The Visual Almanac is the earliest Apple Education multimedia product in my collection. According to the kit’s Laser Disc, pictured on the Domesday86 website:
“The Visual Almanac is composed of 3 parts: the Visual Almanac Videodisc, the Visual Almanac software, and the Visual Almanac Companion (a book). This two-sided videodisc contains an Introduction, over 7000 images and 2 channels of sound organized into 12 collections. It is designed to be used under control of a Macintosh computer.”
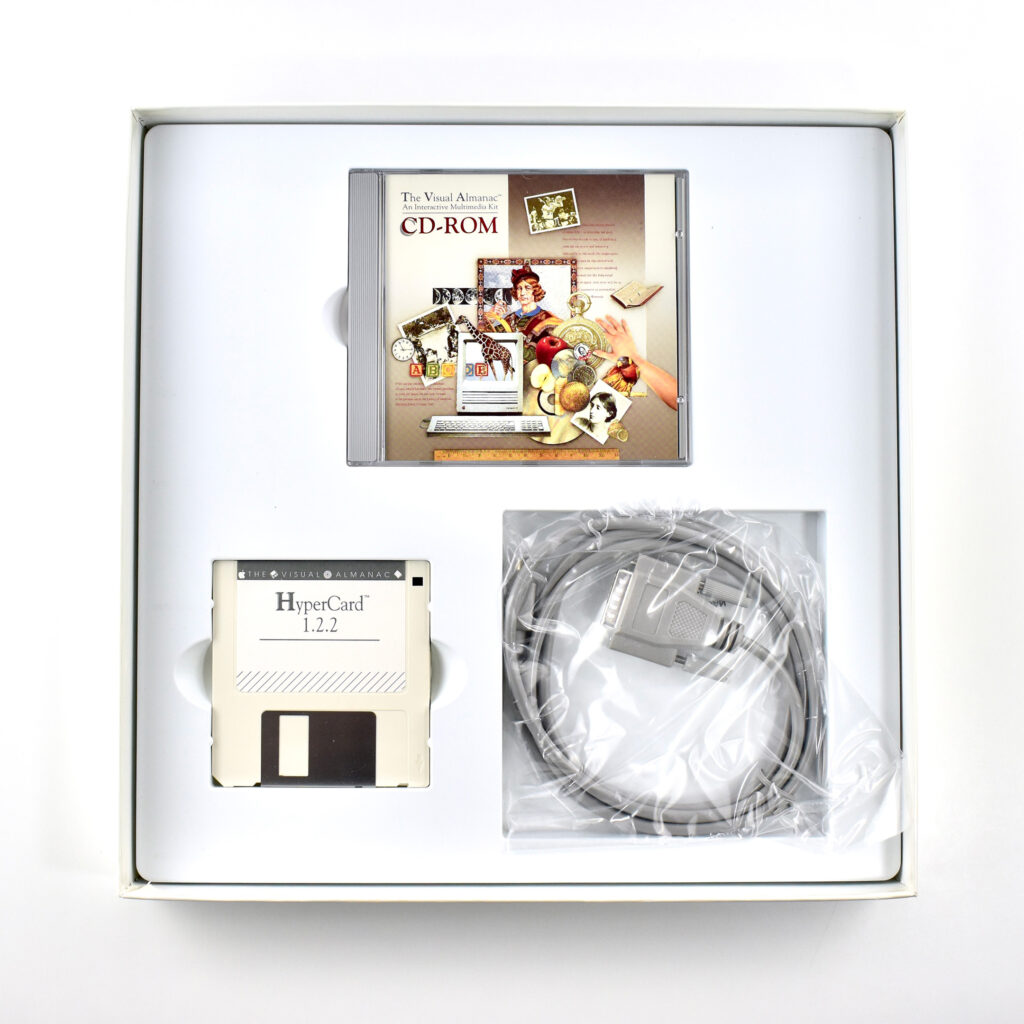
The printed materials include a guide (First Steps in the Visual Almanac) and a spiral-bound book. Media includes three 3.5-inch disks: HyperCard 1.2.2; Visual Almanac Home (home HyperCard stack; Collections Directory (pre-made collections), and a CD-ROM. The kit also includes a cable.
The cable is described as a “LaserDisc Player Serial Lead,” designed to “connect a Pioneer player (with a 15 pin D-Sub connector) to the Apple Macintosh mini-DIN serial port.”
The box containing all the items in the kit measures 12.75 inches square and is 1.5 inches deep. The accompanying spiral-bound book is titled The Visual Almanac: An Interactive Multimedia Kit Companion, measures 11 x 8.5 inches, and contains 216 pages, printed in full color.
The Preface of the book contains a welcome message that states the resource’s intent:
“Welcome to The Visual Almanac! We designed the The Visual Almanac to give everyone a glimpse of potential computer-centered futures and have tried to show how current multimedia technologies might be used to do something new. We tried to make something that could be used now, but would also provoke the development of methodologies, technologies and pedagogies for the future. It is an interactive multimedia kit aimed at children and all their teachers—in schools, in homes and in various public environments—as well as business people, researchers and developers who make educational and other materials for our youth.”
Although the full package is dated January 1990, the accompanying CD-ROM is dated 1989 and the CD (as well as the Laser Disc) specifies that it was “Produced by the Apple Multimedia Lab.”
The box in my collection is missing the accompanying 2-sided LaserDisc that contains the primary content in 78 “collections” for the kit:
Side A Collections
Animals and Plants
Earth View
Everyday Physics
Solar System
Sounds Side A
Side B Collections
American History
Around the World
History of Daily Life
Everyday Objects
Historical Portraits
Sounds Side B
Studies in Time
Special thanks to the Domesday86 website for providing an excellent, detailed entry about this kit that allowed me to better describe this early educational multimedia example.
Source: Apple, Domesday86