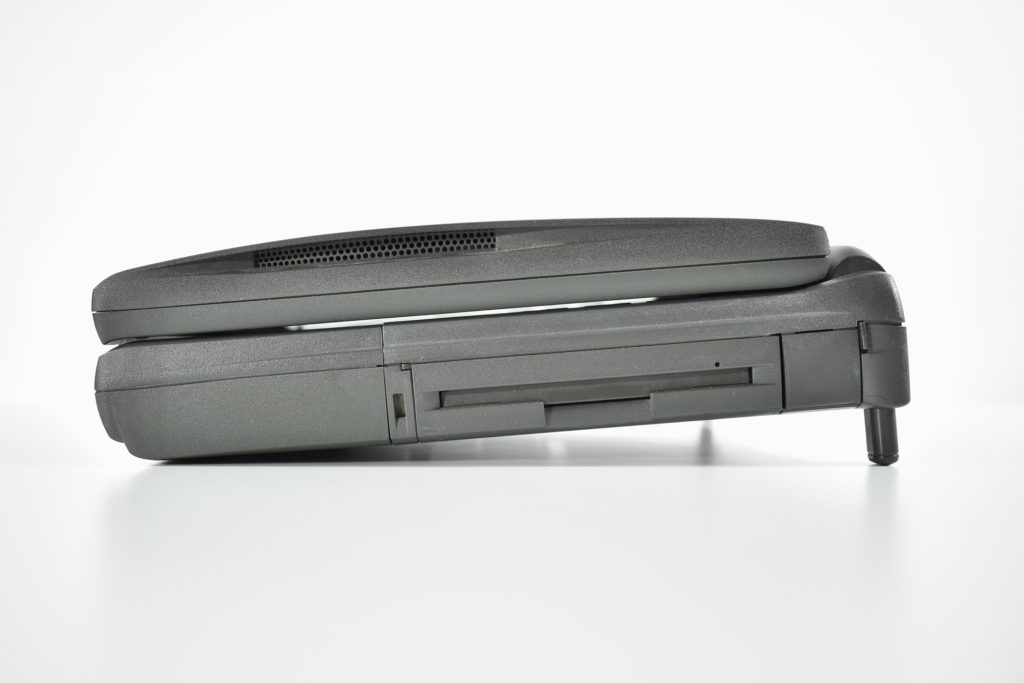
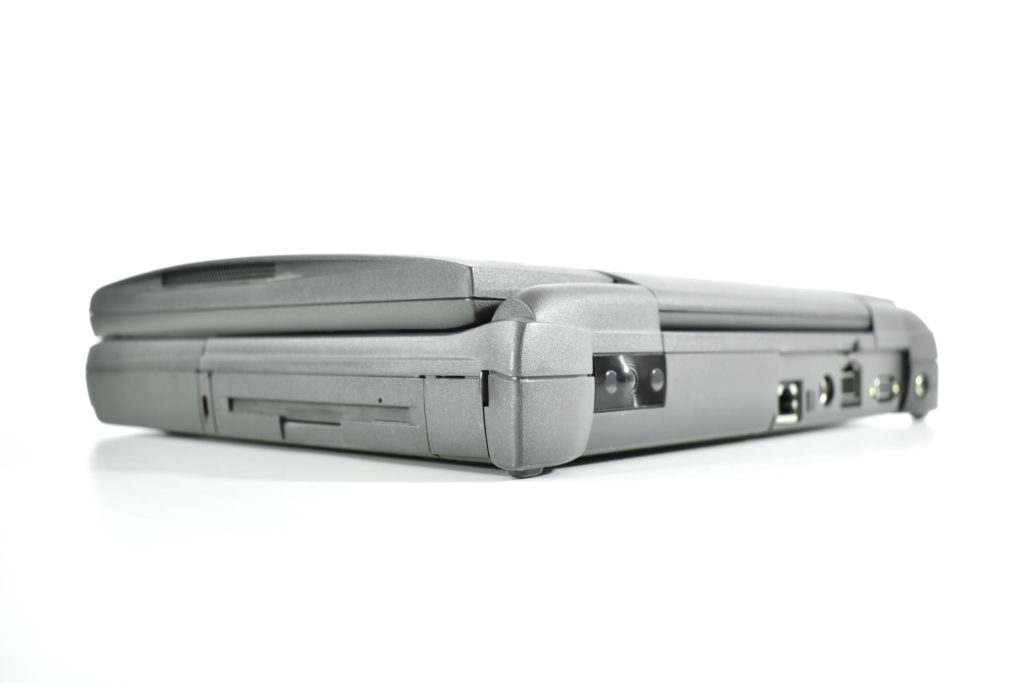
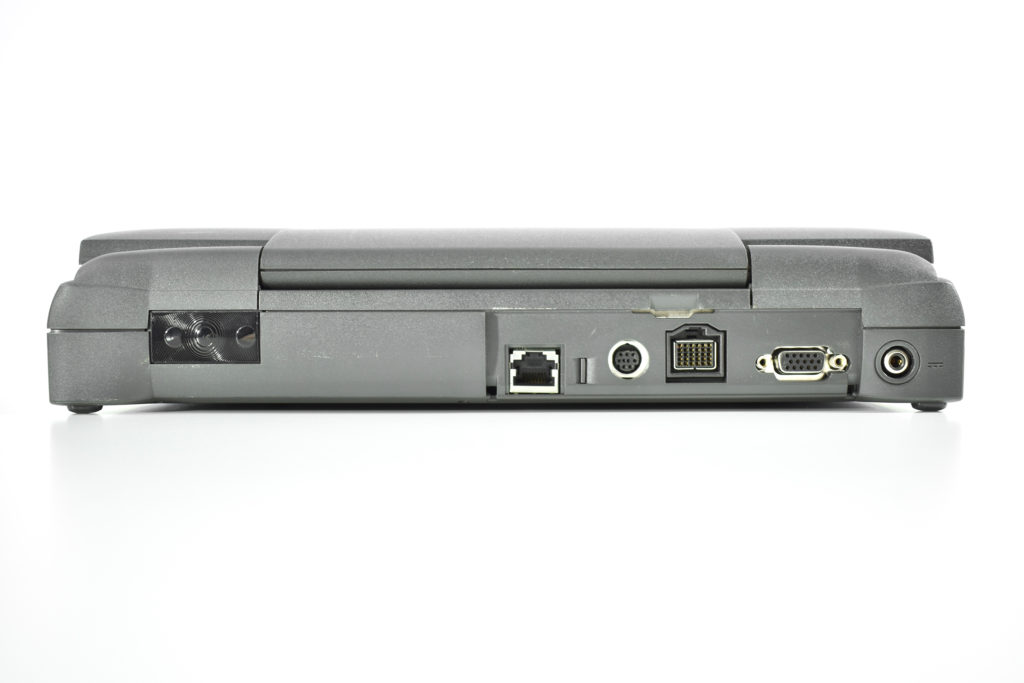
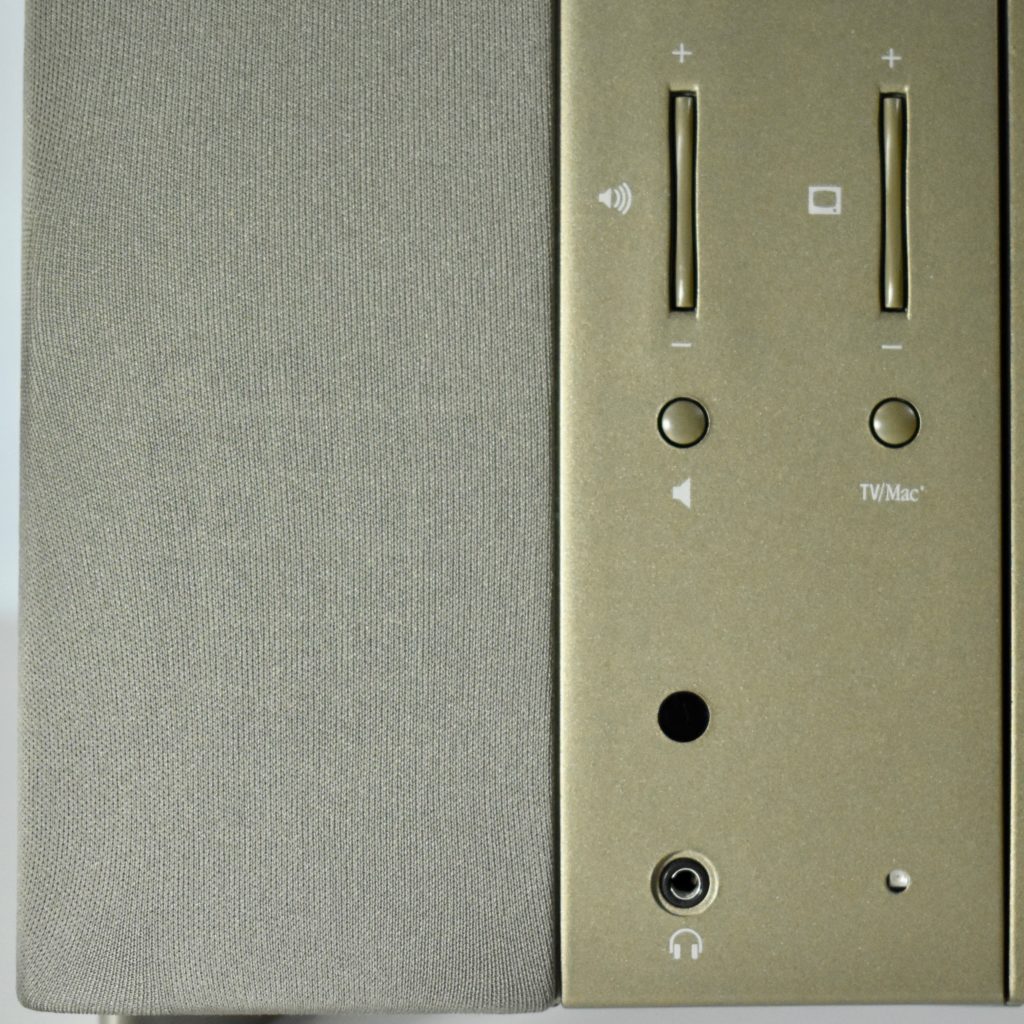
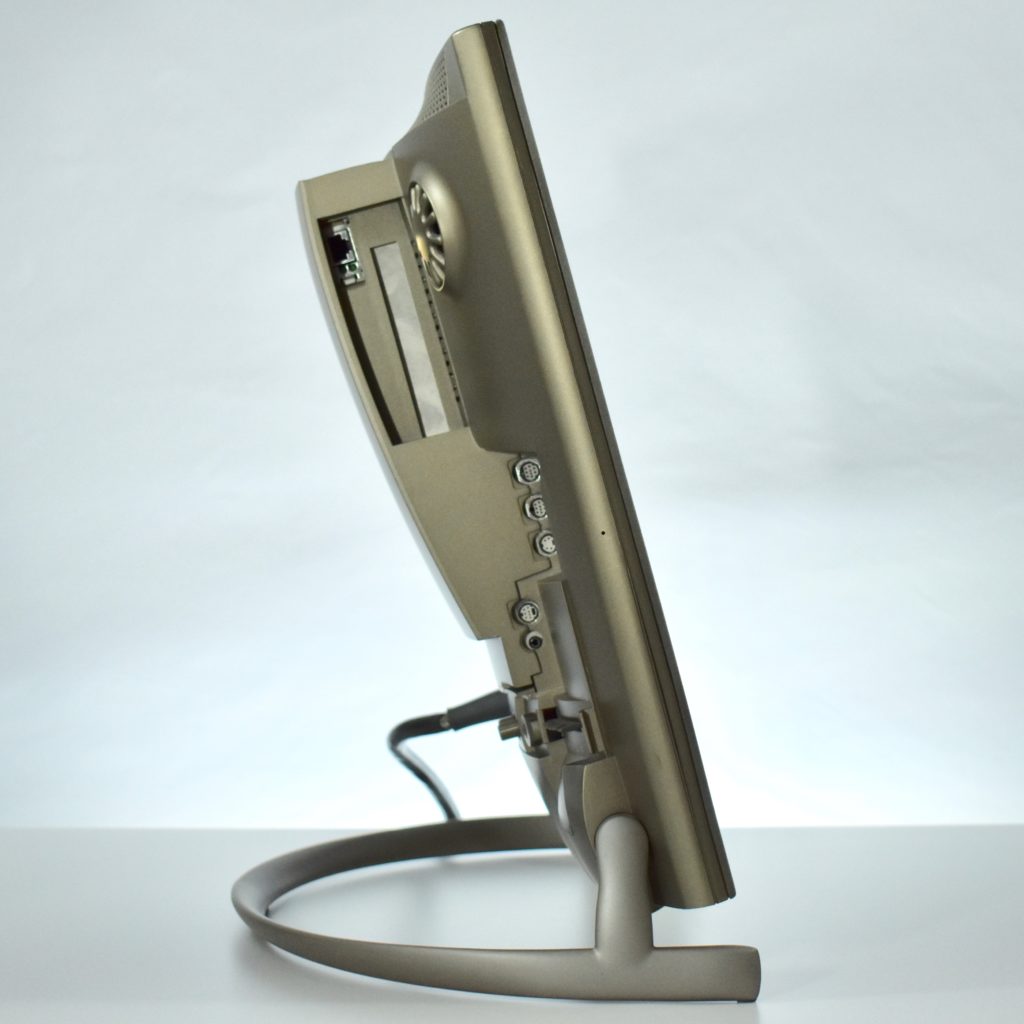
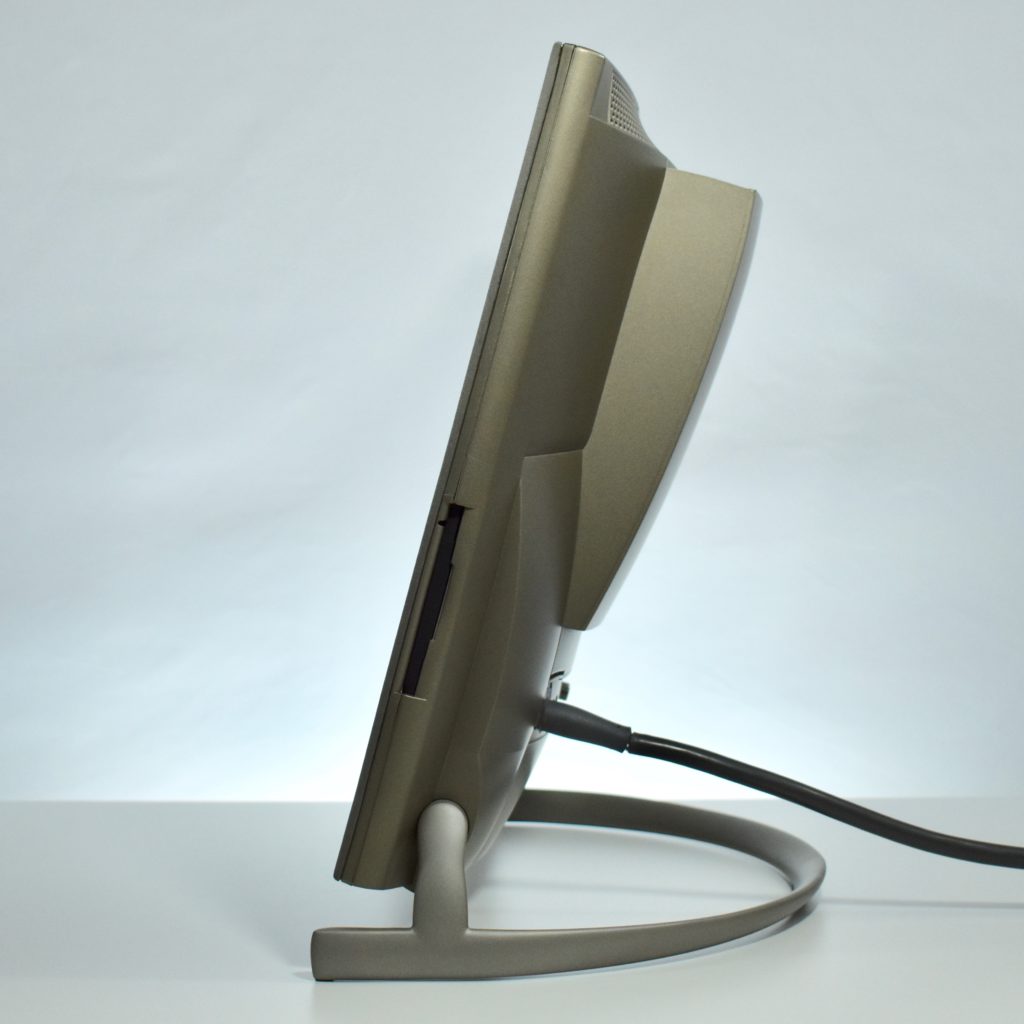
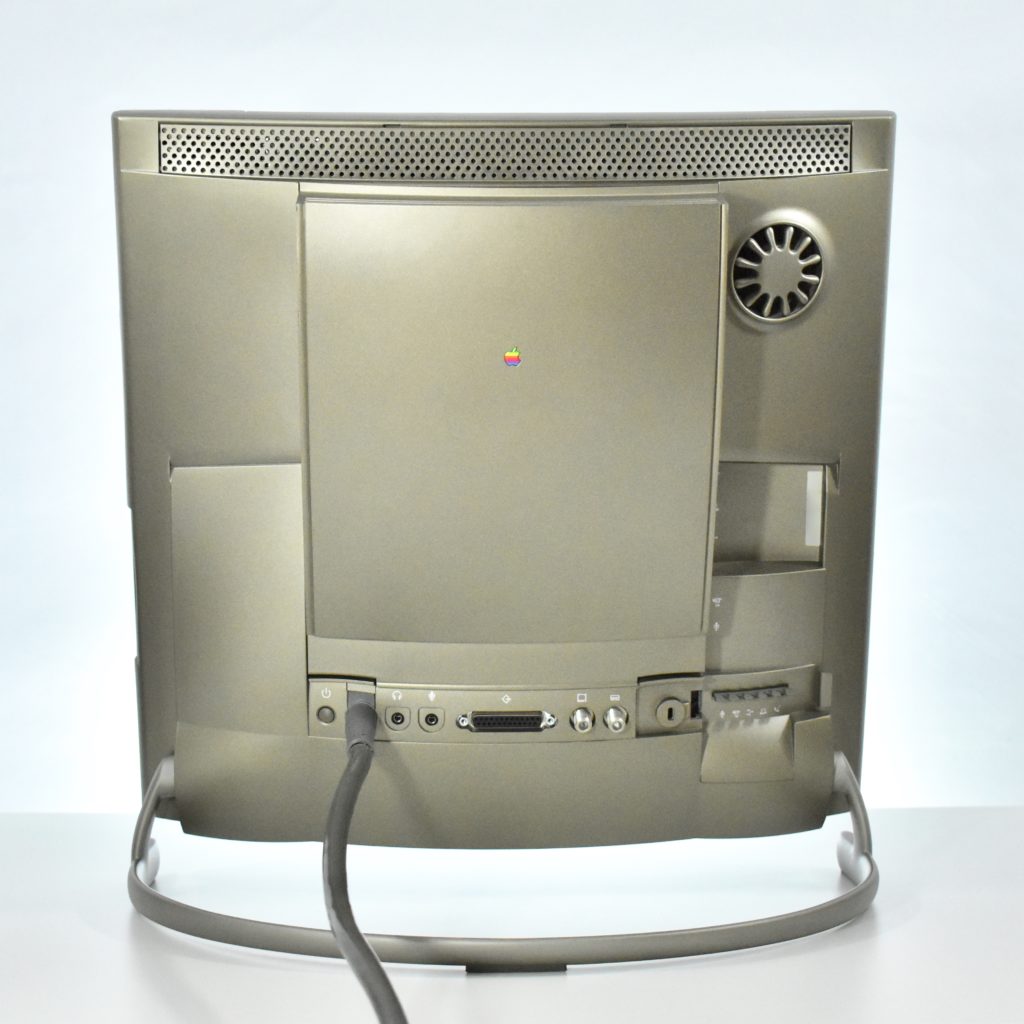
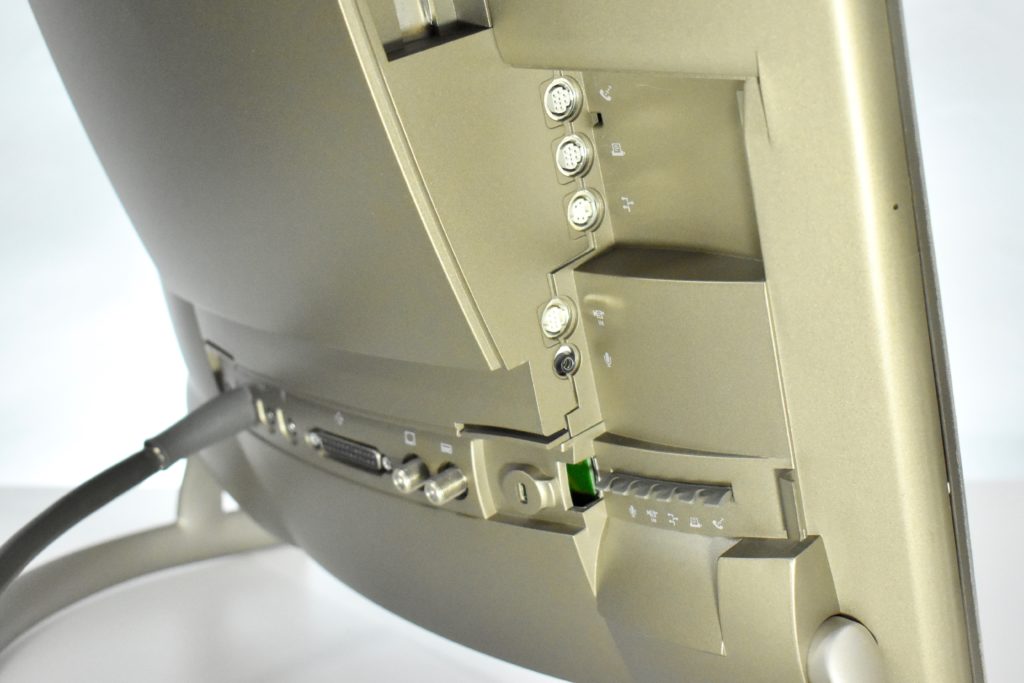
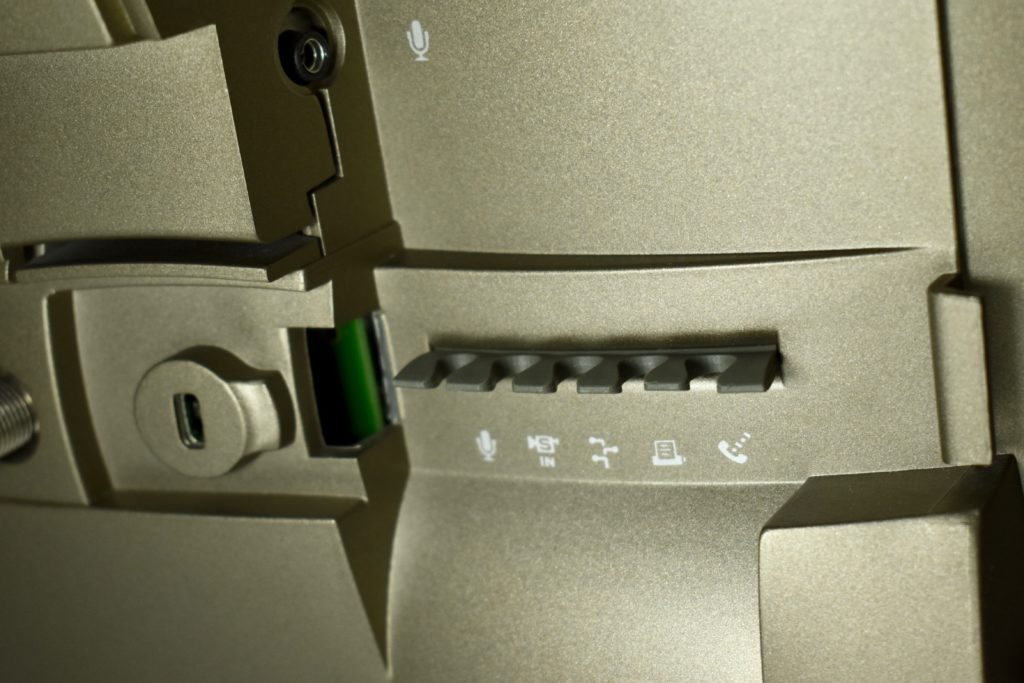
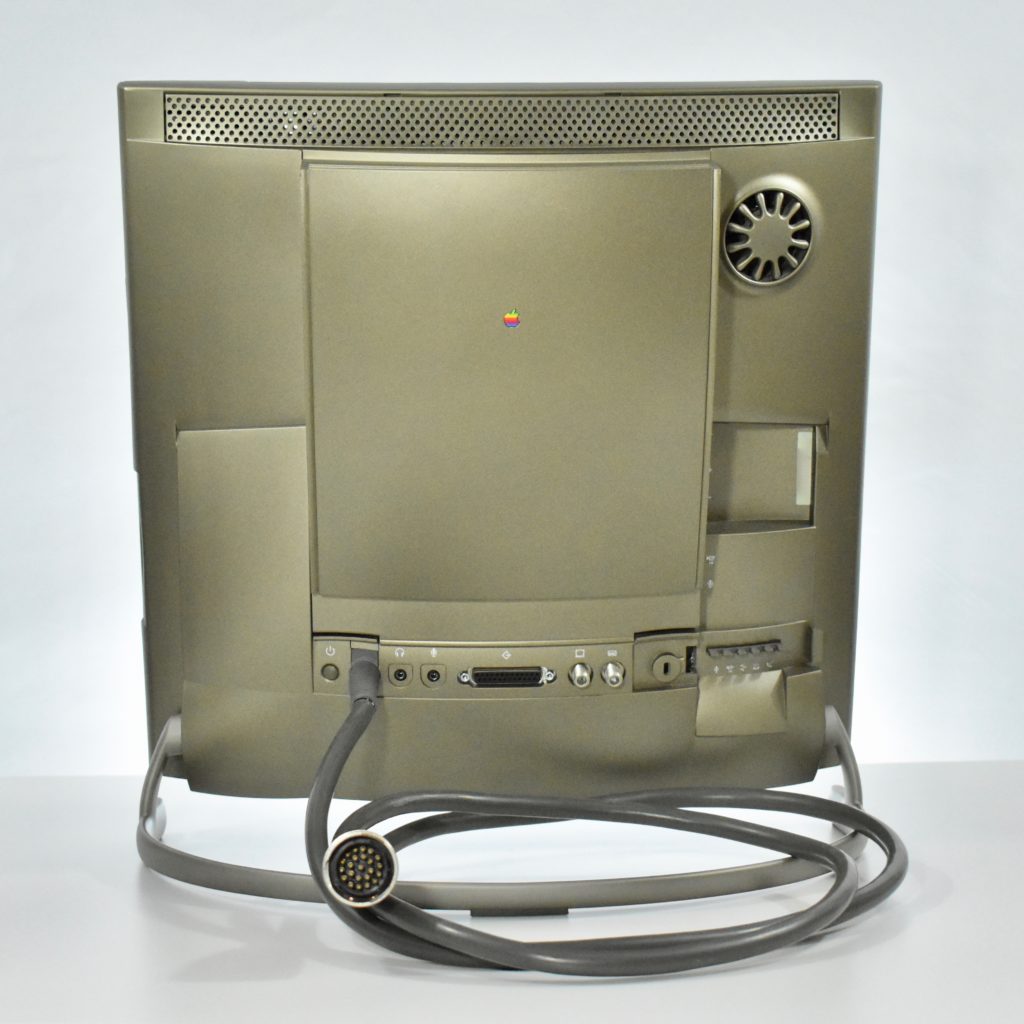
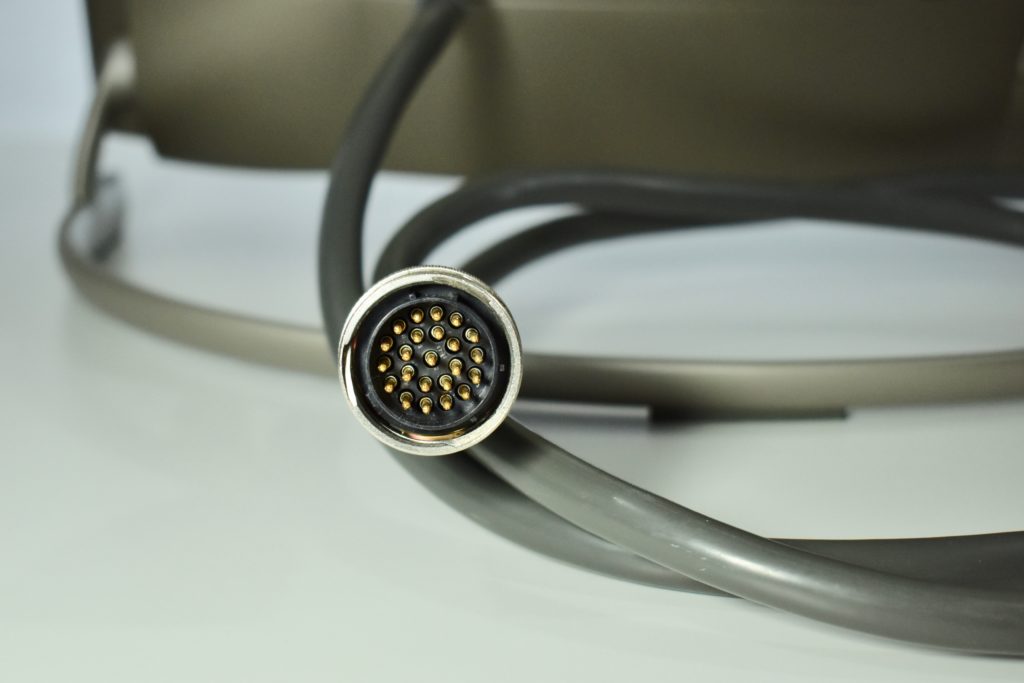
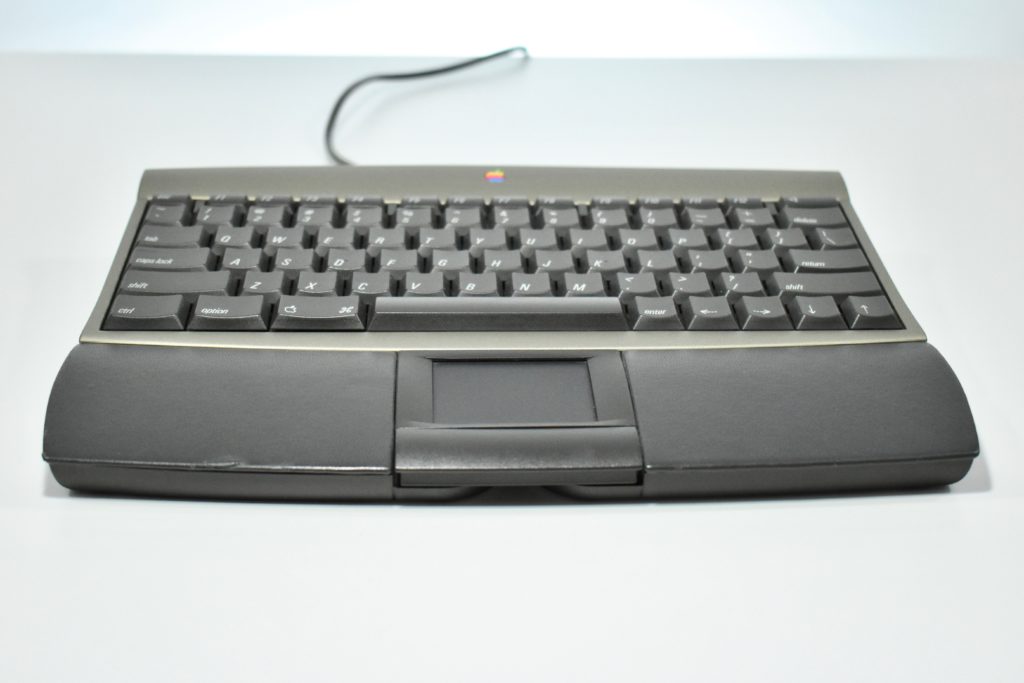
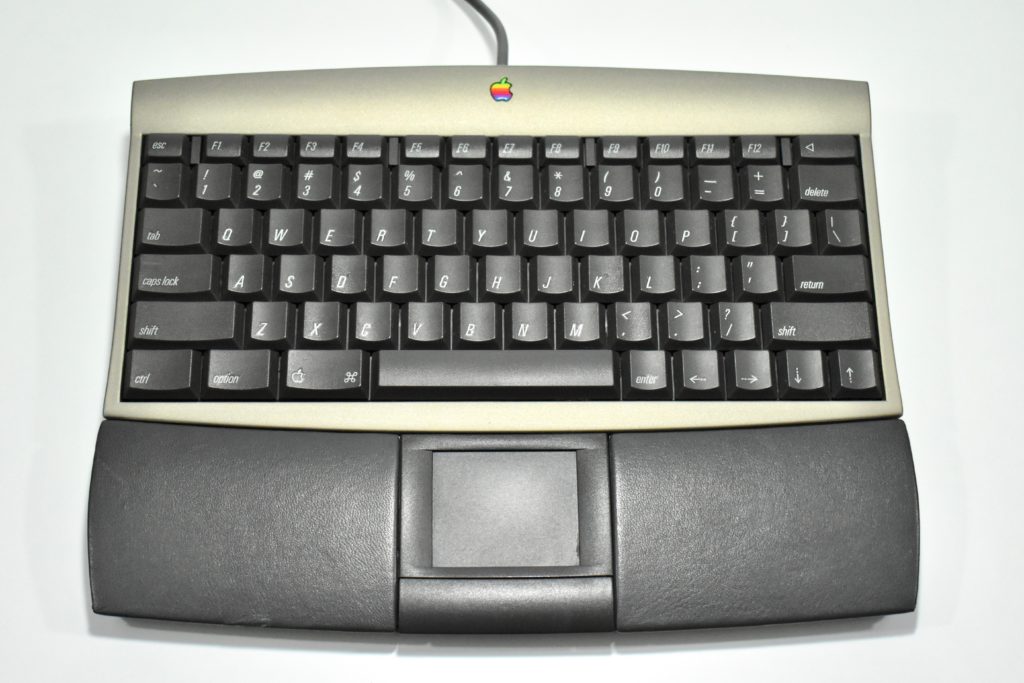
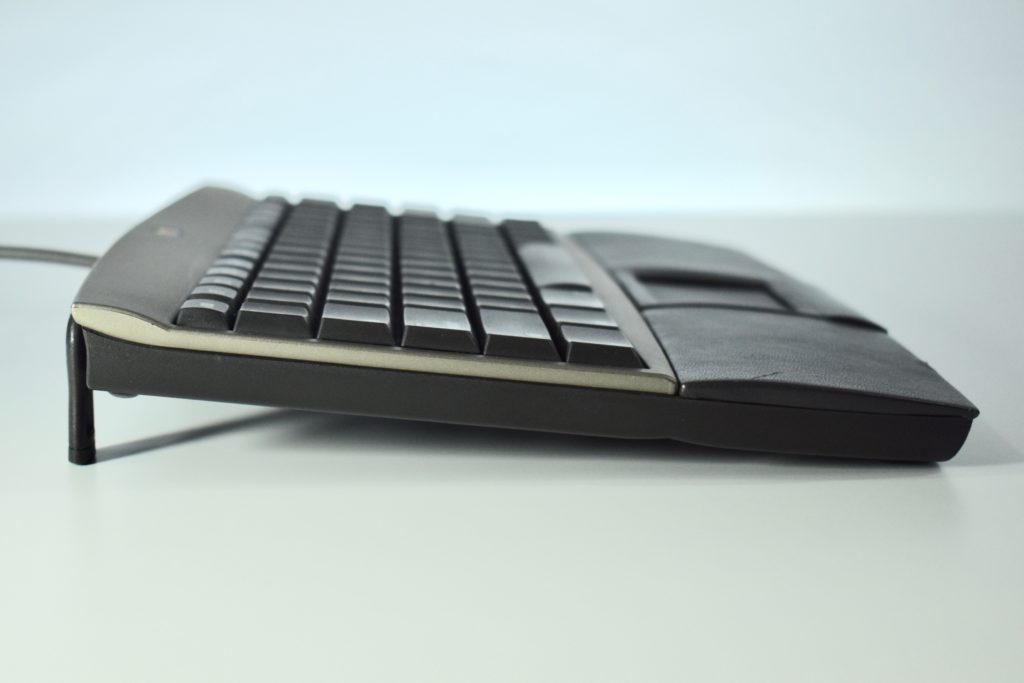
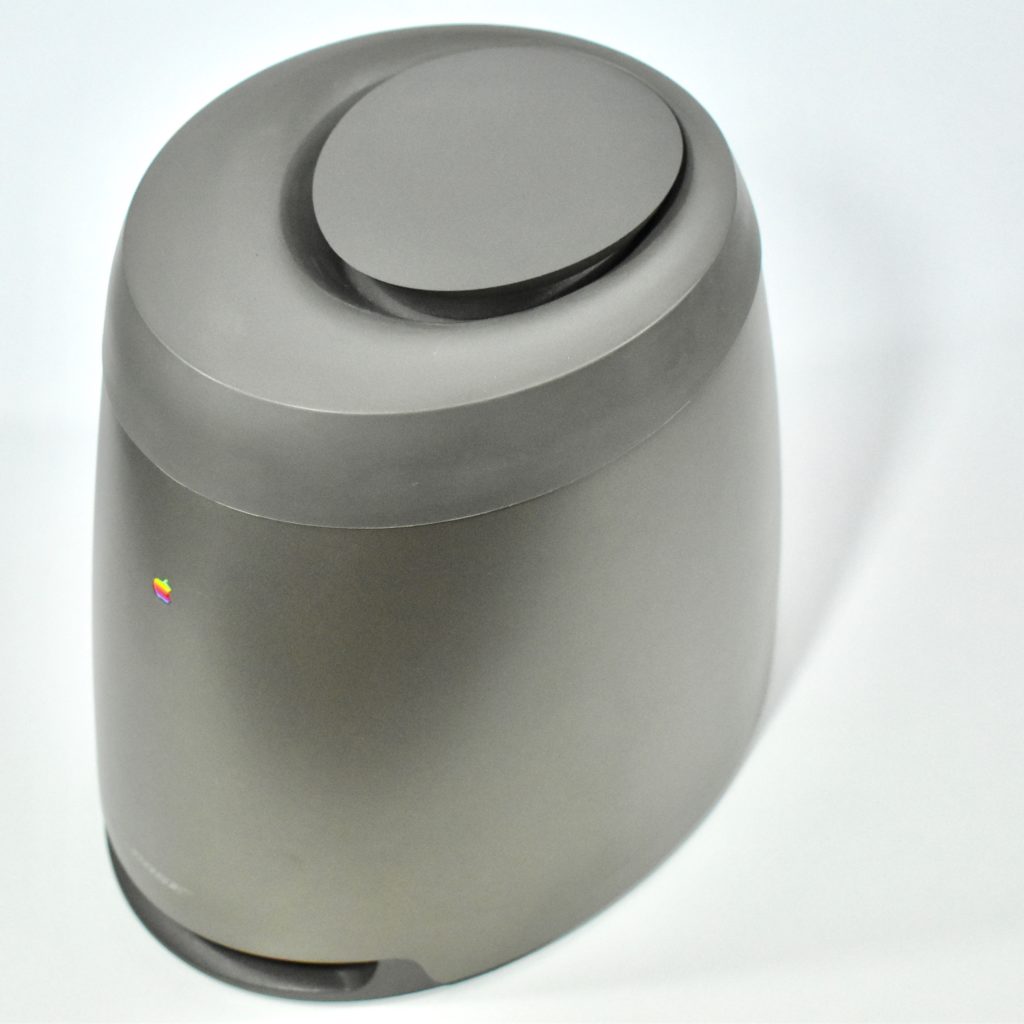
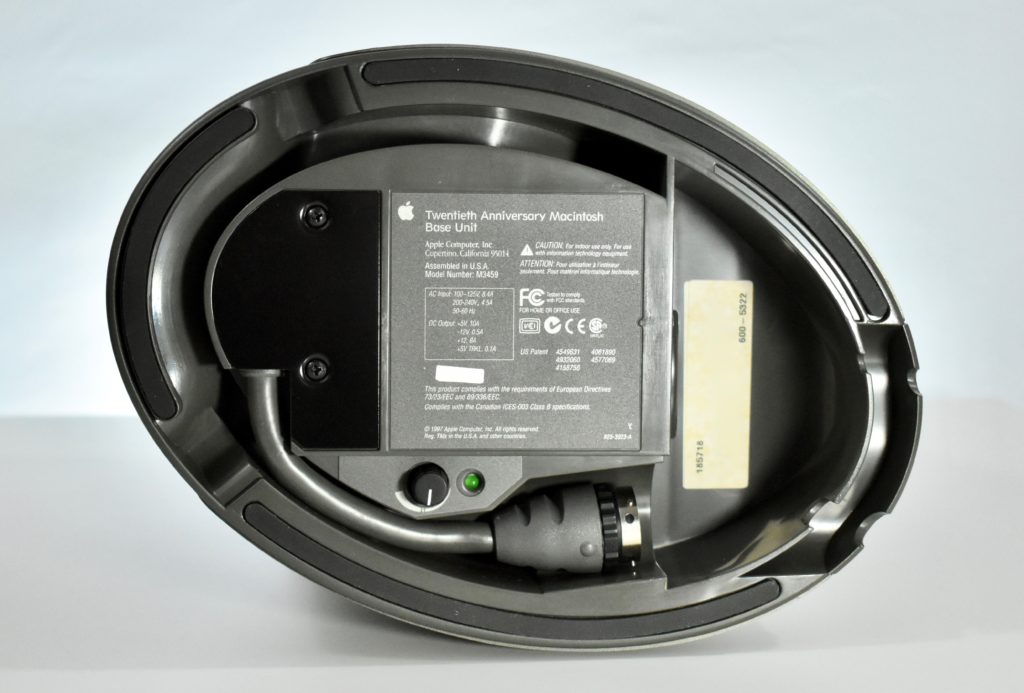
It featured a 250 MHz PowerPC 603e processor, 32 MB of RAM, a 2.0 GB hard drive, a vertical 4X CD-ROM drive, S-video input, TV/FM Radio capability, a floppy Superdrive, and a custom Bose-designed speaker system. The TAM uses a unique ADB (Apple Desktop Bus) keyboard with an integrated trackpad and Italian leather palm rest. It did not ship with a mouse. The TAM includes a base unit that houses a subwoofer and the computer’s power supply, connected by a thick cable.
When powered on, the TAM plays a startup chime unique to this computer.
Apple manufactured 12,000 Twentieth Anniversary Macintosh computers and released 11,601 of them. When first offered, the price was $7,499. Halfway through its product cycle, Apple dropped the price to $3,500. When the product was discontinued in March 1998, the price dropped to $1,995.
When released, the Apple website devoted six full web pages to the TAM. One page boasted “Concierge Service” for TAM owners that described a “Three-Year Limited Hardware Warranty,” “Three-Year Call Telephone Support,” and a setup service:
“On-Site Setup. Apple will arrange to have your TAM delivered to your doorstep. A trained field technician will set up the hardware and basic software, make sure the system is operational, and answer questions you may have about the system.”
Another webpage highlighted the use of the TAM in the 1997 movie Batman and Robin (that also featured the eMate 300).
The Twentieth Anniversary Macintosh was created to celebrate April 1, 1996, the twentieth anniversary of the day that Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne formed Apple Computer. The TAM was announced on March 20, 1997.
The TAM was among the first design projects involving Jonathan Ive, Apple’s long-time CDO (Chief Design Officer).
The release of the Twentieth Anniversary Macintosh marked the appearance of Apple’s first all-in-one desktop computer to use a flat panel display. Another all-in-one flat panel Apple desktop would not be released until 2002 when the first flat panel iMac was released.
Sources: EveryMac.com, Wikipedia.com, Apple at web.archive.com